Oklahoma inmate dies after 'botched' lethal injection
- Published
- comments
Journalist Courtney Francisco witnessed the 'botched' execution
A US death row inmate in Oklahoma died of a heart attack after his execution was halted because the lethal injection of three drugs failed to work properly.
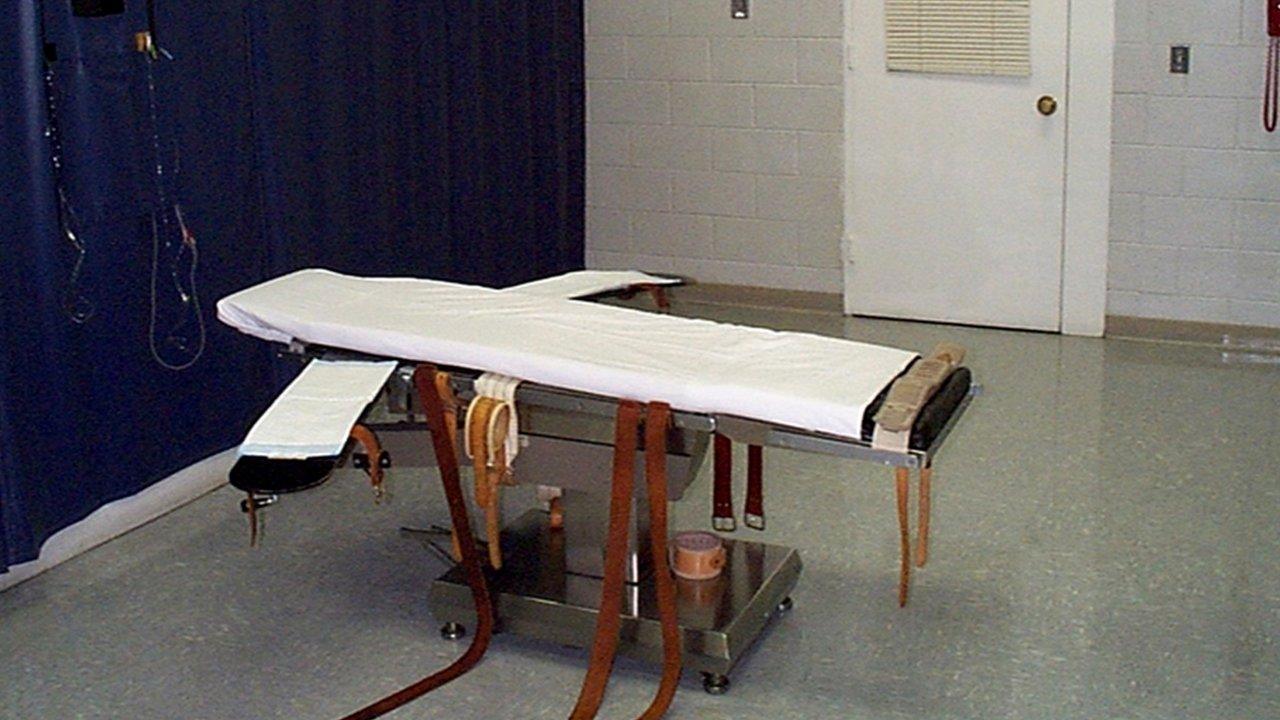
The execution of Clayton Lockett, 38, was stopped after 20 minutes, when one of his veins ruptured, preventing the drugs from taking full effect.
The execution of a fellow inmate, due two hours later, was postponed.
Both men had unsuccessfully challenged a state law that shields the identities of companies supplying the drugs.
The problems surrounding Lockett's execution come amid a wider debate over the legality of the three-drug method and whether its use violates guarantees in the US constitution "against cruel and unusual punishment".
Lockett was sentenced to death for shooting 19-year-old Stephanie Neiman and watching as two accomplices buried her alive in 1999.
Ms Neiman and a friend had interrupted the men as they robbed a home.
'Botched'
Lockett writhed and shook uncontrollably after the drugs were administered, witnesses said.
"We believe that a vein was blown and the drugs weren't working as they were designed to. The director ordered a halt to the execution," Oklahoma Department of Corrections spokesman Jerry Massie said.
But Lockett's lawyer, David Autry, questioned the remarks, insisting his client "had large arms and very prominent veins," according to the Associated Press.
The prisoner was moving his arms and legs and straining his head, mumbling "as if he was trying to talk", Courtney Francisco, a local journalist present at the execution, told the BBC.
Prison officials pulled a curtain across the view of witnesses when it became apparent that something had gone wrong.
"It was a horrible thing to witness. This was totally botched," Mr Autry said.
Oklahoma Governor Mary Fallin said in a statement , externalthat she had ordered a full review of the state's execution procedures.
Calls for investigation
Fellow inmate Charles Warner, 46, had been scheduled to be put to death in the same room two hours later in a rare double execution.

Charles Warner was due to be executed two hours after Lockett
Warner's lawyer, Madeline Cohen, who witnessed Lockett's execution, said he had been "tortured to death" and called for an investigation.
"The state must disclose complete information about the drugs, including their purity, efficacy, source and the results of any testing," she said.
Warner was convicted of the 1997 murder and rape of an 11-month-old girl.
He and Lockett had unsuccessfully challenged an Oklahoma state law that blocks officials from revealing - even in court - the identities of the companies supplying the drugs.
The state maintains the law is necessary to protect the suppliers from legal action and harassment.
Lockett and Warner argued they needed to know the names of the suppliers in order to ensure the quality of the drugs that would be used to kill them and to be certain that they had been obtained legally.
In March, a trial court ruled in their favour, but the state's highest court reversed that decision last week, ruling that "the plaintiffs have no more right to the information they requested than if they were being executed in the electric chair".
US states have encountered increasing problems in obtaining the drugs for lethal injections, amid an embargo by European pharmaceutical firms.
Some have turned to untried combinations of drugs or have sought to obtain the drugs custom-made from compounding pharmacies.
The triple-drug cocktail, first used in Texas in 1982, has become the standard execution method in the US.
It was presented as a more humane replacement for lethal gas and the electric chair, but critics of the three-drug protocol say it could cause unnecessary suffering.
Several US states that still have the death penalty have since switched to a single-drug method.
- Published22 April 2014

- Published15 November 2013
- Published8 August 2012

- Published28 April 2014
