Mortgage rates soar to highest level for 15 years
- Published

Mortgage costs have hit the highest level for 15 years after the rate on a two-year fixed deal surpassed the peak in the aftermath of the mini-budget.
The average rate on such a deal is now 6.66% - a level not seen since August 2008 and the financial crisis.
Mortgage costs have been soaring recently as lenders grapple with inflation and uncertainty over interest rates set by the Bank of England.
Lenders have been questioned by MPs about the impact on customers.
Bank and building society bosses, including representatives from Lloyds and Nationwide, were in front of the Treasury Select Committee.
The hearing covered mortgage stress faced by borrowers, lenders' response to people falling behind on repayments and the wider impact on the UK housing market.
Mortgage providers said people fixing deals at rates now would typically face an increase of about £350 a month in their repayments, but there remained relatively low numbers of people falling behind partly because unemployment remains low.
The committee examined how mortgage-holders are trying to cope, with some people overpaying on current deals and considering extending their term.
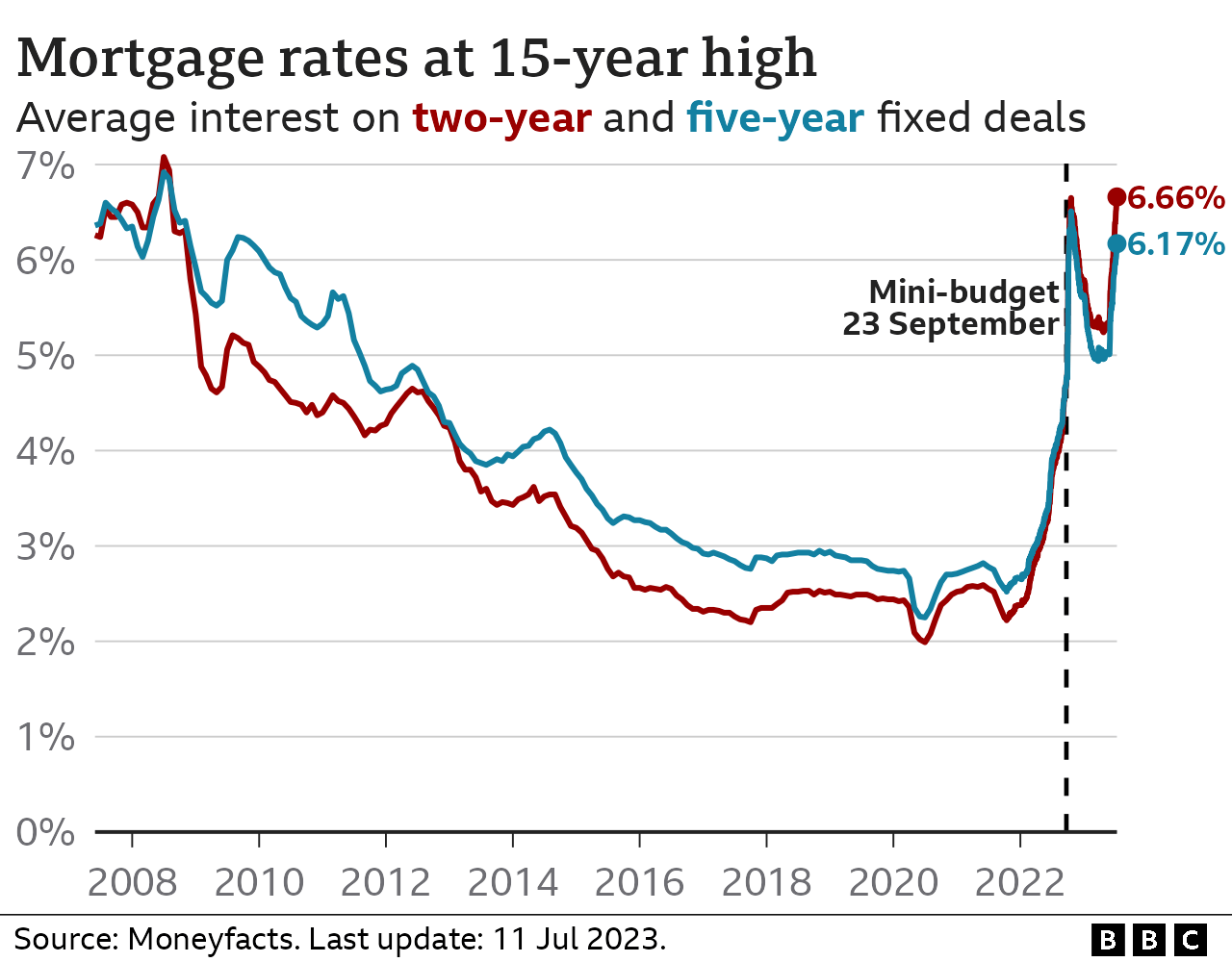
Mortgage rates have risen consistently and - at times - sharply over recent weeks, with the possibility of more increases to come.
Data on wages and rising prices mean markets anticipate that inflation and interest rates will stay higher for longer in the UK than previously expected, which has been reflected in the funding costs of mortgages.
That has pushed the typical two-year mortgage rate above the peak of October last year in the aftermath of the mini-budget during Liz Truss's short-lived premiership, according to the financial information service Moneyfacts.
Mortgage rates 15 years ago hit 7%, as global economies were hit by a banking crisis.
The average rate on a five-year deal remains below the level seen after the mini-budget. The current level is 6.17%, compared to the peak last year of 6.51%.
The Bank of England has been raising its benchmark interest rate in an attempt to tackle the inflation rate which remains stubbornly high. Figures published on Tuesday show UK wages have risen at a record annual pace, fuelling fears that inflation will stay high for longer.
The expectation of further increases has pushed up the cost of funding mortgages, and so lenders have been raising the rates they charge customers.
At the hearing, Andrew Asaam, homes director at Lloyds Banking Group, told MPs this was changing the plans of first-time buyers.
