Bronze Age 'Pompeii' dig set to reveal new secrets
- Published
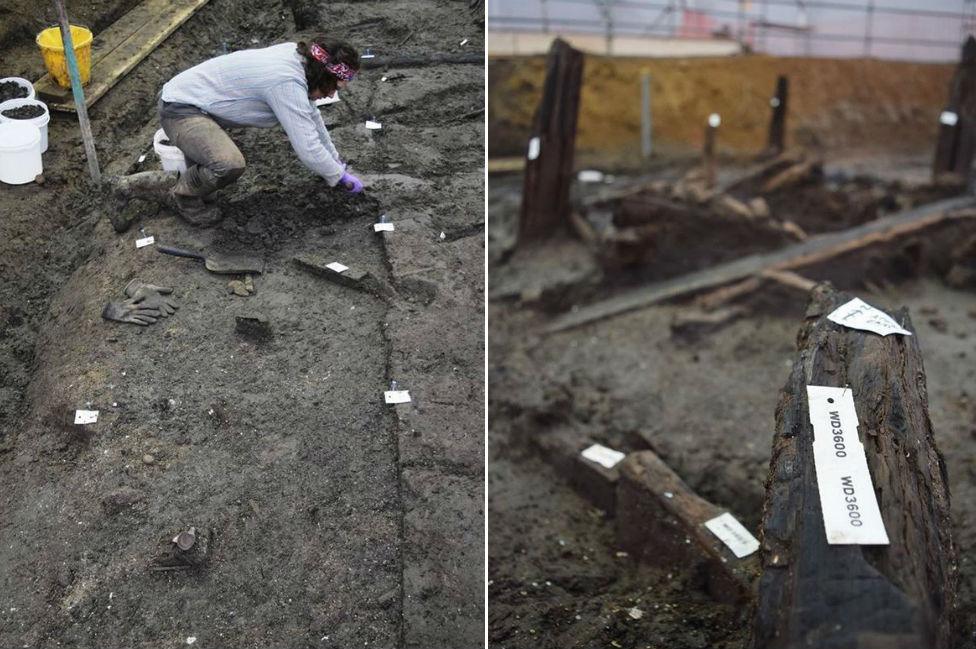

Archaeologists are beginning to look beneath the roof for the house's contents (left) and some of the documented timbers (right)
New details of Bronze Age daily life could be revealed as archaeologists begin digging inside the remains of a roundhouse at what has been dubbed "Britain's Pompeii".
The UK's "best preserved Bronze Age dwellings", found at a Cambridgeshire quarry, date from about 1000-800 BC.
The houses fell into a river during a fire and the collapsed timbers were preserved in the silt.
Archaeologists say they expect to find many of the house contents inside.
The circular wooden houses, built on stilts, formed part of a settlement partially destroyed by fire 3,000 years ago.
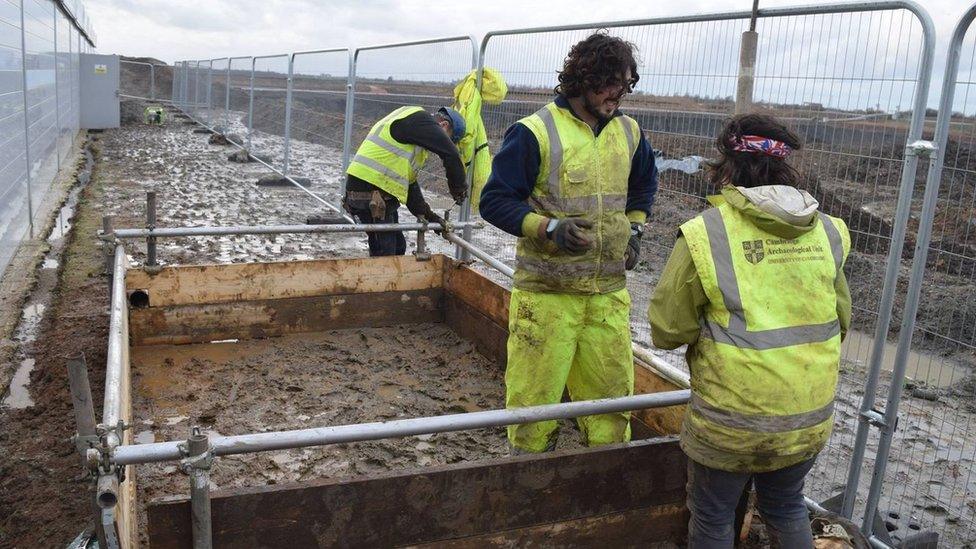

