Gene therapy to halt rare form of sight loss
- Published
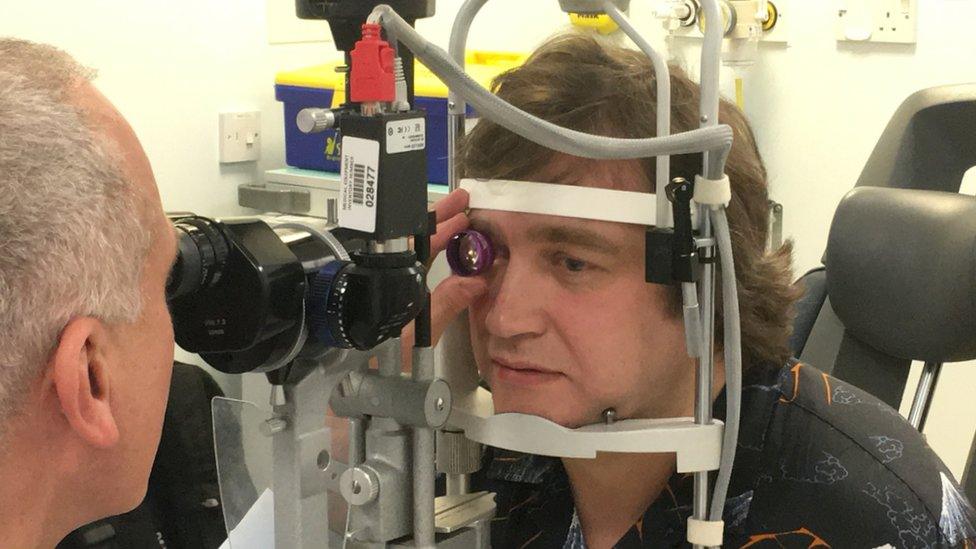
Matthew Wood hopes the gene therapy will help him keep his remaining vision
A new gene therapy has been used to treat patients with a rare inherited eye disorder which causes blindness.
It's hoped the NHS treatment will halt sight loss and even improve vision.
Matthew Wood, 48, one of the first patients to receive the injection, told the BBC: "I value the remaining sight I have so if I can hold on to that it would be a big thing for me."
The treatment costs around £600,000 but NHS England has agreed a discounted price with the manufacturer Novartis.
Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec), has been approved by The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), which estimates that just under 90 people in England will be eligible for the treatment.
The gene therapy is for patients who have retinal dystrophy as a result of inheriting a faulty copy of the RPE65 gene from both parents. The gene is important for providing the pigment that light sensitive cells need to absorb light. Initially this affects night vision but eventually, as the cells die, it can lead to complete blindness.
How it works
An injection is made into the back of the eye - this delivers working copies of the RPE65 gene. These are contained inside a harmless virus, which enables them to penetrate the retinal cells. Once inside the nucleus, the gene provides the instructions to make the RPE65 protein, which is essential for healthy vision.
Matthew Wood started losing his sight as a child, and is now registered blind. However, he does have some peripheral vision and can detect large objects and bright lights. He told the BBC: "Since I was a child I was continually told there was no treatment for this condition, so it's amazing to receive this gene therapy."
Mr Wood, from London, had his right eye treated during an hour-long operation at the John Radcliffe Hospital in Oxford.
His left eye will be injected in a few weeks. The surgery was carried out by Prof Robert MacLaren, who has pioneered research into gene therapies for preventing blindness.
He told the BBC: "This is very exciting - this is the first approved NHS gene therapy for an eye disease, but there are opportunities to use gene therapy to treat other diseases in future, not only in the eye."
The treatment is only suitable for patients who have some remaining vision. It should bring the biggest benefits to children with RPE65 retinal dystrophy, as it could halt sight loss before permanent damage is done.
It is not known how long the benefits of the treatment will last, but it's thought it could be several decades.
Jake Ternent, 23, from Durham, had his gene therapy at Moorfields Eye Hospital in London.
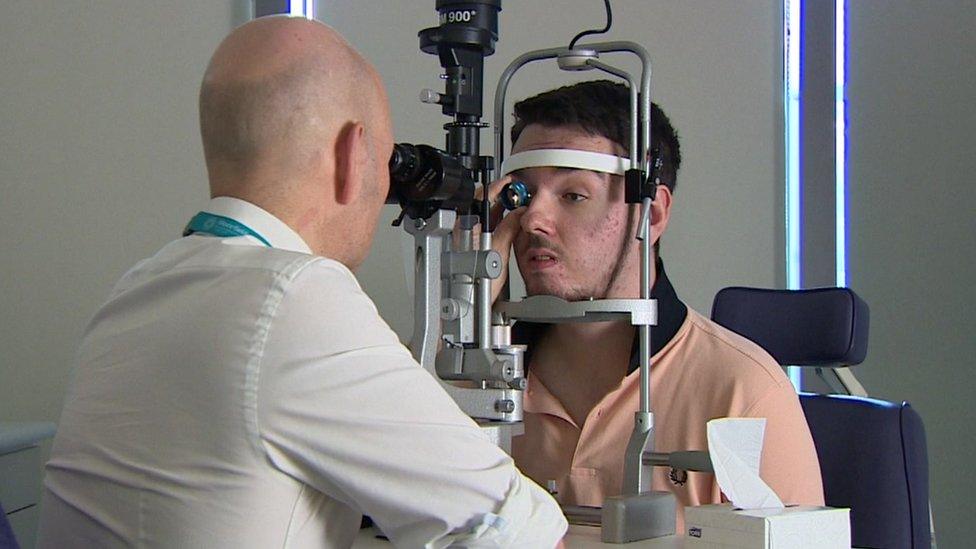
Jake Ternent had his gene therapy at Moorfields Eye Hospital
Like Matthew Wood, he is registered blind, but has some limited sight. He told the BBC: "I hope the treatment could improve my night vision, and possibly even my day vision, which would be incredible. I feel lucky and privileged to get this on the NHS."
Prof James Bainbridge - from Moorfields Eye Hospital - who treated Jake, told the BBC: "To be at the point now where we are able to offer this treatment on the NHS, is truly remarkable. This is the first example of what's anticipated to be a whole new generation of treatments."
It will take a month or two before Matthew and Jake know what changes the gene therapy has made to their vision. But even if it simply prevents further sight loss, both say they will be delighted.
Professor Stephen Powis, NHS medical director, said: "Loss of vision can have a devastating effect, particularly for children and young people, but this truly life-changing treatment offers hope to people with this rare and distressing condition."
Follow Fergus on Twitter., external
- Published4 September 2019

- Published18 February 2019
