Dirty laundry: Are your clothes polluting the ocean?
- Published

In an indoor "Manchester-drizzle-simulating" rain room at the University of Leeds, and in a laundry lab in Plymouth, research is revealing the unexpected environmental cost of the very clothes on our backs.
"Not many people know that lots of our clothes are made of plastic," says Imogen Napper, a PhD student at Plymouth University, "polyester, acrylic."
Ms Napper and Prof Richard Thompson study marine microplastics - fragments and fibres found in the ocean surface, the deep sea and the marine food chain.
And in a recent lab study, they found that polyester and acrylic clothing shed thousands of plastic fibres each time it was washed- sending another source of plastic pollution down the drain and, eventually, into the ocean.
"My friends always make fun of me because they think of marine biology as such a sexy science - it's all turtles, hot countries and bikinis," says Ms Napper.
"But I've been spending hours washing clothes and counting the fibres."
It might not be exotic, but this painstaking "laundry-science" has revealed that an average UK washing load - 6kg (13lb) of fabric - can release:
140,000 fibres from polyester-cotton blend
nearly half a million fibres from polyester
more than 700,000 fibres from acrylic
Fishing for plastic
Some of the plastic found in the ocean has come from clothing, scientists say
That is from every load of synthetic laundry from every UK washing machine. "A lot more fibres were released in the wash than we expected," Ms Napper says.
"They're going down the drain, so they are making their way into the sewage treatment works and maybe, from there, into the marine environment."
Prof Thompson says washing clothes could be a "significant source" of plastic microfibres in the ocean.
"When we sample, we find plastic fibres less than the width of a human hair - in fish, in deep sea sediments, as well as [floating] at the surface."
Changes need to happen "at the design stage", he says; better, harder-wearing and less "disposable" clothing would last longer and be good for the environment.
"The garments [we washed] were similar fleecy garments, and some were shedding fibres much faster than others," Prof Thompson says.
"We need to understand why some garments wear out much more quickly than others, so we can try to minimise unnecessary emissions of plastic."
And scientists now have the backing of possibly the most wholesome of British organisations; the Women's Institute, decided just last month to campaign, external for what they called "innovative solutions" to the problem of microplastic fibres in the ocean.
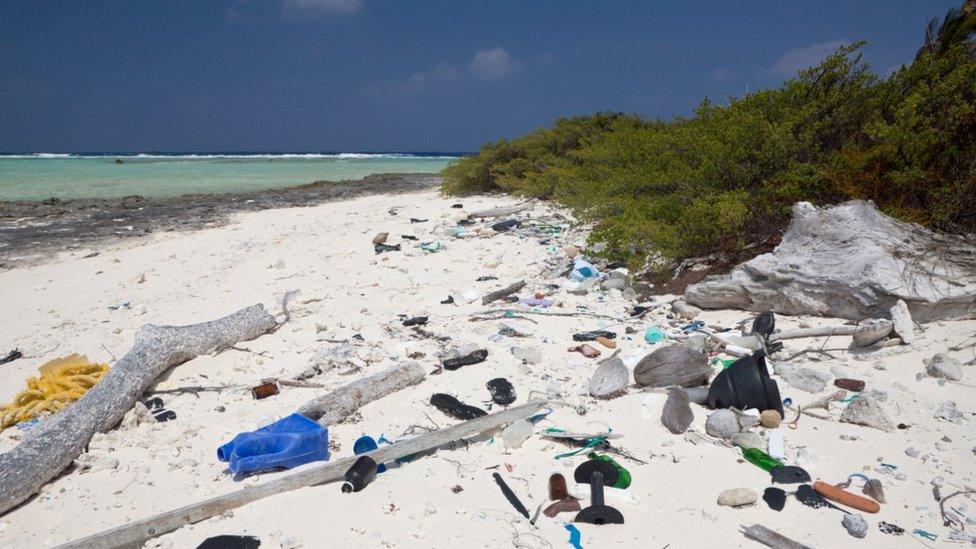