A wet sieving station will allow the team to examine sediment from inside one of the houses. "Even the tiniest vertebrate remains and glass beads will be recovered using this method."
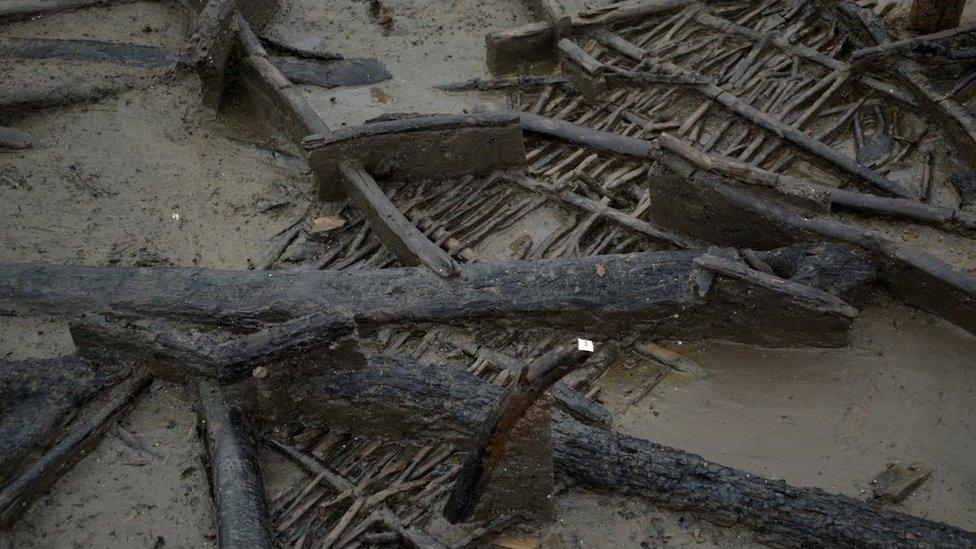

Charred timbers lying over a collapsed wall are likely to be covering the contents of the house
The site, at Must Farm quarry near Whittlesey, was described as "unique" by David Gibson, from Cambridge Archaeological Unit, which is leading the excavation.
Most Bronze Age sites have no timber remaining, just post-holes - but here, the stilts, roof structure and walls have been unearthed.
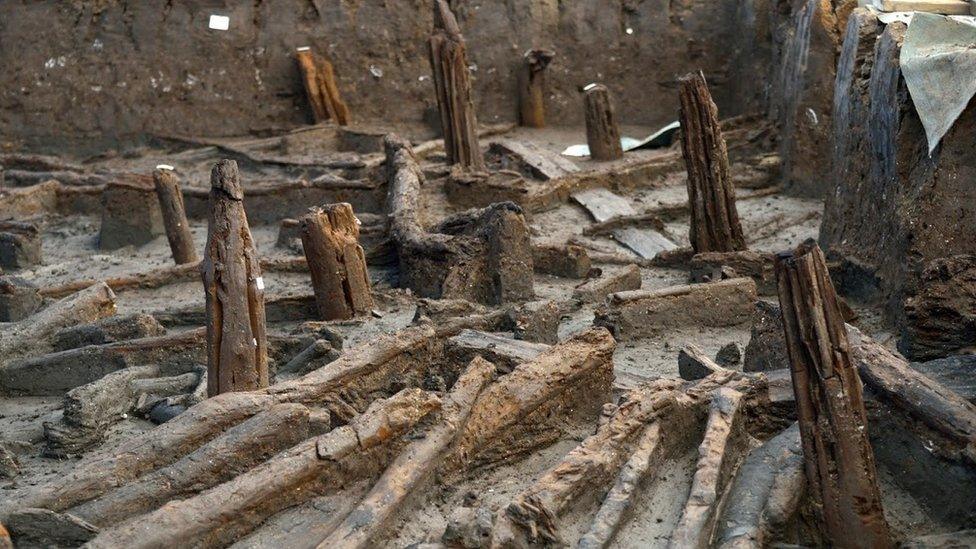

