Bob Dole: From WW2 casualty to top Republican
- Published

Bob Dole, a World War Two veteran who went on to be a long-time Republican senator and US presidential candidate, has died aged 98.
His death was announced in a statement from the Elizabeth Dole Foundation: "It is with heavy hearts we announce that Senator Robert Joseph Dole died early this morning in his sleep. At his death, at age 98, he had served the United States of America faithfully for 79 years."
Earlier this year Dole had said that he was receiving treatment for lung cancer.
His political career was marked by a decade-long stint as the top Republican in the US Senate, and running unsuccessfully for the White House against Bill Clinton in 1996.
But decades before his bid for the presidency, on 14 April 1945, Bob Dole was lying on a World War Two battlefield in northern Italy, left for dead.
Despite his lack of combat experience, the young 10th Mountain Division lieutenant had been ordered to lead an attack on a German machine-gun post.
Three-quarters of his squad lay strewn on the battlefield. When he ran to help a fallen soldier, gunfire and enemy shells shattered Dole's right arm and upper back.
He fell unconscious, and an army sergeant rolled him to safety. He gave him a huge dose of morphine and painted an "M" on his forehead - in Dole's own blood - to stop passing medics giving a second, lethal hit.
"I gave him a shot because he's gone," the man told his commanding officer. "At least he'll have some comfort."
That Dole survived was a miracle. That he went on to rebuild his broken body - and become one of the Republican Party's longest-serving senators and a presidential candidate - was a tribute to his determination. Many believed the survival and determination were linked.
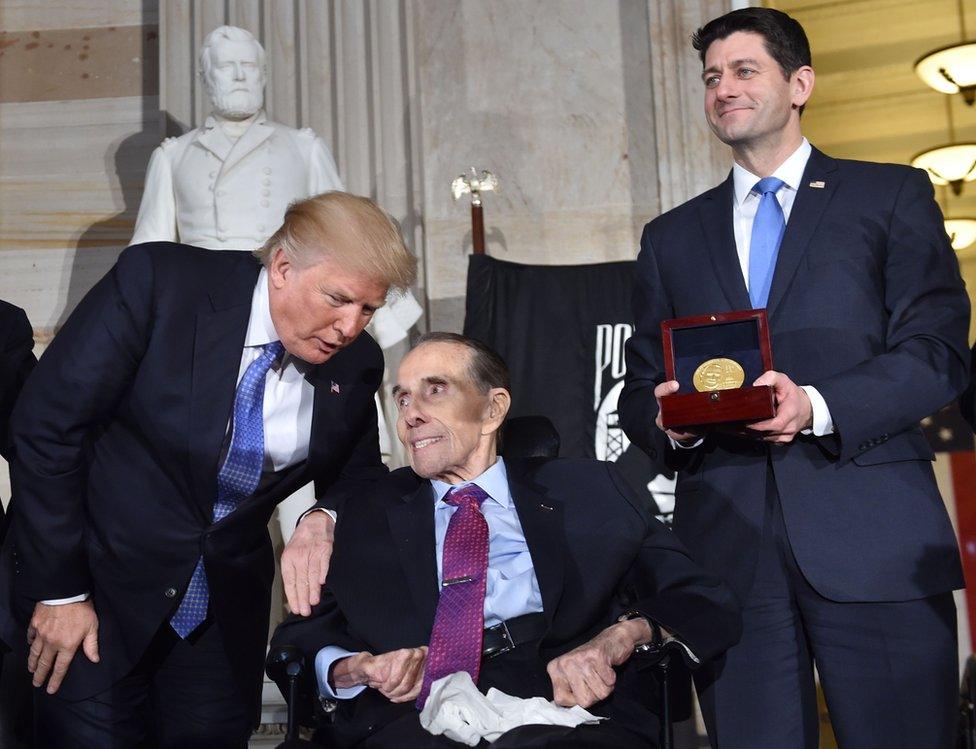

Dole receives the Congressional Gold Medal from President Trump and House Speaker Paul Ryan in 2018
Robert Joseph Dole was born on 22 July 1923 and grew up in the Dust Bowl of Kansas during the Great Depression. It was a provincial childhood, 200 miles (320km) from the nearest midsized city. As a youth, Bobby only left Kansas once, on a fishing trip to the mountains of nearby Colorado.
