What does hot weather do to the body?

- Published
Hot weather during the summer can affect anyone, but some people run a greater risk of serious harm.
Experts recommend checking on those who may be more vulnerable, such as older people and babies.
What does extreme heat do to our bodies?
As the body gets hotter, blood vessels open up. This leads to lower blood pressure and makes the heart work harder to push the blood around the body.
This process can cause mild symptoms such as an itchy heat rash or swollen feet.
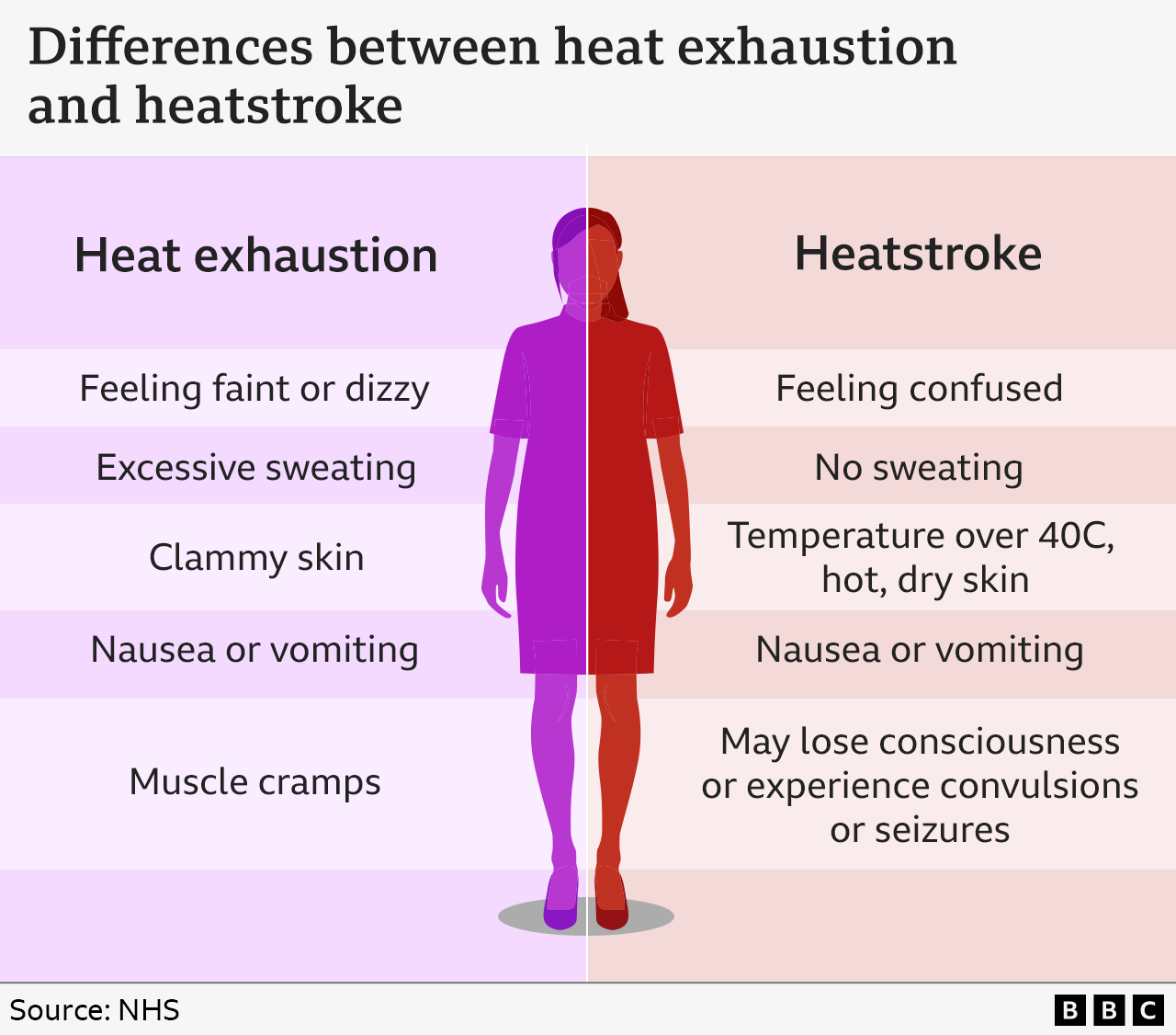
At the same time, sweating leads to the loss of fluids and salt and, crucially, the balance between them in the body changes.
This, combined with the lowered blood pressure, can lead to heat exhaustion. Symptoms include:
dizziness
nausea
fainting
confusion
muscle cramps
headaches
heavy sweating
tiredness
If blood pressure drops too far, the risk of heart attacks rises.
Why do bodies react this way to heat?
Our bodies strive to keep a core temperature of about 37C whether we are in a snowstorm or a heatwave.
That is the temperature at which our bodies have evolved to work.
But as the weather gets hotter, it is harder for the body to keep its core temperature down.
It opens more blood vessels near the skin to lose heat to our surroundings and starts sweating.
As the sweat evaporates, it dramatically increases the heat lost from the skin.

