AstraZeneca: A product of successful mergers?
- Published

Although AstraZeneca is often referred to as a UK company, the pharmaceutical giant operates in more than 100 countries, and manufactures drugs in 16 places around the globe.
The 15-year-old firm employs almost 52,000 people - 6,700 in the UK - and made a pre-tax profit of $3.3bn (£2bn) in 2013.
The company invests heavily in science research and development in the UK and has sites across the country - leading to fears that a takeover by US drugs giant Pfizer would negatively impact the UK economy.
But, somewhat ironically, AstraZeneca's history is a labyrinthine list of mergers, dating back to the late 19th Century.

1800s:
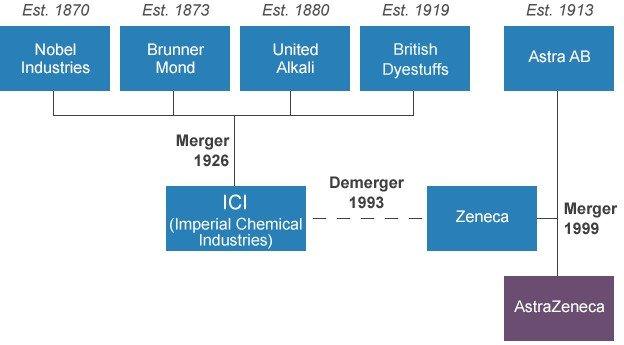
AstraZeneca's earliest roots can be traced to several companies founded in the late 1800s.
Nobel Industries was founded in 1870 by Swedish chemist and industrialist Alfred Nobel for the production of the new explosive dynamite. It later diversified into the production of blasting gelatin and ballistite, which was a precursor of cordite, an explosive used in weaponry.
Chemical manufacturing firm Brunner Mond was formed in Cheshire as a partnership in 1873 (becoming a limited company in 1881) by John Brunner and Ludwig Mond.
United Alkali was formed in 1890 when 48 chemical companies from the Tyne, Scotland, Ireland and Lancashire merged.

1910s:
Meanwhile, in 1913 Astra AB was founded in Sodertalje, Sweden, as an international pharmaceutical group engaged in the research, development, manufacture and marketing of pharmaceutical products.

1926:

In 1926 Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was formed by the merger of British Dyestuffs Corporation, United Alkali, Brunner Mond and Nobel Industries.
The plan for the new company was agreed on board the Cunard vessel Aquitania on a voyage from New York to Southampton.
The architects of the merger were Sir Harry McGowan, chief executive of Nobel Industries and Sir Alfred Mond, later Lord Melchett, chairman of Brunner, Mond & Company, who became the first ICI chairman.

1990s:
In 1993 ICI hived off its chemical and pharmaceutical business as part of a planned demerger, calling it Zeneca.
In 1999 Zeneca merged with Swedish pharmaceuticals firm Astra, external.
- Published14 May 2014