Scientists discover new type of ice by accident
- Published
- comments
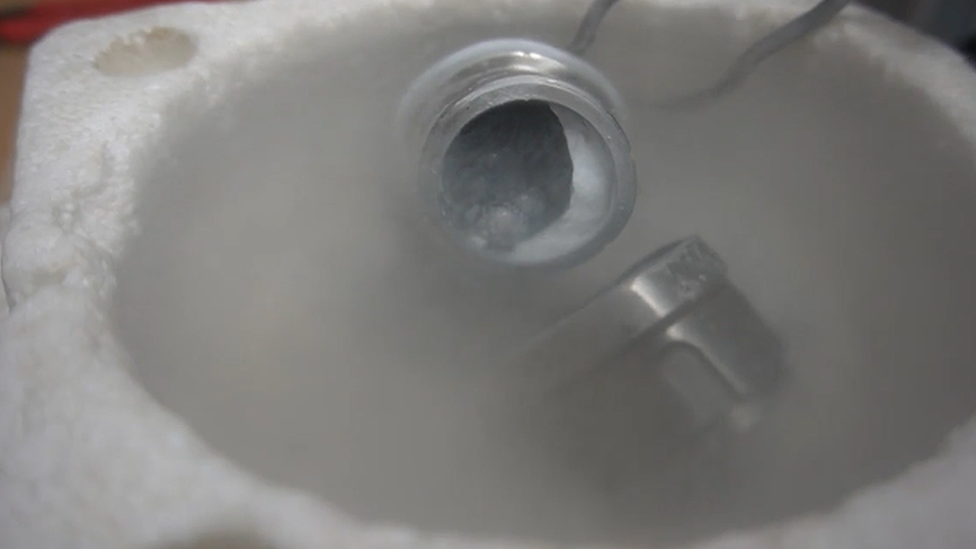

Inside that tube you can see the new ice that the scientists have discovered!
Some scientists at UCL and the University of Cambridge have done something really cool!
No, literally: they've managed to create a brand new type of ice.
It's a powdery substance with some properties similar to water, and the researchers think it may exist on the icy moons of some of the planets in our solar system.
The scientists involved in the experiment think it could teach us lots of important things about water and how it behaves.

It's quite different to the ice we're used to
How was the new ice made?
It sort of happened by accident.
"It was one of those Friday afternoon experiments where you just do it and see what happens," explained Christoph Salzmann, a physical chemist at University College London and co-author of the paper.
They shook ordinary ice with steel balls in a jar cooled to -200 degrees Celsius in a process called ball milling, and to their surprise, something amazing happened!

This is what the experiment started off looking like
Lead author Dr Alexander Rosu-Finsen, who carried out the experimental work while at UCL Chemistry, said: "We shook the ice like crazy for a long time and destroyed the crystal structure.
"Rather than ending up with smaller pieces of ice, we realised that we had come up with an entirely new kind of thing, with some remarkable properties."
How is the new ice different to ordinary ice?
After discovering the new ice, the scientists examined it with X-rays to learn more about it.
Ice is water in its frozen form
Water freezes when it reaches temperatures below 0 degrees Celsius
If water freezes quickly, ice can appear cloudy, as air bubbles get trapped inside
Ice that is attached to a coastline is called fast ice
Ice floats in water, which is unusual behaviour for the solid form of a liquid
They wanted to see how its molecules were arranged - these are groups of atoms, which are the building blocks of everything in the universe.
However when they looked closely, they found that the ice didn't have an organised structure at all, which makes it amorphous (a fancy word for not having a defined shape).
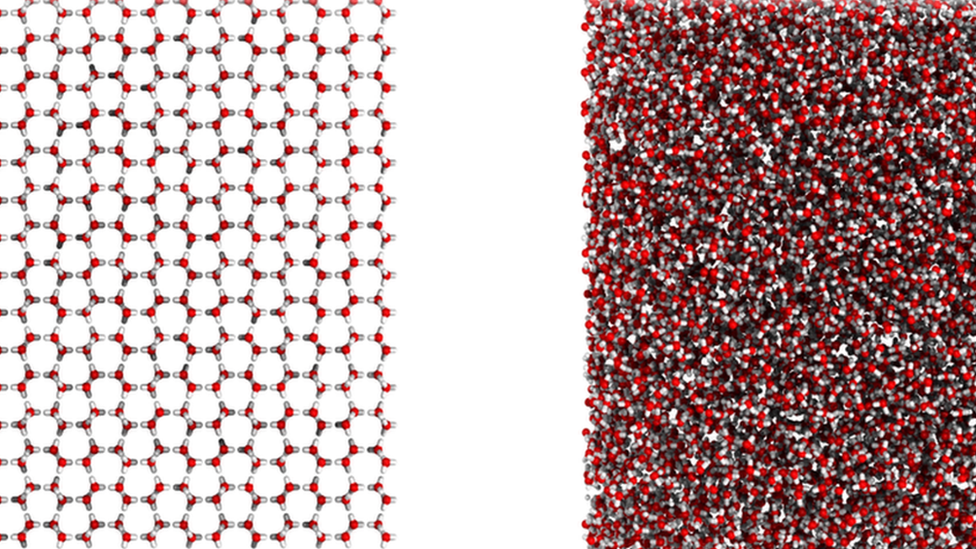
The team were able to create computer images of the new ice - on the left you can see the structure of ordinary ice, and on the right is what they discovered
This is different to the ice that we're used to, which forms hexagonal (six-sided) patterns.
It also has a similar density to water, because of this, the researchers called it medium-density amorphous ice, or MDA.
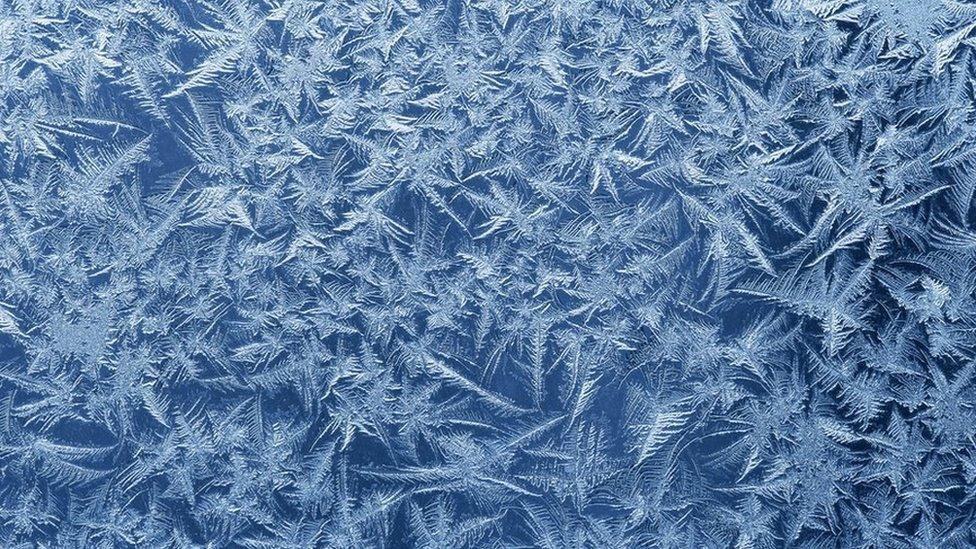