"People are either putting down a larger deposit or buying a smaller property because affordability is tighter," he told MPs. "We won't lend as much now, so people are moderating what they can afford to buy."
Remortgaging shift
People coming off fixed deals and looking for a new one could potentially have to pay hundreds of pounds more a month.
Around 2.4 million fixed-rate mortgages are due to end between now and the end of 2024, according to figures from banking trade association UK Finance.
Aaron Strutt, from mortgage broker Trinity Financial, said that the uncertainty of the situation made it difficult for lenders to price mortgages. A rush of people trying to secure deals at lower rates had meant the money allocated by some providers to lend in mortgages was drained.
He added that there was evidence of a split with large numbers of people renewing with their existing lender, without the requirement for further affordability assessments.
The recent rises in mortgage costs are also likely to have a knock-on effect on renters who could face higher payments as landlords seek to recoup the rising cost of higher mortgages. Squeezed landlords may decide to sell properties, which could lead to fewer homes available to rent, according to the National Residential Landlords Association.
Following a meeting with Chancellor Jeremy Hunt, lenders agreed to some flexibility and making sure homes are not swiftly repossessed from those struggling to pay.
Labour is also planning to hold its own mortgage summit in the coming days.

What happens if I miss a mortgage payment?
A shortfall equivalent to two or more months' repayments means you are officially in arrears
Your lender must then treat you fairly by considering any requests about changing how you pay, perhaps with lower repayments for a short period
Any arrangement you come to will be reflected on your credit file - affecting your ability to borrow money in the future

Sign up for our morning newsletter and get BBC News in your inbox.

Are you struggling to pay your mortgage? Have you recently renewed a two-year fixed deal? You can share your experiences by emailing haveyoursay@bbc.co.uk, external.
Please include a contact number if you are willing to speak to a BBC journalist. You can also get in touch in the following ways:
WhatsApp: +44 7756 165803
Tweet: @BBC_HaveYourSay, external
Please read our terms & conditions and privacy policy
If you are reading this page and can't see the form you will need to visit the mobile version of the BBC website to submit your question or comment or you can email us at HaveYourSay@bbc.co.uk, external. Please include your name, age and location with any submission.
- Published8 July 2023
- Published9 January 2024

- Published8 January 2024

- Published25 June 2023

- Published23 June 2023