His salesmen parents struggled financially - their four children sharing a single room - but preached the values of hard work and religious devotion.
They "taught me to put my trust in God, not government," he later said, "and never confuse the two."
There were no books at home. "Be a doer, not a stewer," was the family motto - with Dole encouraged to play outside at every opportunity.
While his friends studied for college, Bob shot hoops and worked serving ice cream at a local drugstore.
At the University of Kansas, he studied medicine but did not treat college as a place to expand the mind. Intellectually lazy, he partied and became a star athlete, competing at basketball and football as well as on the track.
Then came the war, Dole's enlistment in the army - and the day that changed his life.
He lay near death for nine hours on that Italian battleground, with injuries including a fractured shoulder, a broken neck and spine, paralysis, a ruined kidney and bits of shrapnel. The hidden iron in his soul had, fortunately, been left intact.
For his service, he was awarded two Purple Hearts and a Bronze Star but the hardest battle was yet to come. More than three years were spent in recovery, stuck in a sterile hospital room in Michigan fighting off boredom, blood clots and infections that nearly claimed his life.
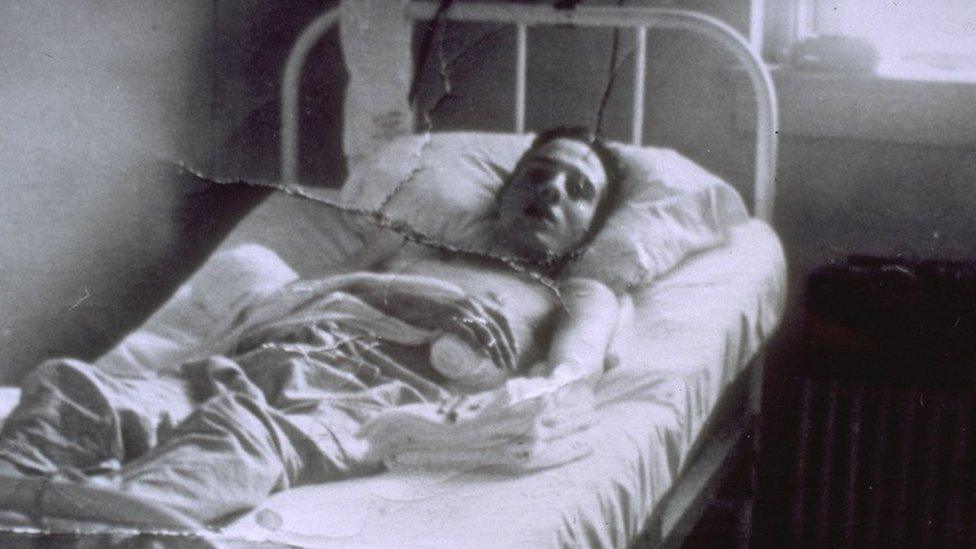
Bob Dole spent 39 months recovering from his injuries in hospital after the war
Facing amputation of his arm, he was fortunate to encounter a maverick surgeon who performed multiple operations, free of charge. Dole credited him with an impact on his life second only to his family.
Demoralised and robbed of his ability to lead the outdoor life he loved, Dole began to read. Unable to hold the books, he used a projector to beam the pages onto the ceiling above the bed.
He devoured the works of Plato, George Washington and, his favourite, Abraham Lincoln. "It was a way to maintain sanity, I guess," he said.
He met an occupational therapist, Phyllis Holden, and took her to an officers' club dance. Three months later they married - despite the objections of her parents who believed Dole was in no fit state to care for her. She shook him out of his "funk".
Returning home, they rigged up a rope-and-pulley system to build up his strength. He kept it there for more than half a century, to remind him how far he had come.