How can I stay safe in the heat?
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) recommends looking out for those who may struggle to keep cool, such as older people, those with underlying conditions and and those who live alone.
Other advice includes:
staying cool indoors by closing curtains on rooms that face the sun
drinking plenty of fluids and avoiding too much alcohol
keeping out of the sun between 11:00 and 15:00 when the sun's rays are strongest
staying in the shade, using sunscreen with a high SPF and UVA rating, and wearing a wide-brimmed hat
avoiding physical exercise in the hottest part of the day
carrying water with you if travelling
Anyone tempted to cool off in rivers and open water should consult local warning signs and consider any hidden dangers, external.
No one - especially babies, young children and animals - should ever be left in a locked vehicle.

What should I do if I think someone has heat exhaustion or heatstroke?
If you see someone you think has heat exhaustion, the NHS says you should:, external
move them to a cool place
get them to lie down and raise their feet slightly
get them to drink plenty of water - sports or rehydration drinks are also OK
cool their skin - spray or sponge them with cool water and fan them. Cold packs around the armpits or neck are good too
If they can be cooled down within half an hour, then heat exhaustion is not normally serious.
However, if they do not recover within 30 minutes, then they are at risk of heatstroke.
This is a medical emergency and you should call 999 immediately.
People with heatstroke may stop sweating even though they are too hot. Their temperature could go over 40C and they might have seizures or lose consciousness.
Who is most at risk from hot weather?
People who are older or have some long-term conditions - such as heart disease - are sometimes less able to cope with the strain heat puts on the body.
Diabetes can make the body lose water more quickly and some complications of the disease can alter blood vessels and the ability to sweat.
Children and those who are less mobile may also be more vulnerable. Brain diseases, such as dementia, can also leave people unaware of the heat or unable to do anything about it.
People who are homeless will also be more exposed to the sun. Those living in top-floor flats will also face higher temperatures.
Heatwaves: The New Normal?
How hot is too hot? From heat labs to firefighting helicopter pilots and wineries, we look at how extreme heat impacts people and environments in the UK.
Do some drugs increase the risk of hot weather?
Yes - but the NHS says people should keep taking their medication as normal, and focus on staying cool and hydrated.
Diuretics - sometimes called "water pills" - increase the amount of water the body expels. They are taken widely, including for heart failure. In high temperatures, they increase the dangers of dehydration and imbalances in key minerals in the body.
Antihypertensives - which lower blood pressure - can combine with the blood vessels that are dilating to cope with the heat and cause dangerous drops in blood pressure.
Some drugs for epilepsy and Parkinson's can block sweating and make it harder for the body to cool itself.
Other drugs such as lithium or statins can become more concentrated and problematic in the blood if there is too much fluid loss.

Does heat kill?
During 2022 - which saw the highest recorded temperature in England at 40.3°C - there were an estimated 2,985 so-called "excess deaths" as a result of the heat, external.
Most heat-related excess deaths are due to heart attacks and strokes caused by the strain of trying to keep body temperatures stable.
The higher death rate starts to kick in once the thermometer passes 25C-26C.
However, evidence suggests the deaths tend to be caused by higher temperatures in spring or early summer rather than during "peak summer".
This could be because we start to change our day-to-day behaviour as summer progresses and we get more used to dealing with the heat.
The evidence from previous heatwaves is the increase in deaths happens very quickly - within the first 24 hours of a heatwave.
Get in touch
What questions do you have about the heat?