Artemis: Nasa calls off new Moon rocket launch
- Published
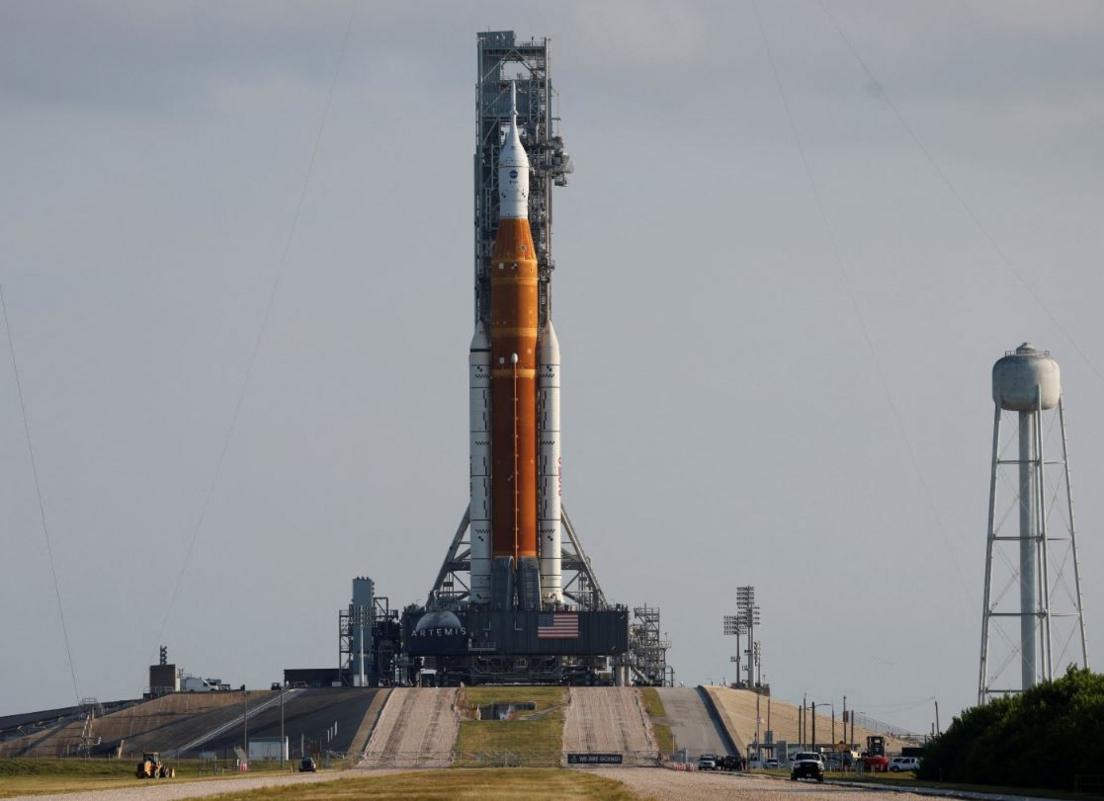