The stilts that held the houses can be seen, together with collapsed roof timbers
Mr Gibson said they had uncovered two houses, and possibly a third. However, as only about half the site remains he said the settlement could have consisted of up to six dwellings.
'Delicate task'
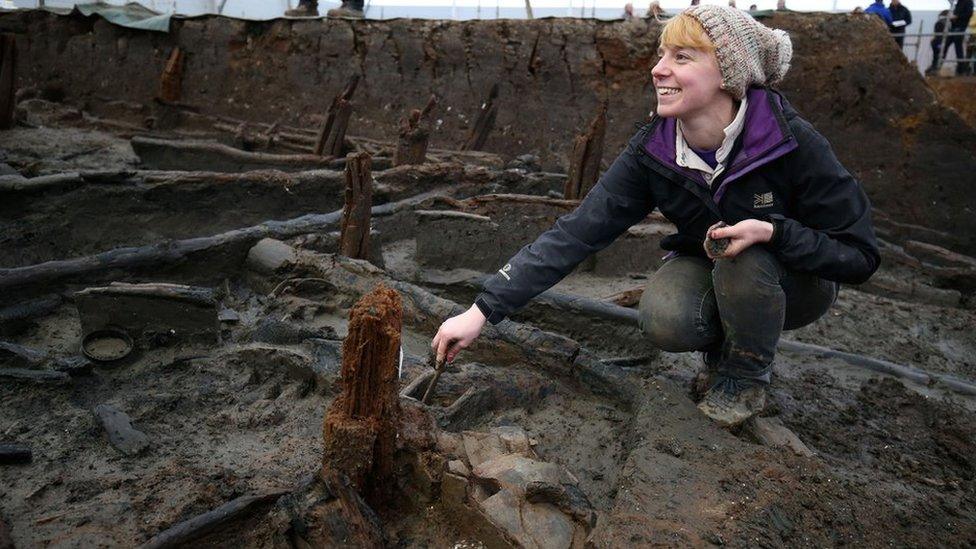
