Skripal attack: Second Salisbury suspect 'decorated' by Putin
- Published
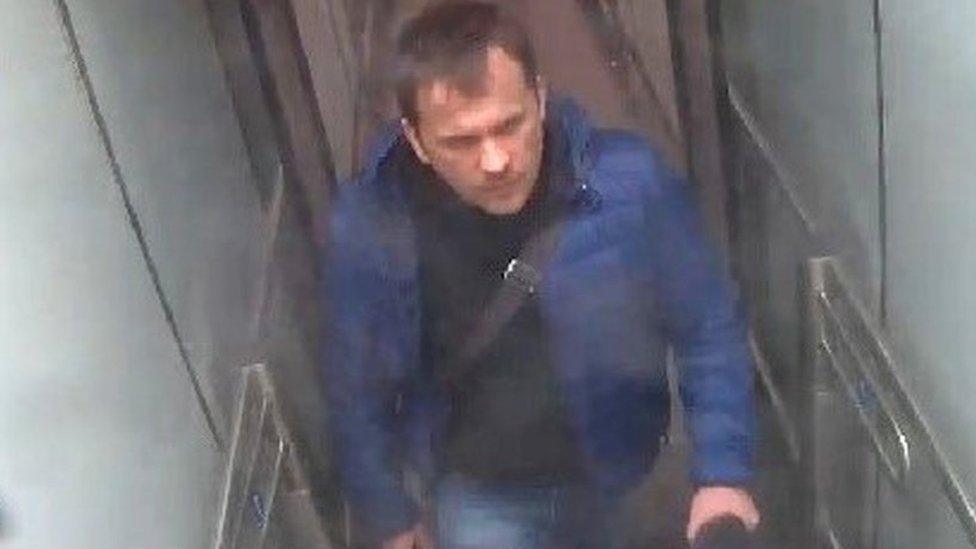

CCTV footage issued by the Met Police of the man now identified as Alexander Mishkin
The second suspect in the Salisbury poisoning case was a doctor and highly decorated Russian military intelligence officer, an investigative website says.
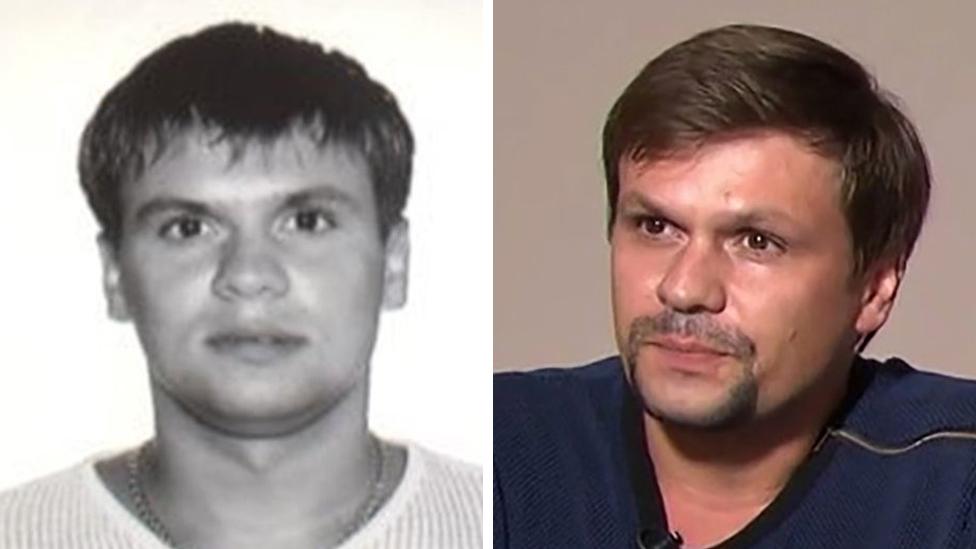
Bellingcat said it used a combination of online material and leaked documents to identify Alexander Mishkin, 39, as a person linked to the attack in March.
It said President Vladimir Putin had presented him with the Hero of the Russian Federation award in 2014.
When asked about the naming of Dr Mishkin, the Kremlin would not comment.
Last month, Bellingcat named the first suspect as Anatoliy Chepiga, a claim also rejected by Russia which says it was not prepared to discuss reports or media articles on the case.
At a news conference held in the Houses of Parliament on Tuesday, Bellingcat investigator Cristo Grozev said Dr Mishkin - like Mr Chepiga - was a member of the GRU and given the celebrated award for "actions in Ukraine".
He said Dr Mishkin's grandmother has a photograph that has "been seen by everybody in the village" of President Putin shaking his hand and giving him the award.
The BBC has contacted two people who knew Dr Mishkin as a child in Loyga in the north of Russia, and they confirmed from photographs that he was the man seen in images released by police after the Salisbury attack.