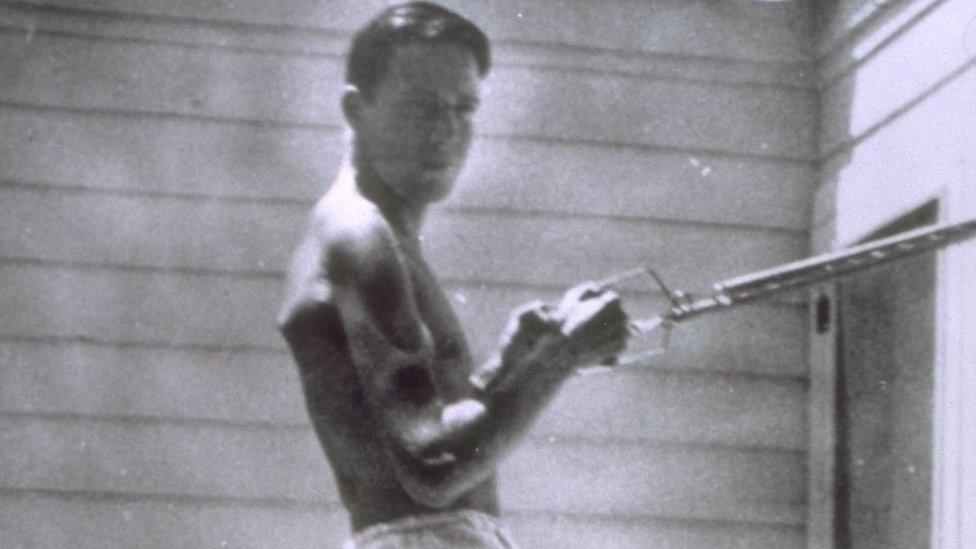

Dole using his rope-and-pulley system at his house to help him get stronger
He never regained use of his arm and right hand, spending the rest of his life limply holding a pen to discourage innocent offers of a handshake. What he lacked physically, however, he now made up with drive.
Unable to write notes, he recorded law school lectures and stayed up all night transcribing them left-handed. He could only write brief notes in his final exams, but they were sharp enough to pass.
Encouraged to enter politics, Dole took advice. He was a moderate but saw sense in the argument that "if you want to do something politically in Kansas, you'd better declare yourself a Republican".
In 1950, he was elected to the state legislature with the help of a campaign featuring a female singing group, Dolls for Dole.
A decade later, he made it to Washington as a member of the House of Representatives for a rural area of Kansas that had only just permitted alcohol and saw a 'commie' under every rock.
Politics began to consume him, and he built a reputation as the conservative his district expected. The family made the long drive home each summer in a car crammed with pets and luggage. One year their dog died from the heat.
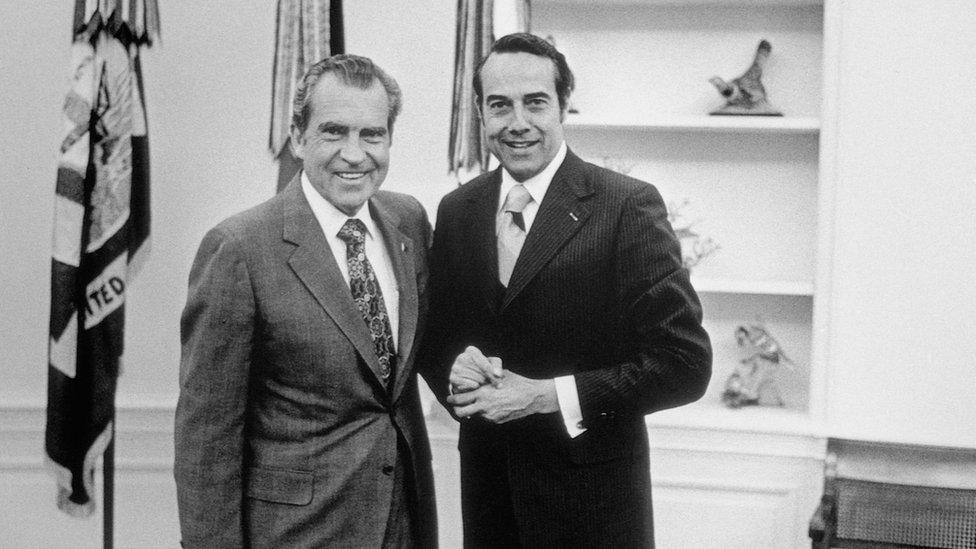

With Richard Nixon in the Oval Office. Years later, Dole held back tears while giving the eulogy at his funeral
In 1968 - the same year Richard Nixon became president - Dole reached the Senate. But his dedication to politics took a toll on his marriage and at the end of his first term, he divorced.