The team is about half-way through the eight-month dig to uncover the secrets of the site and the people who lived there.
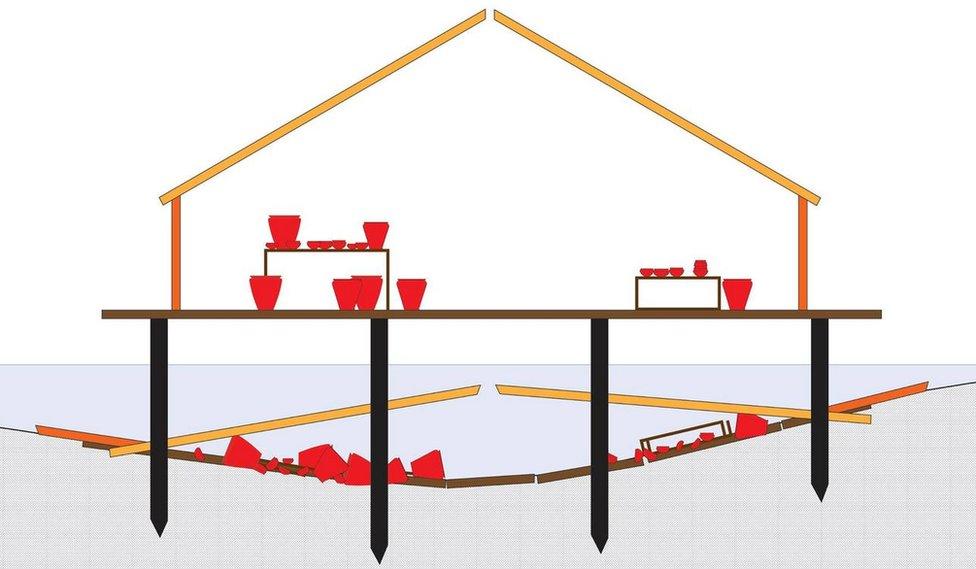
The diagram shows a roundhouse before and after the fire. It is thought the floor collapsed and the roof fell in, covering the house's contents
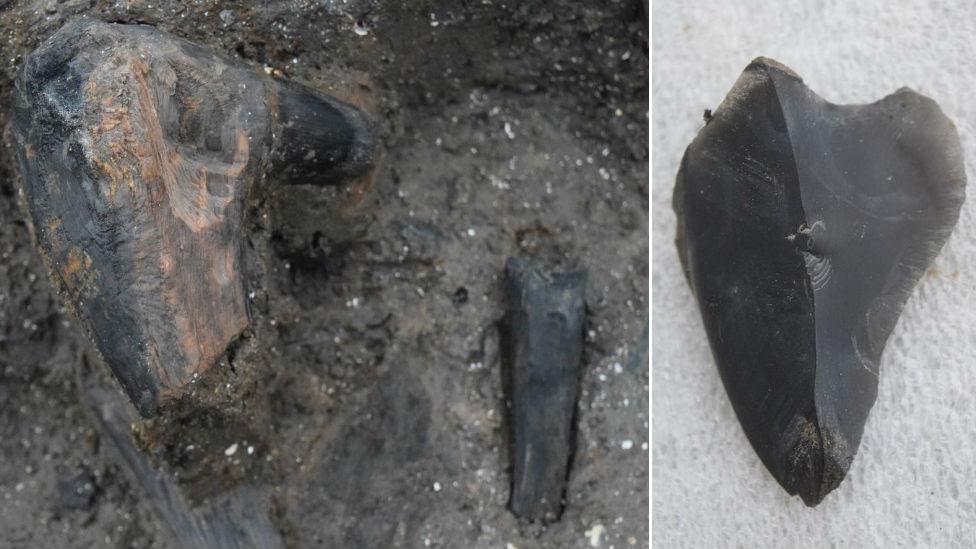