Ice can create beautiful patterns like this frost on a window
The researchers involved in the experiment think that the newly discovered ice may be the true glassy state of liquid water - that is, a precise copy of liquid water in solid form, in the same way that glass in windows is the solid form of liquid silicon dioxide.
Although some scientists don't think it's like glassy water at all, but something else entirely.
Out of this world
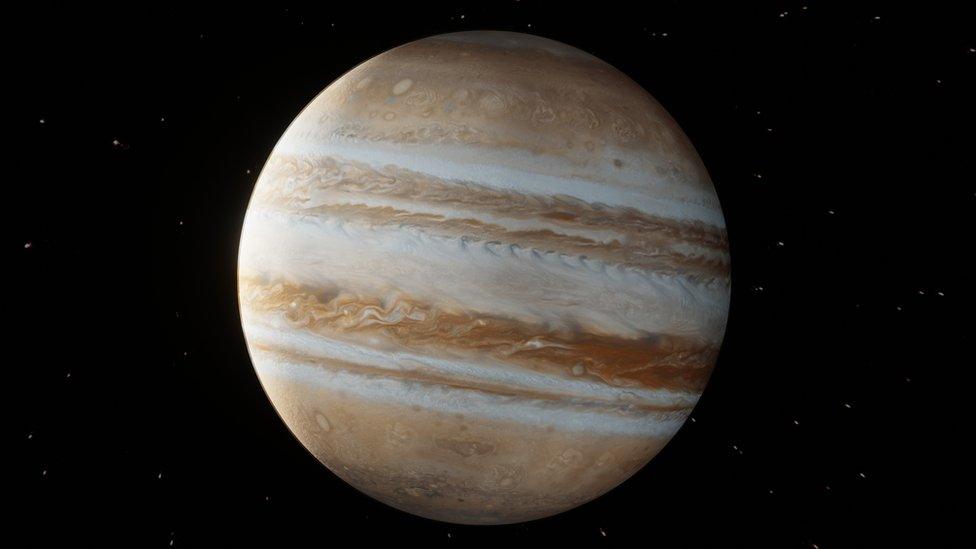

Jupiter's moons may contain some of this ice
They believe that MDA may exist inside ice moons of planets like Jupiter and Saturn, as tides on these gas giants could potentially recreate the forces the scientists created by shaking their jar.
On top of that, the team found that when MDA was warmed up and re-crystallised, it released a huge and explosive amount of heat, meaning it could potentially trigger "icequakes" on these moons such as Jupiter's Ganymede, which is covered with ice that can be kilometres thick.
- Published19 May 2022

- Published26 January 2021

- Published23 April 2022