Covid-19: Debunking the latest wave of medical misinformation
- Published
False claims about chemical contents of Covid tests have spread online
Posts spreading unverified theories about the pandemic continue to spread on social media platforms.
We've examined the latest wave of false information covering subjects including Covid testing kits and vaccines.
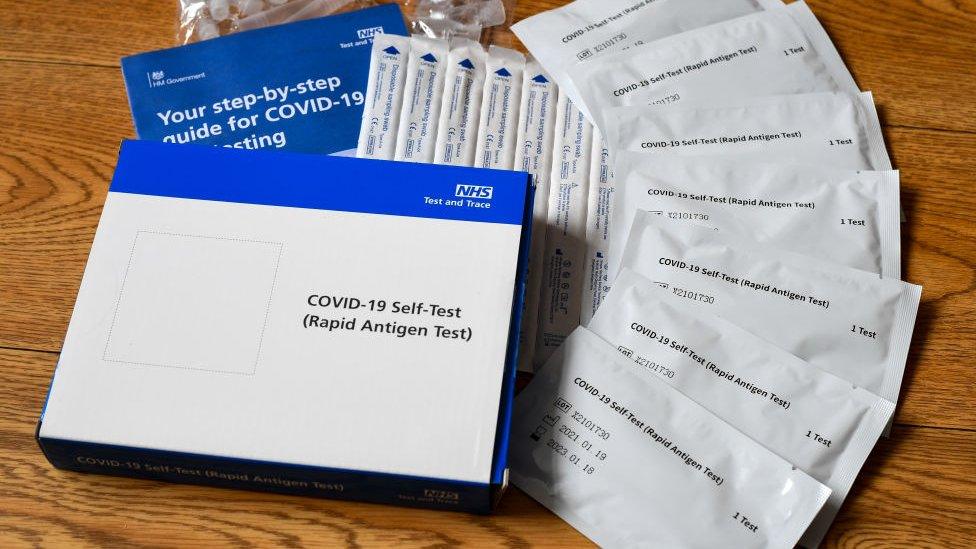
Test swabs don't contain cancer-causing chemical
Lateral flow tests for coronavirus are becoming widespread in workplaces and schools, but viral Facebook posts are incorrectly claiming that they are a cancer risk.
The videos and photos claim that they contain ethylene oxide, a known carcinogen. The packaging for the NHS test kits says "sterilised in ethylene oxide", but this only tells part of the story.
The Department of Health and Social Care told us that while the chemical is used in gaseous form to sterilise test swabs, the amounts used are well within safety limits and are "rigorously tested and are safe to use on a regular basis".

