Manchester attack fire crews 'sent away from arena blast'
- Published
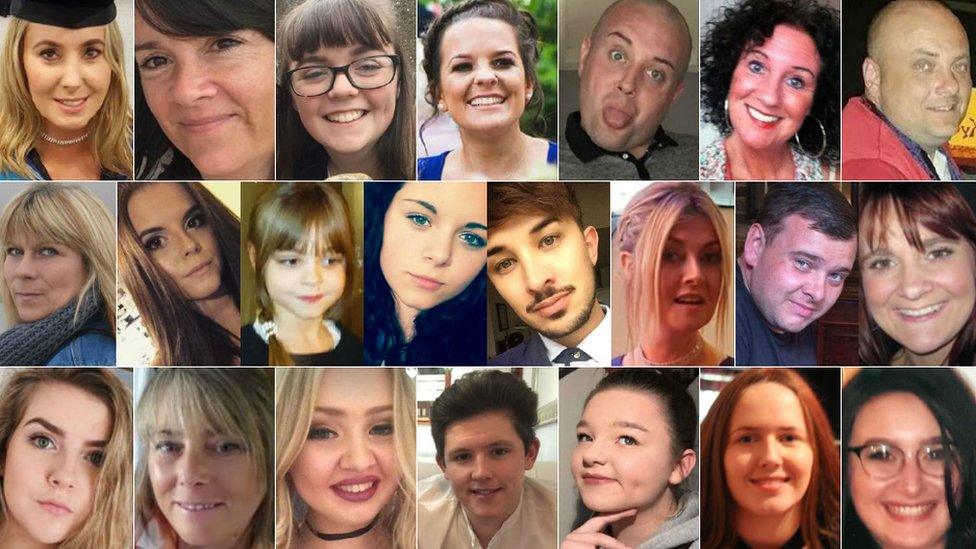

Twenty-two people were killed in the blast on 22 May
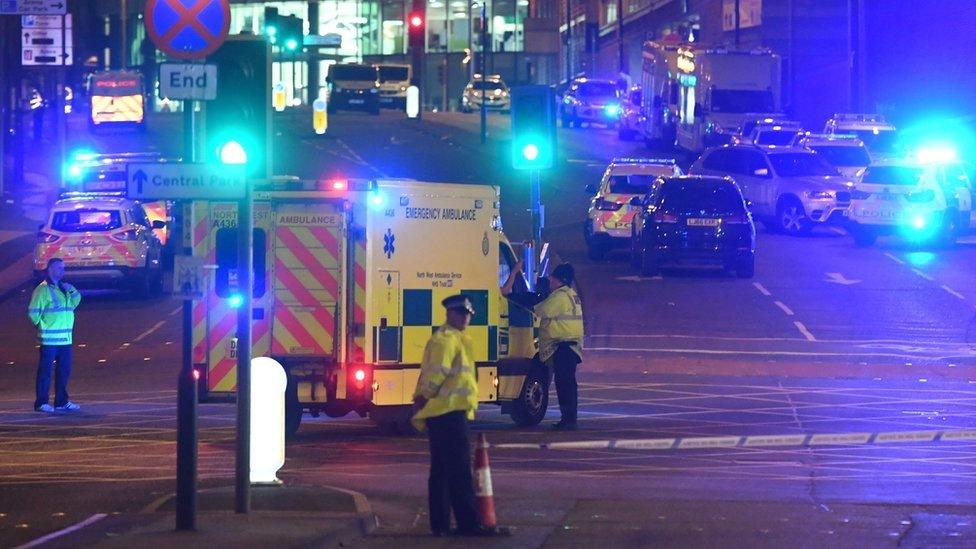
Firefighters who heard the Manchester Arena bomb go off were sent away from the scene despite a paramedic arriving within 11 minutes, a report says.
"Out of the loop" crews took two hours to attend the scene of the deadly blast, which killed 22 people last May.
A report by Lord Kerslake, external found poor communication meant chief fire officers were "risk-averse" and kept emergency trained responders away.
The fire service's chief apologised "unreservedly" for the failures.
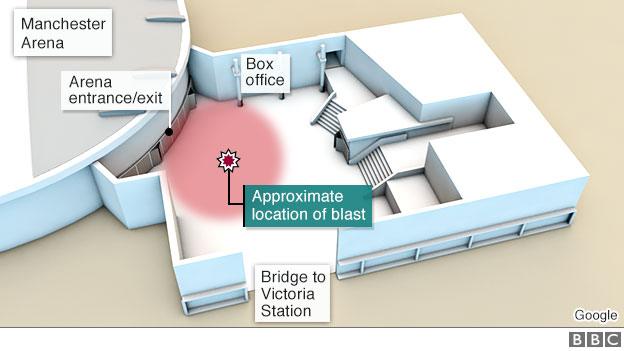
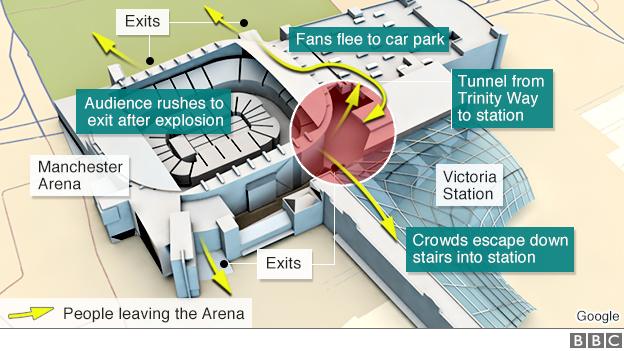
Suicide bomber Salman Abedi detonated a home-made device at 22:31 BST as 14,000 people streamed out of an Ariana Grande concert on 22 May, leaving more than 700 injured.
