Study contradicts Rees-Mogg over hydrogen for heating
- Published

Business Secretary Jacob Rees-Mogg has spoken in favour of hydrogen for heating
A new study has cast doubt on government claims that hydrogen could be used to heat homes and so cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The report, published in the journal Joule, analysed more than 30 studies that looked at hydrogen and heating.
All those studies found that hydrogen was much less efficient and more costly than alternatives like heat pumps
Last week the Business Secretary Jacob Rees-Mogg told the Commons that hydrogen was a "silver bullet".
Hydrogen, unlike fossil fuels, doesn't give off CO2 when it burns, leading to hopes it could play a key role in decarbonising the economy.
What is hydrogen energy and why is it important?
Mr Rees-Mogg said hydrogen could be used as a way to store excess renewable power, and "with some adjustments piped through to people's houses to heat them during the winter."
Many energy scientists agree with Mr Rees-Mogg's assessment that hydrogen could play a role in storing energy, for example on a windy or sunny day when renewables are generating more electricity than the grid needs. Many also see it having a future in specialist industries that will prove hard to electrify, like shipping, steel production or aviation.
"Using hydrogen for heating may sound attractive at first glance," says Jan Rosenow the report's author and Europe Director at the energy think-tank the Regulatory Assistance Project.
"However, all of the independent research on this topic comes to the same conclusion: heating with hydrogen is a lot less efficient and more expensive than alternatives such as heat pumps, district heating and solar thermal," he said.
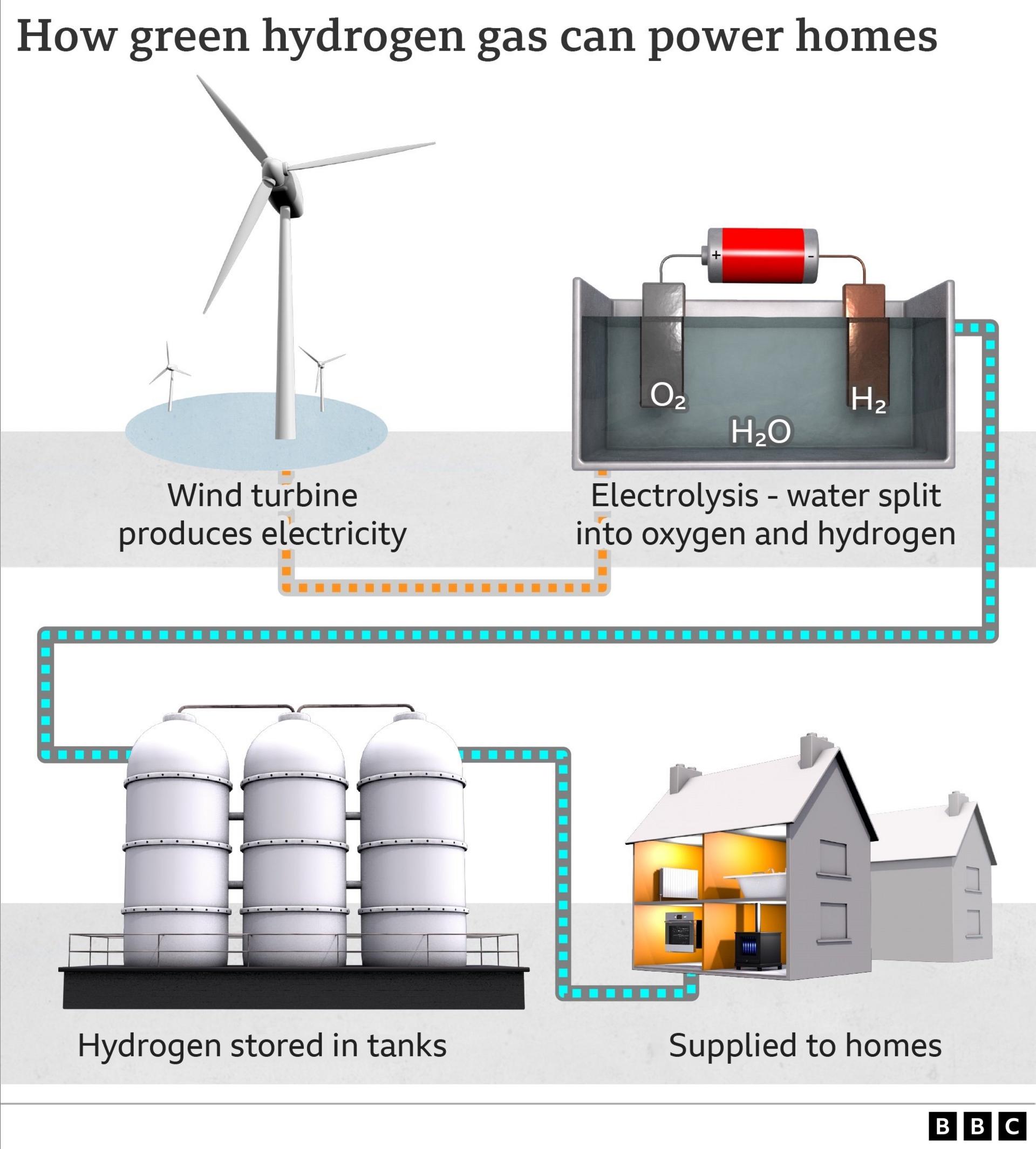
The appeal of hydrogen is that it doesn't release CO2 when burnt, and that it can be made from water, an almost limitless resource. But it's no miracle energy source, with big challenges associated with how the hydrogen is made. Most of the world's hydrogen is currently manufactured using fossil fuels (referred to as grey hydrogen), a process which is more polluting than just using methane gas.
So for hydrogen to be considered "green", electricity from renewable sources has to be used to electrolyse water. The problem is that the process is inefficient.
Generating electricity from wind or solar, converting it into hydrogen and then burning the hydrogen at home uses more energy than just using the electricity to directly heat a home, with a heat pump.
"In the UK, heating homes with green hydrogen would use approximately six times more renewable electricity than heat pumps," says David Cebon of the Hydrogen Science Coalition and Professor of Mechanical Engineering in Cambridge University.
"We do not have the time or resources to waste further investigating hydrogen's role in home heating, especially when the well-known laws of thermodynamics determine the answer," he said.
The report said there was a risk that discussion of hydrogen for heating in the future led to a delay in the deployment of clean heating technologies that are already available today.
"Low carbon hydrogen could play an important role in helping decarbonising heat in buildings," a spokesperson from the Mr Rees-Mogg's ministry the Department of Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) told BBC News.
"But the government has been clear that a decision on this will not be made until 2026, allowing for full consideration of relevant evidence.
The government is currently offering £5,000 grants to encourage people to swap their fossil fuel burning boilers for heat pumps.
Follow Jonah on Twitter @jonahfisherBBC, external
Related topics
- Published22 August 2022

- Published14 May 2021

- Published4 November 2021
