Biodiversity: 'Humans can save animals from extinction if they act'
- Published
- comments
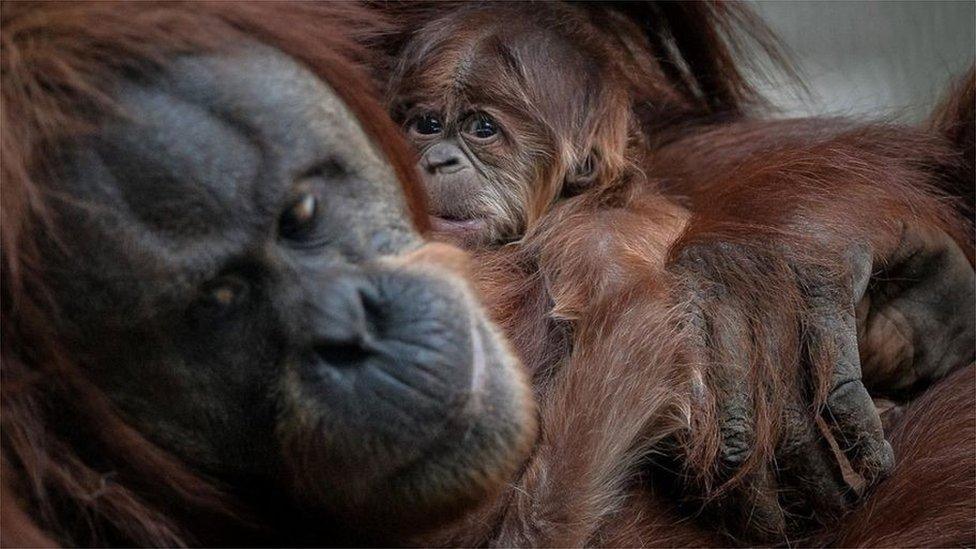

Most of the world's orangutans live outside of protected areas and are still threatened by their habitats being destroyed by human farmers and loggers
Humans could save thousands of species from extinction if they act.
That's according to a team of scientists who have warned that hundreds of thousands of mammals could be lost if human activity doesn't change.
The new research - which has been published in the scientific journal Science Advances - suggests that over 550 species of mammal could go extinct this century alone - following in the footsteps of the mammoth and sabre-toothed cat.
However, with better conservation plans put into place, this could be avoided, the scientists have said.

What is conservation?
The term conservation means preventing injury, decay or the waste of something.
There are conversation efforts all over the world to protect the natural habitats of wildlife which are threatened by human behaviours like logging and farming around rivers, forests and other natural resources.
In the article, it is claimed that humans are almost entirely responsible for the extinction of mammals in the past decades.
This is supported by a 2019 United Nations report which said that hundreds of thousands of species of animals and plants are facing extinction because of human activity.
The report pointed towards what is called called a 'biodiversity crisis.
What is biodiversity and how are humans impacting on it?

Biodiversity is the range of animals, plants and microorganisms in a given area. It is the foundation that supports all life and each member plays an important role.
If the numbers of one species are affected, there are almost always knock-on consequences to other living things in the ecosystem.
For example, if a disease suddenly wipes out the plants in a pond, it might affect the fish and birds living in that habitat because they have less food to eat.
The future of our species on Earth depends on maintaining high biodiversity.
It's predicted that biodiversity loss will have a massive impact on our food and medicine supply.
As the human population grows, so too does the amount of waste we produce, which pollutes our land, air and oceans. This, combined with deforestation, over fishing and global warming is reducing biodiversity.
The good news is that conservation work can help reverse this. The goal of conservation is to protect species from extinction, maintain habitats and ecosystems.
For example, scientists believe that marine life could recover by 50-90% by 2050 if action including tackling climate change and restoring habitats happens on a large scale.
- Published5 September 2020

- Published21 August 2020
- Published3 September 2020