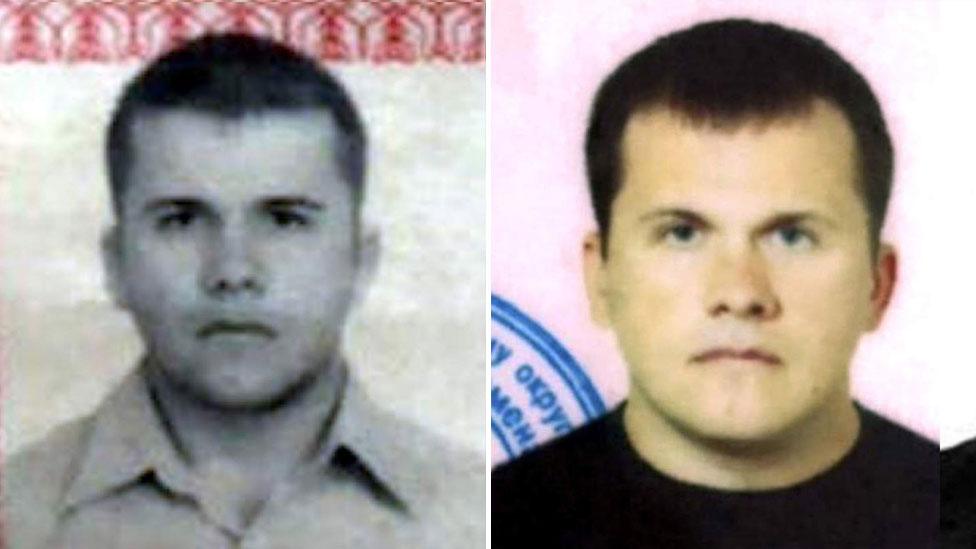
Bellingcat has issued three photos of the man identified as Alexander Mishkin, including his passport image
Bellingcat, a UK-based website, said both Dr Mishkin's real passport and the false passport he travelled to the UK on in the name of Alexander Petrov carried the same date of birth.
Outlining in detail how it identified the Salisbury suspect as Dr Mishkin, Bellingcat said, external it had pieced together his identity using various databases online, including telephone and car insurance records, and later obtained copies of his passport and driving licence.
It also used social media to contact hundreds of people who may have been at military academy with Dr Mishkin.
Most people did not respond to the inquiry but one, who requested complete anonymity, said they had recognised Dr Mishkin as the suspect who was interviewed under the name of Alexander Petrov by the RT television channel.
Mr Grozev said: "That person told us everybody from his class, his department, was contacted two weeks ago and told not to talk to the media."
Bellingcat said Dr Mishkin completed his medical studies at a faculty which trains doctors for Russia's naval armed forces and around the same period was recruited by the GRU.
It said he made several trips to Ukraine, including during the 2013-14 unrest.
What has been happening in Ukraine?
In spring 2014 mass demonstrations in central Kiev over the government's decision to suspend the signing of an association agreement with the EU ended in bloodshed and the ousting of pro-Moscow President Viktor Yanukovych.
Soon afterwards Russian troops annexed the Ukrainian territory of Crimea, and unrest broke out in mainly Russian-speaking eastern areas of the country.
The unrest became a full-scale insurgency, and rebels seized large swathes of territory. Since then, thousands of people have died in fighting between the rebels and Ukrainian government forces.
Moscow denies sending regular troops and heavy weapons to the separatists, but admits that Russian "volunteers" are helping the rebels.