His decision to leave Phyllis shocked her. But, in the course of their last year together, Dole had eaten just two meals with his wife and daughter. It is a measure of the degree to which politics now obsessed him that he consulted Nixon about potential damage to the Republican Party before informing her.
By 1972, he was Republican national chairman and with a new partner, Elizabeth Hanford, who shared his enthusiasm for politics. They married three years later.
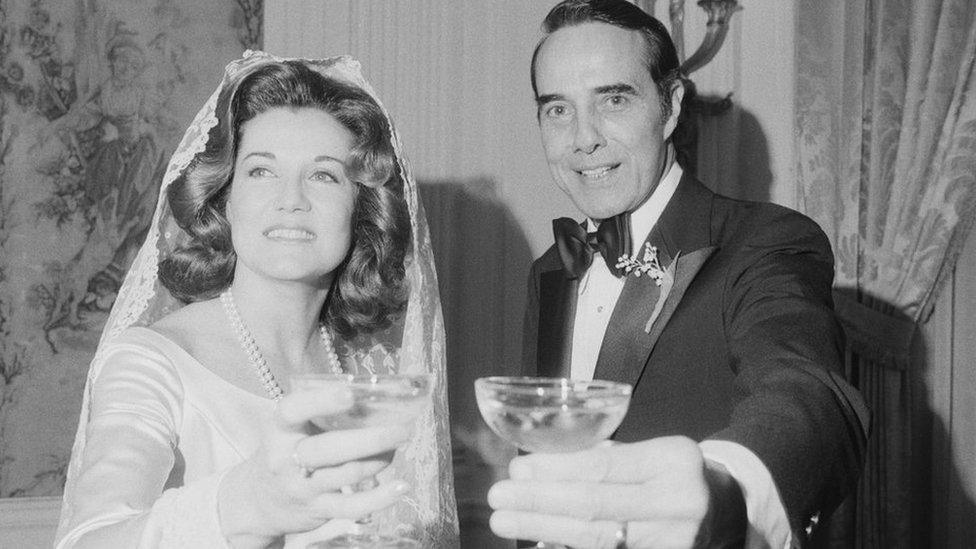

Bob Dole married his second wife, Elizabeth Hanford, in 1975
Elizabeth Dole would later become Ronald Reagan's secretary of transportation and eventually won a seat in the Senate herself.
With a reputation for blunt speaking, Dole became incumbent Gerald Ford's vice-presidential running mate in 1976, but they lost. During the campaign Dole blundered in the debate against his opposite number, Walter Mondale, describing America's 20th Century conflicts as "Democrat wars". It was a phrase that would come back to haunt him.
Public speaking was his weakness as a politician: he was naturally taciturn, couldn't physically write speeches and was loath to rehearse or read words others had written.
He was a natural in the House and Senate; at the backend of politics he could do deals, make trade-offs and build consensus. Out front - in the bear-pit of a national election - he lacked the magic ingredient required for success.
Jimmy Carter, Reagan and later Bill Clinton had the common touch and easy delivery that Dole could never muster. On the stump, they were fluent but he was staccato, with speeches riddled with random clichés.