Nasa has called off the launch of its big new Moon rocket - the Space Launch System (SLS).
Controllers struggled to get an engine on the 100m-tall vehicle cooled down to its correct operating temperature.
They had previously worried about what appeared to be a crack high up on the rocket but eventually determined it was merely frost build-up.
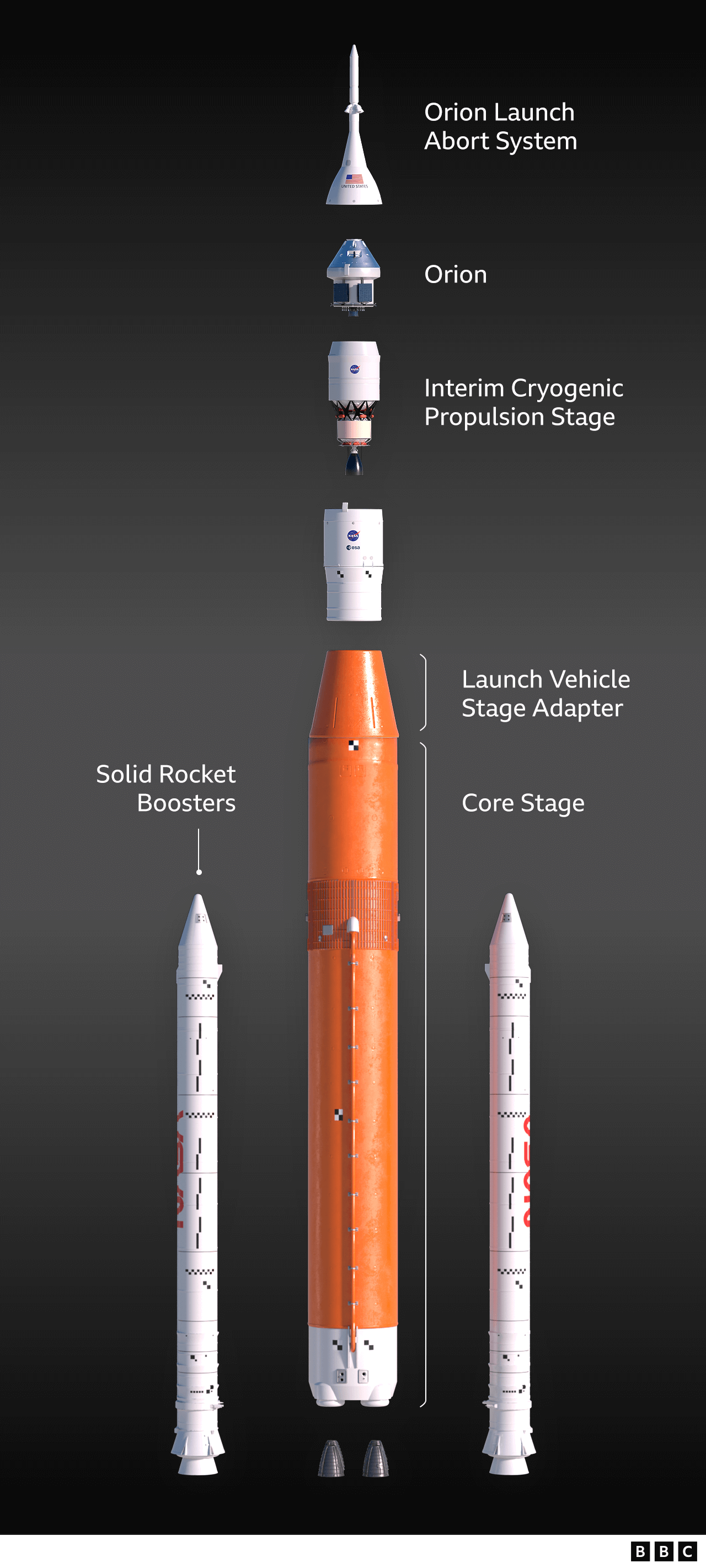
The SLS is the biggest rocket ever developed by Nasa. It will be used to send astronauts back to the Moon.
The maiden flight, part of Nasa's Artemis programme, is just a demonstration with no-one on board. But ever more complex missions are planned for the future that will see people live on the lunar surface for weeks at a time.
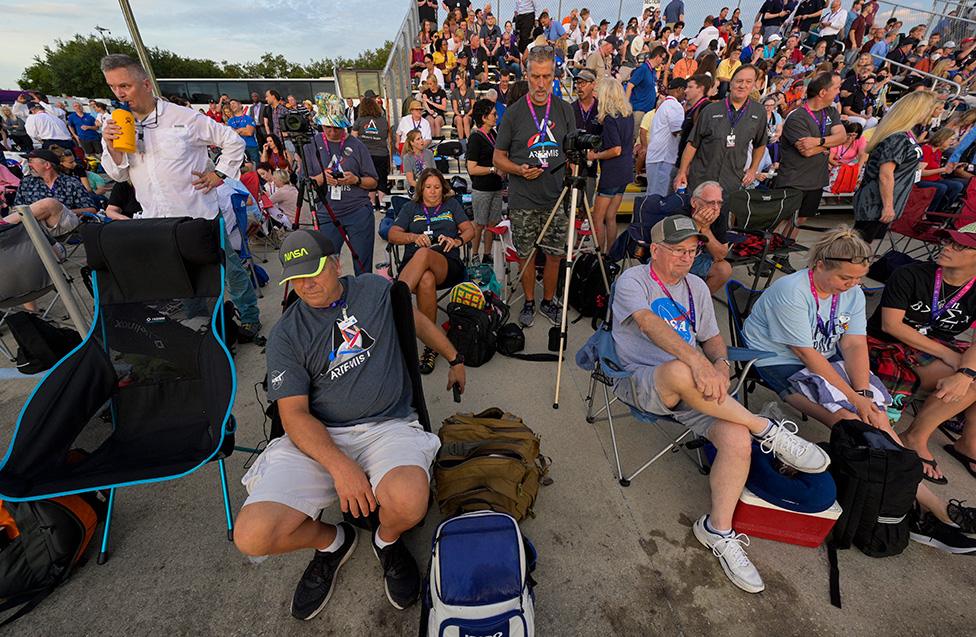