On the trail of Alexander Mishkin
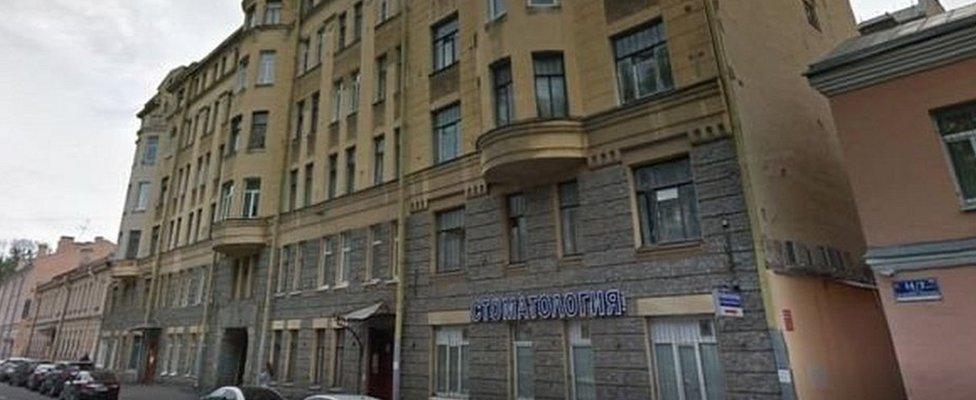

Dr Mishkin is believed to have lived in this St Petersburg building about a decade ago
The tiny village of Loyga in the Russian far north is not the kind of place you would expect to be at the centre of an international spy scandal.
With fewer than 1,000 inhabitants, it has rail access but no paved roads. It's too small even to show up on Google Maps.
But Loyga has proved crucial to piecing together the story of the real "Alexander Petrov" - the second man the UK authorities suspect over the Skripal poisoning case in Salisbury.

How are the suspects linked to the Salisbury poisoning?
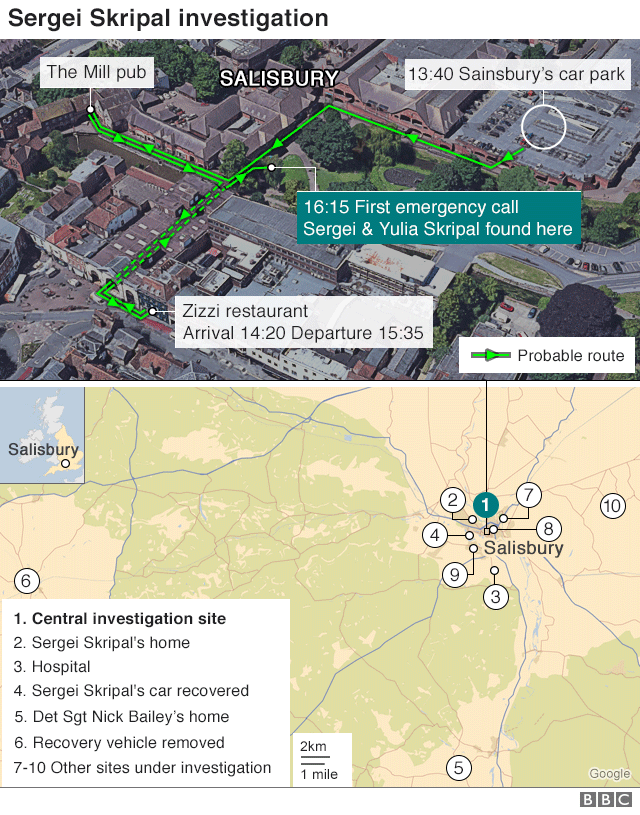
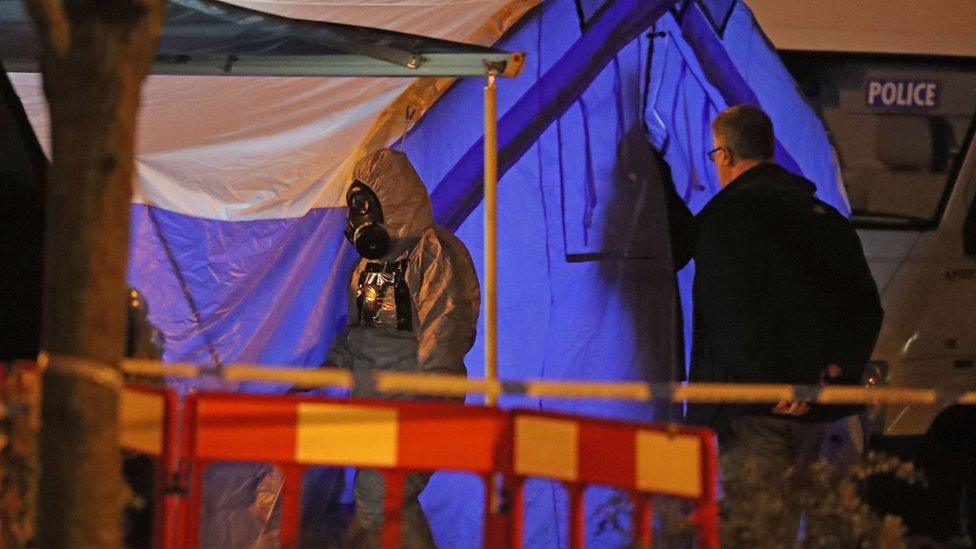
Former GRU officer Sergei Skripal - who sold secrets to MI6 - and his daughter Yulia survived being poisoned with Novichok on 4 March.
The attack left Mr Skripal and Yulia critically ill, but Dawn Sturgess, 44, was later exposed to the same nerve agent and died in hospital.
London's Metropolitan Police and the Crown Prosecution Service said last month that there was enough evidence to charge Dr Mishkin and Mr Chepiga with attempted murder over the Salisbury attack.
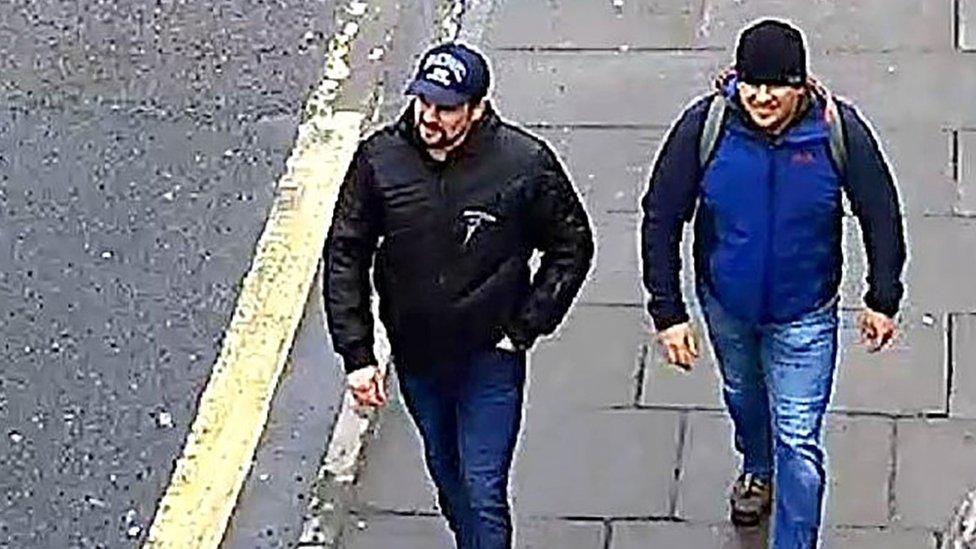