A broken axe haft (handle) has been found recently (left) and a flint cutting tool, but most of the contents of the houses are believed to be still buried
In the past week they reached what they described as "a milestone", documenting their 1,000th piece of wood.
"The information gathered from all this wood is critical in understanding the houses alongside the fire that destroyed them," the team wrote on Facebook, external.
"The slightly daunting aspect is that we have at least a few thousand pieces of wood still to go."
Researchers have also now started work on the "occupation deposits" underneath one of the roundhouses.

Bronze Age Europe and Britain
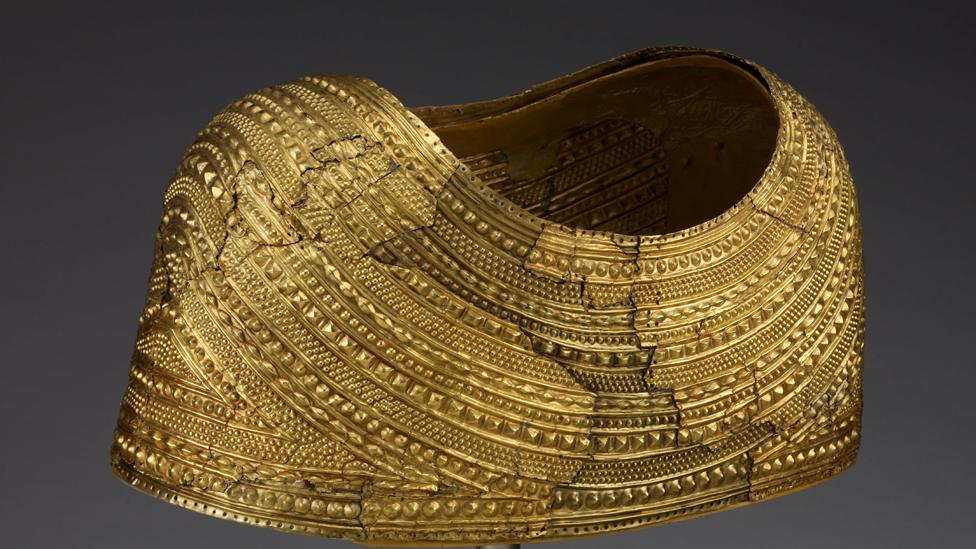

Gold cape discovered in Mold, north Wales - a supreme example of Bronze Age art
The Bronze Age in Britain lasted from between 2500 and 2000BC until the use of iron became common, between 800-650BC
It came after metalworkers discovered that adding tin to copper produced bronze, used for tools and weaponry which were much more hard-wearing
The Greek poems of Homer - though composed later - look back to a time when bronze weapons were used
In Britain, the Bronze Age lasted until about 800BC. Use of bronze seems to have coincided with fresh migration of people from the continent.
Classic Bronze Age remains include sophisticated axes, precious gold objects, and round burial mounds or "barrows" of which many can still be seen in Britain

"This is going to be a particularly delicate task that will take some time," they said.
"We are starting at the edges of the structures and we can't wait to see what begins to appear as we move closer."
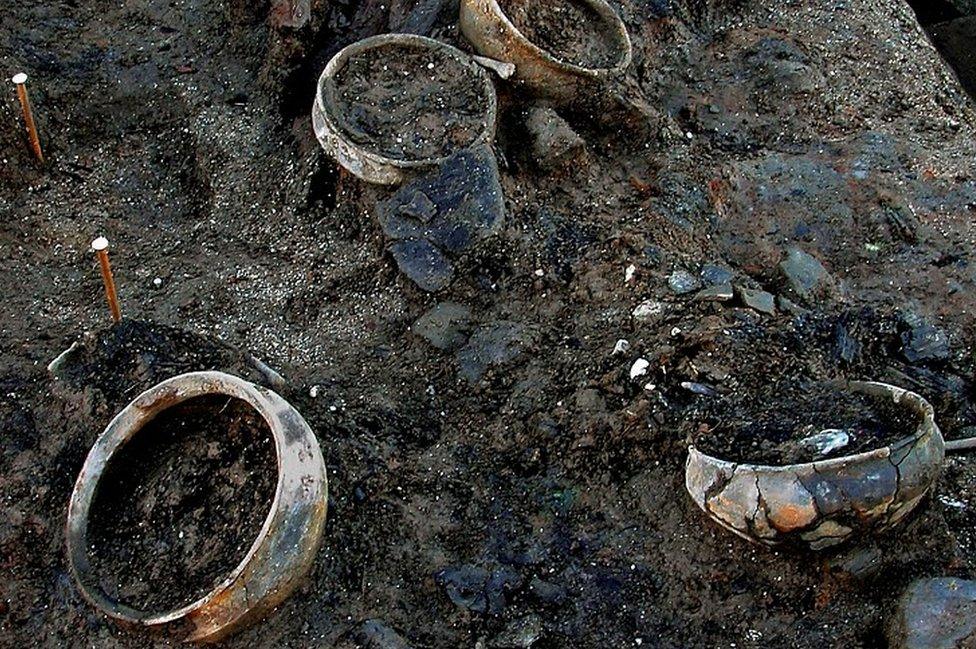