There was disappointment for the thousands of spectators who came to see the rocket launch
The scrub will have disappointed the hundreds of thousands of spectators, external who had gathered on local beaches and causeways to see the most powerful rocket in 50 years fly skyward.
But Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson, himself a one-time astronaut, said the cautious approach was the right one.
"We don't launch until it's right," he stressed. "And I think it's just illustrative that this is a very complicated machine, a very complicated system. And all those things have to work. You don't want to light the candle until it's ready to go."
Nasa has the option to try again on Friday, if the engine issue can be resolved by then.
However, if controllers have to roll the rocket back to Kennedy's assembly building to swap out the engine, it will introduce several weeks' delay.
The issue does not seem to be with the engine itself, but rather with the system that conditions it for flight.
The power unit mustn't be shocked by the sudden injection of super-cold propellants; it must instead be brought down to the correct operating temperature slowly before launch by bleeding through some liquid hydrogen from its core-stage tank above.
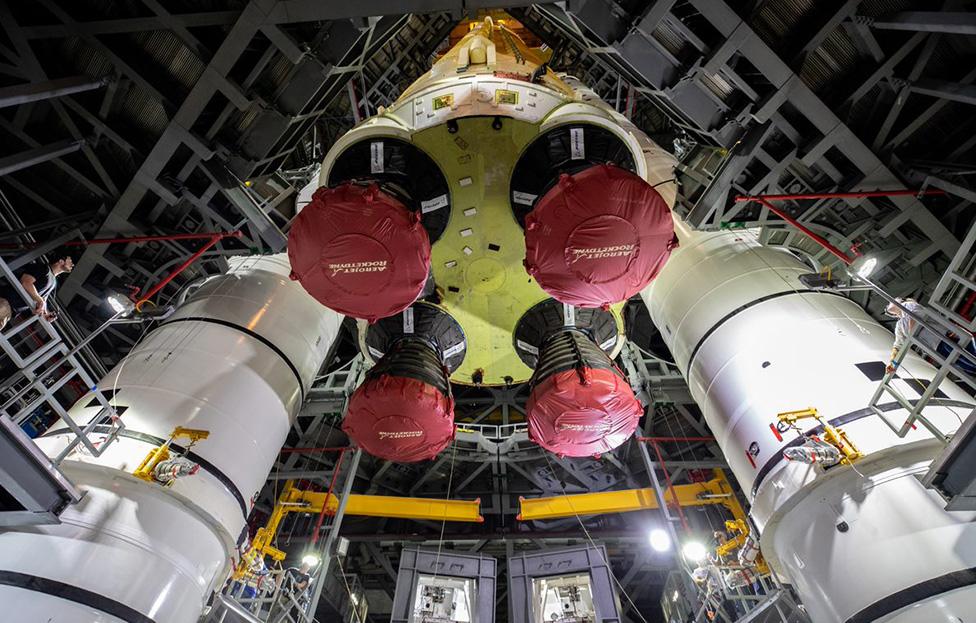

The SLS has four engines at the base of the core stage, one of which wouldn't chill down properly
Mike Sarafin, Nasa's Artemis mission manager, said teams needed time to review the data to determine why this chill-down didn't work for engine No 3, but he was of the view that a roll-back was unlikely.
"If we can resolve this operationally out on the pad in the next 48 hours, 72 hours, Friday is definitely in play," he told reporters.
Mr Sarafin revealed that a venting valve was also playing up on the rocket at the time of the scrub.
Nasa will have to be mindful of the weather as it looks at new launch opportunities. Conditions here in Florida are very dynamic at this time of year. Electrical storms frequently pass over the spaceport. It's best to try to launch in the morning. It's generally calmer. But the opportunity this Friday and on Monday next are afternoon launch windows.
Even during this countdown there were moments when the weather was no-go for rain and lightning.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

When the SLS does eventually lift off, the rocket's job will be to propel a test capsule, called Orion, far from the Earth.
This spacecraft will loop around the Moon on a big arc before returning home to a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean six weeks later.
Orion will be uncrewed for the first mission, but - assuming all the hardware works as it should - astronauts will climb aboard for a future series of missions, starting in 2024.
The current mission's chief objective actually comes right at the end of the 42-day flight.
Engineers are most concerned to see that Orion's heatshield will cope with the extreme temperatures it will encounter on re-entry to Earth's atmosphere.
Orion will be coming in very fast - at 38,000km/h (24,000mph), or 32 times the speed of sound.
"Even the reinforced carbon-carbon that protected the shuttle was only good for around 3,000F (1,600C)," said Mike Hawes, the Orion programme manager at aerospace manufacturer Lockheed Martin.
"Now, we're coming in at more than 4,000F (2,200C). We've gone back to the Apollo ablative material called Avcoat. It's in blocks with a gap filler, and testing that is a high priority."
The European Space Agency has provided the service module for Orion. This is the rear section that pushes the capsule through space. It's an in-kind contribution that Europe hopes will lead to its nationals being included in future journeys to the surface of the Moon.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.
Several missions are being planned - currently it's up to Artemis IX.
By that stage there should be habitats and roving vehicles on the Moon for astronauts to use.
Ultimately, Artemis is seen as a proving ground to get people to Mars, but that's unlikely before the 2040s.
"You know, this is an incredibly hard business. We're trying to do something that hasn't been done in over 50 years, and we're doing it with new technology," Mr Sarafin said. "Seeing smoke and fire is something that everybody enjoys. We're not going to let another hurdle deter us from trying to achieve that next step."

US Vice President Kamala Harris inspected future Orion capsules under construction