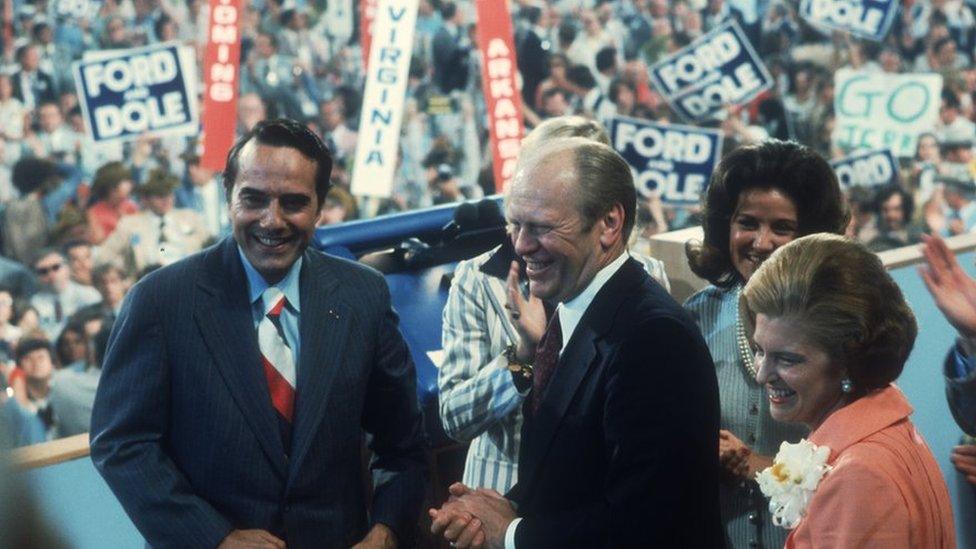

Dole became Gerald Ford's vice-presidential running mate in 1976
Nor did he have the thing Americans call "vision". His personal story was the stuff of presidents but when asked what he wanted for the country, he struggled - responding with vague fatuities and empty slogans.
In 1988, when George HW Bush beat him in the New Hampshire primary, he boiled over on television and demanded his opponent "stop lying about my record".
He was irritated at Bush's campaign ads and constant posing for the cameras, with photocalls driving trucks and shovelling snow. Dole knew he physically couldn't do the same and the frustration made him snap.
He nursed his grievances in the Senate. With his eye still on a national campaign, politically he tacked to the centre ground. With fellow Republican John McCain, he reached across the aisle in a series of bipartisan initiatives, in particular on disability rights.
His colleagues in the Senate remembered his ability to listen in meetings (he still couldn't take notes) and his air of inscrutability. McCain knew him for a decade before he discovered Dole had worn a memory bracelet with McCain's name on it throughout his captivity in Vietnam.
Dole for president
In 1996, the 73-year-old finally got to run for president. He went up against Bill Clinton, a formidable force with the advantage of incumbency and a booming economy. As a campaigner, Dole had met his match.
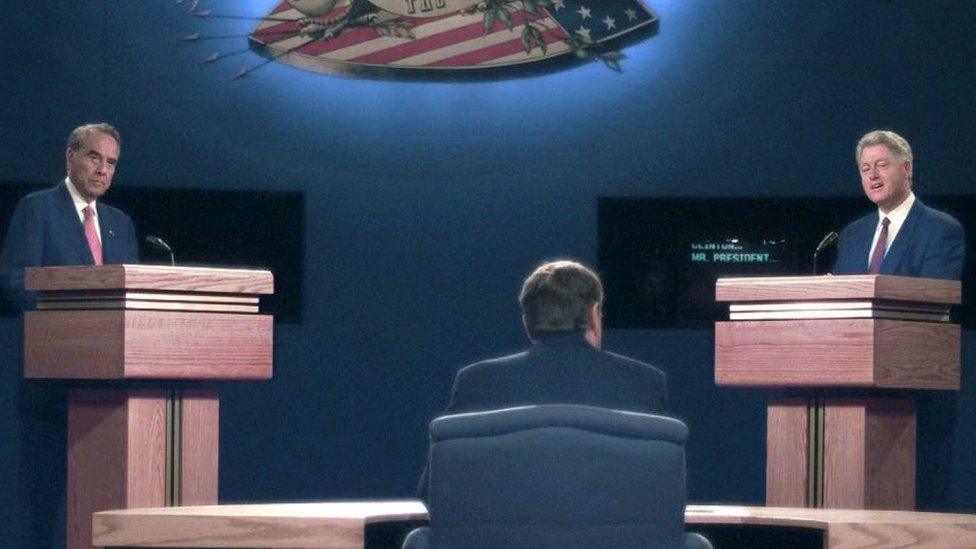

Dole takes on Bill Clinton during the 1996 presidential campaign
In his speech accepting the nomination, he left an open goal. "Let me be the bridge to an America that only the unknowing call myth." he said. "Let me be the bridge to a time of tranquillity, faith and confidence in action."