A video posted on Facebook misinterprets why ethylene oxide appears in the test kit instructions
In fact, up to half of all US medical devices, external are sterilised with ethylene oxide, which is an effective method that doesn't damage equipment. Further stages in the sterilisation process remove the gas almost entirely.
The US Centers for Disease Control says that while acute exposure to the chemical - many times greater than any residual chemical that might be left in a test swab - can increase the risk of cancer, these tiny amounts are not harmful.
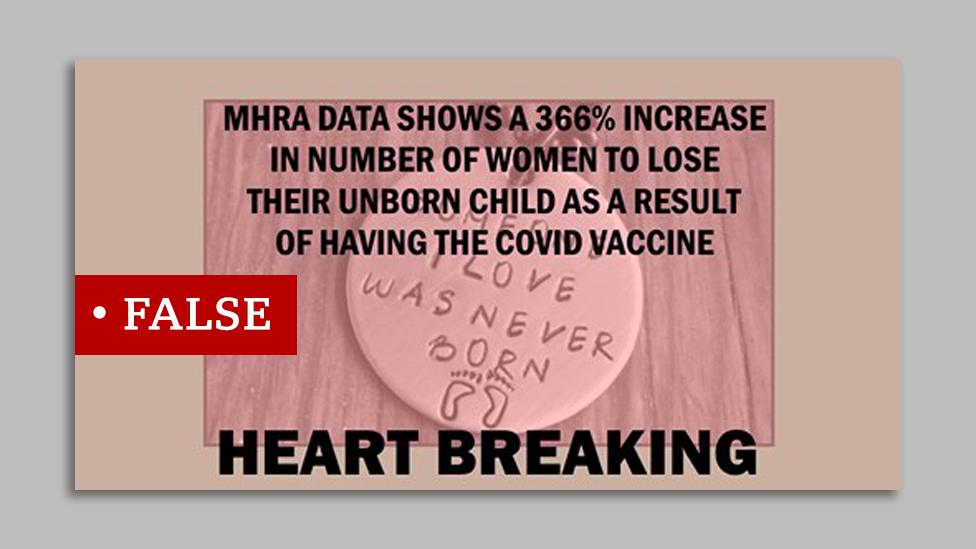
Misunderstanding miscarriages
A blog post claiming that rates of miscarriage "as a result" of receiving a Covid-19 vaccine have increased by 366% has been shared widely on social media.
There is no evidence that Covid-19 vaccines can increase the risk of miscarriage.
The figures used in the blog post are a distorted interpretation of data from the yellow card scheme of the UK medicines regulator, the MHRA. The scheme allows health professionals and the public to report medical incidents or suspected side effects of medicines, so that their quality and safety can be monitored and very rare side effects picked up.
Data showing a miscarriage occurred after a vaccine does not mean that the two events are linked.
Miscarriage is sadly very common, and among women who know they're pregnant, about one in eight pregnancies will end in miscarriage, according to the NHS. Identifying miscarriages that happen after a vaccine allows the MHRA to assess whether the number of miscarriages in the vaccinated population is any higher than usual.
The claim that miscarriages among vaccinated people have increased by 366% is taken from an increase in the number of miscarriages reported to the yellow card scheme since Covid-19 vaccines first started being rolled out in December and January. It doesn't take into account the fact that millions more people have been vaccinated since January - which would lead to an expected increase in reports to the yellow card scheme.
In a response to the Reuters news agency, external about the claims, the MHRA said: "There is no pattern to suggest an elevated risk of miscarriage related to exposure to the Covid-19 vaccines in pregnancy."
But it added that current advice does not routinely recommend Covid-19 vaccines for pregnant women because of limited data, and that individuals at high risk from the virus could talk to a doctor about vaccination.

Mutant claims go viral
A recent cause taken up by anti-vaccination activists concerns the spread of new coronavirus variants.
Many referred to statements published by Geert Vanden Bossche, a Belgian veterinarian and vaccine researcher.
He says he supports vaccines, but in a series of letters warns about the dangers of Covid-19 vaccinations, which he says risk creating new variants of coronavirus that may "result in a global catastrophe without equal".
The World Health Organization says that as more people get vaccinated it expects "virus circulation to decrease, which will then lead to fewer mutations.", external
All viruses mutate as they make copies of themselves to spread and thrive.
Viruses do this in different ways, including while inside the bodies of people who have already been vaccinated but who are still developing an immune response. This may drive the virus to evolve to escape the effects of such immunity.
Scientists are studying whether the vaccines still work against new strains of the virus and from where such mutations come.
These types of mutations might be happening even now at a low level, says Dr Julian Tang, a virologist at the University of Leicester, "but this is less of a concern relatively, compared to getting more people vaccinated against the virus strain that is still circulating widely, globally."
There are risks associated with mutations that evolve in largely vaccinated populations, says Dr Ravi Gupta, a microbiologist at University of Cambridge who has been researching new variants., external But he says: "The benefits of mass vaccination to curb transmission...outweigh the risks."
As such, according to the experts we spoke to, there's no evidence that vaccines will lead to more dangerous variants that would merit the drastic change in strategy being suggested by Mr Bossche.
We requested a comment from Mr Bossche, who referred us to his website where he has previously responded to questions about his work.

The Russian doctor
Finally, a post that echoes another familiar theme of pandemic-related misinformation - the totally fabricated link between 5G electro-magnetic radiation and coronavirus.
Russian doctors have performed post-mortem examinations on Covid-19 patients and discovered proof that Covid "does not exist as a virus", claim the posts on secure messaging app Telegram which say the people examined died of "electromagnetic radiation". There's no evidence of this happening.
A near identical post - claiming to cite Italian health authorities and doctors - went viral in spring last year. These theories simultaneously referred to radiation poisoning and claimed that Covid is caused by a bacteria and not a virus - which is also incorrect.
The recent iteration of the copy and paste postings are incorrectly sourced to the Russian health authorities this time.
The claim has been circulating on Facebook in Austria and Germany since at least late February and a shortened version of the message was shared in big anti-vaccine and QAnon conspiracy channels on Telegram.
Additional reporting by Olga Robinson and Alistair Coleman.


Related topics
- Published2 April
- Published13 February 2021

- Published15 April 2020