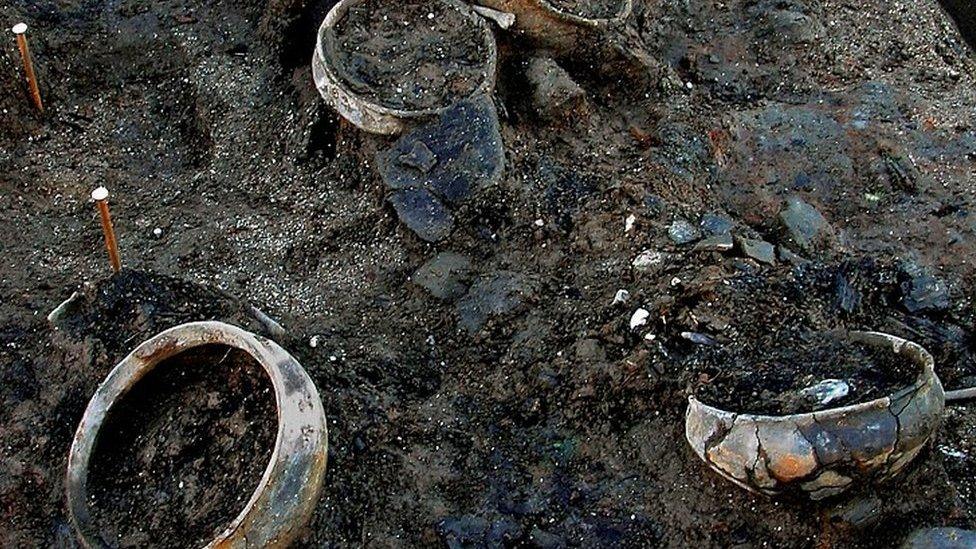
After analysing pots found at the site, archaeologists found some contained food
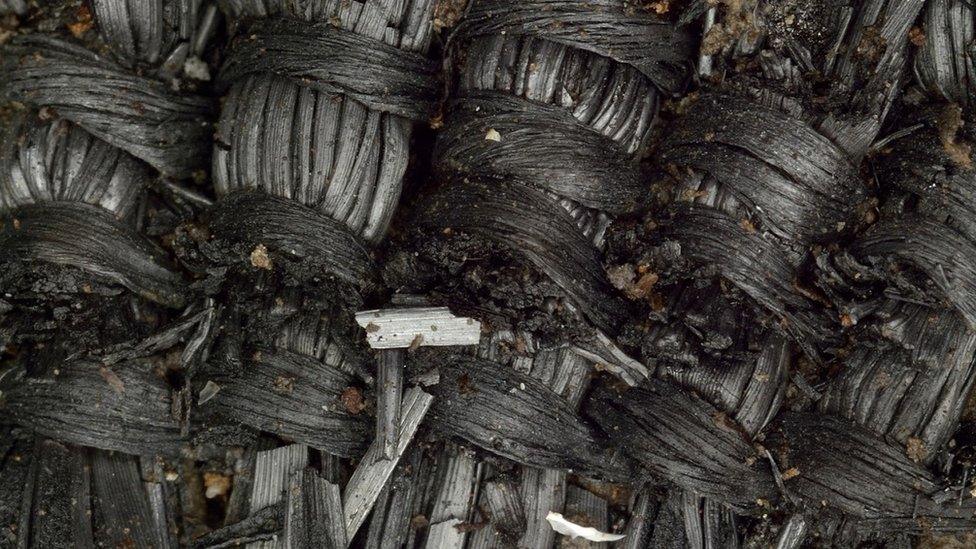