Clinton's response was cutting: the country needed a bridge to the future and not the past.
Dole failed to find the national cheerleader within him, couldn't stand spin doctors and was cursed with the smile of an undertaker.
"A Dark Man for Dark Times," said one Democrat bumper sticker. The oldest first-time presidential candidate in history lost gracefully and by a landslide.
Retiring from public office, Dole remained active - becoming a regular on Sunday political talk shows and an influential elder statesman of American politics.
He picked up his career in the law, appeared in TV commercials for Dunkin' Donuts and Viagra, and wrote a book on jokes told by US presidents, ranking them by their sense of humour.
His endorsement in presidential campaigns remained valuable. He backed moderate Republicans like Marco Rubio and Mitt Romney - with less enthusiasm for his party's emerging right.
In 2019, Congress unanimously voted his promotion from captain to colonel for his service during World War Two. He accepted the honour gracefully, although he quipped that, "I was happy being a captain and it pays the same."
Two years later - when Dole had been diagnosed with advanced lung cancer - newly elected President Joe Biden was one of the first to visit the veteran Republican at home. It was a mark of the respect in which Bob Dole was held on both sides of the political divide.
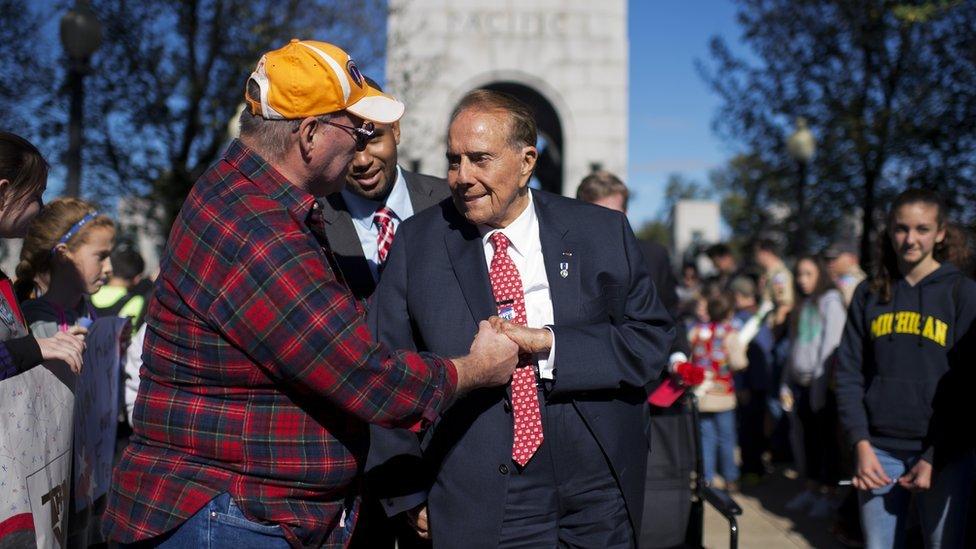

Dole, at the age of 92, greets supporters at the WWII Memorial on Veterans Day in 2015
In 2005, Dole wrote his life story. He recalled that moment on the battlefield in Italy, just three weeks before the German surrender.
He told how he thought he'd end up on a street corner "selling pencils"; about how meeting injured troops in Iraq brought back memories; and of the debt America owes to its fighting men.
He will be remembered as one of his country's most distinguished public servants - a man who displayed tremendous courage in battle and fortitude in recovery.
At his great friend Richard Nixon's funeral, Dole described him in words many would apply to the speaker himself: "Brave, unafraid of controversy and living every day of his life to the hilt."
Related topics
- Published5 December 2021