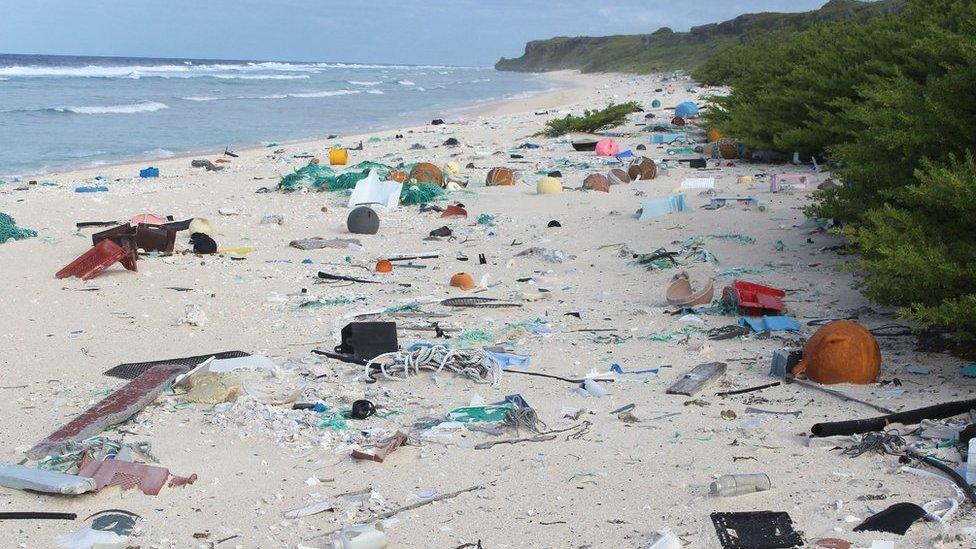
Our plastic rubbish has floated to islands that are thousands of miles from the nearest human population
Toxic raincoats
Prof Richard Blackburn, head of the sustainable materials research group at the University of Leeds, external, agrees that textile-makers need to think about what happens "in use", when we wear and wash our clothes.
"People don't consider it," he says. "So, potentially, the pollution could be caused by us - the consumers - rather than the manufacturers."
Prof Blackburn's colleague in Leeds, Philippa Hill, was also drawn to the subject of laundry - by chemical coatings being washed off outdoor clothing.
Chemical coating make our nylon raincoats repel water - but they could come off in the wash
The waterproofing most high-end, rain-proof jackets are treated with consists of perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs), which are persistent and potentially toxic pollutants.
Coating textiles and other materials with PFCs makes them resistant to stains, grease, and water. They are also used in some non-stick pans and food packaging.
These molecules sit on top of the (usually nylon) outer fabric like a protective layer of chemical barbed wire - the tip of every barb pushes away water molecules, which are too large to pass through the spaces in between. Air molecules can pass through freely, resulting in a non-sweaty, breathable, waterproof jacket.

Fluorochemical coatings have been used for decades to make nylon jackets water-repellent, but breathable
But, as Dr Andrew Sweetman, from the Lancaster Environment Centre, external, points out, lab and field studies have shown that some PFCs can accumulate in the tissues of fish and other wildlife as they consume contaminated food and water - building up a dose that can become harmful.
Essentially, they don't degrade," he explains to BBC News. "So if we take samples from waterways, as a result of their widespread use and persistence, we basically find them wherever we look."

Scientists report finding fluorinated chemicals in waterways 'wherever they look'
And while textiles manufacturers have to abide by regulations to limit the pollution they release into waterways, Prof Blackburn says, "there are no limits on what we can release from our own homes".
Prof Blackburn and Ms Hill compared PFC-coated fabric with that treated with more benign oil-based coatings that also repel water.
"We took samples of fabrics that had been coated with the different treatments," says Prof Blackburn.
"And we'd carry out industry-standard tests - showering them with water and measuring their performance.
"We demonstrated that new coatings - that are not based on [fluorochemicals, or PFCs,] give just as good water-repellency as the fluorochemical coatings that have been around for decades."
A campaign last year by Greenpeace spurred several outdoor brands to promise to end their use of PFCs in their clothing
And a representative of the European Outdoor Group (EOG) - the body that represents the outdoor industry - said of Prof Blackburn and Ms Hill's research: "This is the kind of data we need to make decisions on.
"It's a real challenge, but brands are very keen to have this information and to move away from PFCs."
However, Prof Blackburn also makes the point that in comparison with the environmental footprint of the natural fibre cotton, many synthetics are actually "pretty clean".
"I always tell my new students that to grow 1kg of cotton consumes the amount of water you've drunk in your lifetime," he says.
And bringing into the mainstream what are currently relatively niche "bio-plastic" fabrics could help clean up the industry further.

Clothes from rubbish
These bio-synthetics are available and gradually becoming more popular:
lyocell, external- a fibre made from trees
PLA fabric, external made from fermented food waste
artificial vegan, external leather made from pineapple
Henry Ford developed soybean-based plastic fibres, external. Casein fibres - made from milk , external- have also been developed.
But, Prof Blackburn says, "these never received the research focus or attention, with the advent of the petrochemical synthetic fibre industry".
He cites further examples, of fibres made from fermented food waste and fruit skins.
"Poly[lactic acid] fibre or PLA is made by fermenting waste corn to make lactic acid, which is then polymerised to make this bio-polyester," he says.
"That's a great fibre, but has largely been used for packaging - the [fabric research] has fallen by the wayside."
But while the new research puts pressure on the textile and clothing manufacturers to clean up their act, there is something we can all very easily do to reduce the impact of what we wear on the environment.
"We are unsustainably addicted to consumption," says Prof Blackburn.
"I cannot emphasise enough how much of a step-change it would be for sustainability if we bought fewer items of clothing per year, wore them for longer and threw them away less often."
- Published16 May 2017

- Published11 March 2017