These preserved Bronze Age textiles were made from plant fibres
Although a number of items including tools, bowls still containing food, and textiles have been found around the Must Farm site, the contents of the roundhouses themselves are most likely buried in silt beneath the wooden roof.
"This roof is sitting on top of, and currently sealing, all of the remains of the building's interior," the team said.
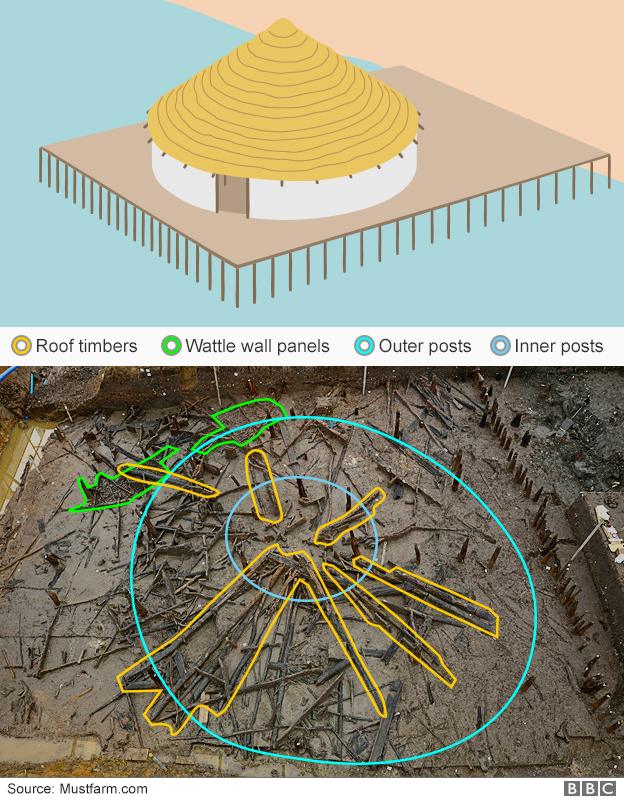
Artist's impression of what one of the roundhouses might have looked like
"These remains are most likely a source of lots of new information about homes during this period of prehistory."
While these are likely to include "exciting finds associated with the dwelling - pots, querns, metalwork and textiles", archaeologists said the artefacts would also help them understand how the site was formed and how it was used.
Mr Gibson said it was possible some of the artefacts could still be situ, for example, if a number of pots and bowls were found in one place it might suggest this was where the family cooked and ate within their home.
The excavation is being jointly funded by Historic England and quarry owner Forterra.
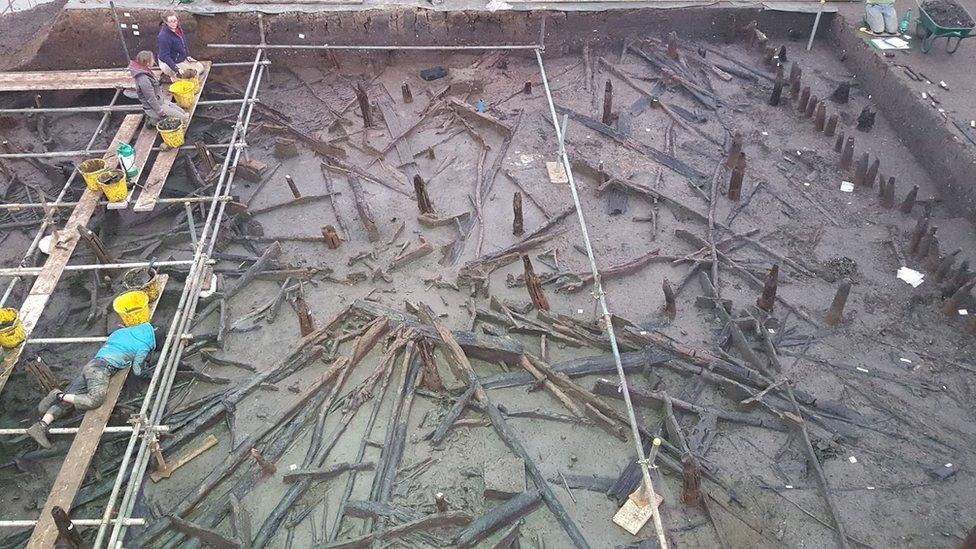

Archaeologists work on a wooden platform as they uncover the houses
- Published12 January 2016

- Published12 January 2016

- Published12 January 2016