Police issued CCTV of the two suspects in Salisbury on the day of the attack on Sergei Skripal
Detectives said the pair arrived in the UK using passports bearing the names Alexander Petrov and Ruslan Boshirov on 2 March, although they had said it was likely the men were travelling under aliases.
The movements of the suspects, who are alleged to have smeared Novichok on a door handle of Mr Skripal's home, were captured in a series of CCTV images that were released by police.
The event sparked a series of accusations and denials between the UK and Russian governments, culminating in diplomatic expulsions and international sanctions.


Analysis


By Gordon Corera, BBC security correspondent
It took longer for investigators at the Bellingcat website to identify Alexander Mishkin because he has an even sparser digital footprint than the first man to be named, Anatoly Chepiga.
But using databases and passport details they concluded that this was the real name of the man who came to Salisbury as Alexander Petrov.
Facial recognition experts were asked to examine two photos 15 years apart and use techniques of simulated age progression to establish the match.
Last Thursday, four GRU officers were exposed for trying to hack into communications of the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons in the Netherlands at the time it was investigating the Salisbury poisoning.
Dr Mishkin's identification will raise more questions about how easy it has been to expose supposedly undercover intelligence officers and undermine Russia's official account that the two men who came to Salisbury were there to see the cathedral spire.
Recent reports in the Russian media suggest that Vladimir Putin - himself a former spy chief - is unhappy with the GRU's performance - and that a purge could be on the way.

- Published9 October 2018

- Published9 October 2018

- Published27 September 2018

- Published8 October 2018

- Published3 October 2018

- Published27 September 2018

- Published5 September 2018