According to the report, the first North West Ambulance Service (NWAS) paramedic arrived at 22:42 and was told the incident was a "suicide bomber" by police.
A police duty inspector declared Operation Plato, a plan for dealing with a suspected marauding armed terrorist, and wrongly assumed others were aware.
Despite protocol allowing emergency workers to continue treating the injured, a senior fire officer "stuck to rules" and kept emergency responders 500m (1,600ft) away from any zone of danger.
Survivor Martin Hibbert says he is "sure" firefighters "would have been a great help" in the immediate aftermath of the blast
It was "fortuitous" the ambulance service was not informed, otherwise it might have pulled out paramedics who instead stayed and saved lives, the 224-page report said.
The report also said the fire officer was unable to get through to the force duty inspector.
As a result, Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service (GMFRS) was "brought to the point of paralysis", to the "immense frustration on the firefighters' faces".
The fire service and the control room "felt they had let down the people of Greater Manchester" on the night of the blast, Lord Kerslake's report said.
His report also found:
An early decision was taken to base crews at Philips Park Fire Station - about two miles away from the arena - rather than with police at the city's cathedral car park
This hampered communication and awareness of what was happening at the scene
The fire service was "effectively outside the loop [and had] little awareness of what was happening at the arena"
There were "strategic oversights" by police commanders that led to confusion over whether an "active shooter" was on the loose
"Poor communications" meant fire crews only arrived two hours and six minutes after the bombing. The average response time is under six minutes.
The report made more than 50 recommendations but states its panel of experts was not there to answer the question of: "Would the earlier arrival of GMFRS at the scene have made any difference to the medical outcomes of the injured?"
"This is a question that only the coronial inquests can decide," the report said.
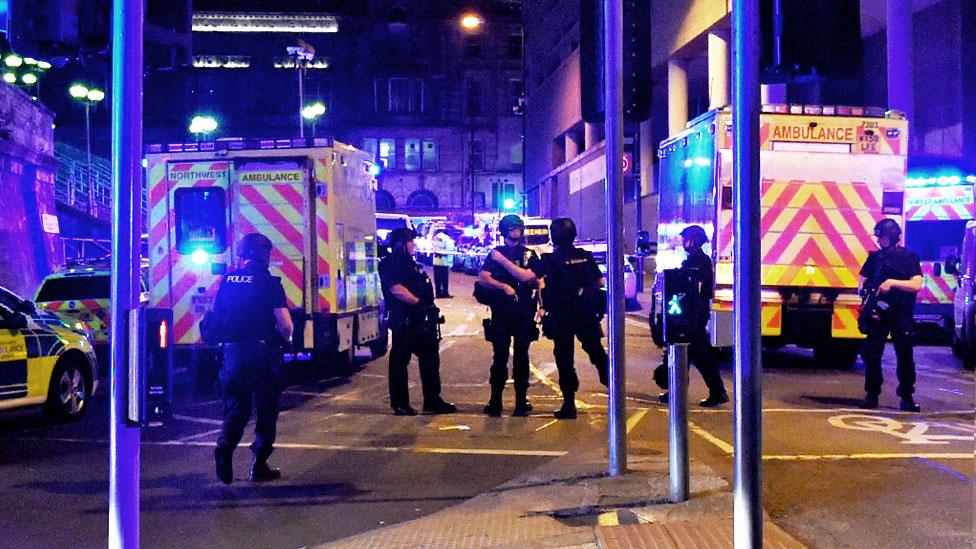

The report found "strategic oversights" by police commanders led to confusion over whether an "active shooter" was on the scene
Speaking after the report's publication, Lord Kerslake said the "unspeakable attack" had been a "brutal and real-world test" of the emergency services' response.
He said "not one single reason or one individual" was to blame for the errors, but a "most unfortunate combination" of "poor communications and poor procedures".
Lord Kerslake said that "deep down" the errors were prompted by failings in "operational culture".
But he conceded that it was "quite extraordinary that [the fire service] did not pick up what was happening."
"They should have gone forward not back," he said.
"The firefighters wanted to go forward but they were not able to. The discipline of the fire service meant that they could not self-deploy."
Manchester attack: 'There weren't enough staff'
Phone line failure 'catastrophic'
Lord Kerslake also singled out Vodafone for criticism, following the "catastrophic failure" of an 0800 phone line designed to help concerned people get information on the night of the attack.
The subsequent delays caused "significant stress and upset" to families.
Lord Kerslake said: "A number were reduced to a frantic search around the hospitals of Greater Manchester to find out more."
Vodafone has apologised for the distress caused and said it had undertaken a major upgrade of the system.
However, Lord Kerslake said the company "should also apologise directly to the families" for whom the failure of this "vital" system "made the experience of this truly terrible evening even worse."
'Reputation damaged'
Greater Manchester Mayor Andy Burnham also praised the emergency services but said the fire service "fell well short" of the standards it sets for itself.
The report was not designed to criticise firefighters themselves, he said, but to "ensure they are supported" by the "best possible leadership and culture".
Mr Burnham said he would now ask for a further detailed review into how the service works with other agencies.
He said he would also ask the prime minister and Home Office to "consider national guidance" over how to respond to further attacks.
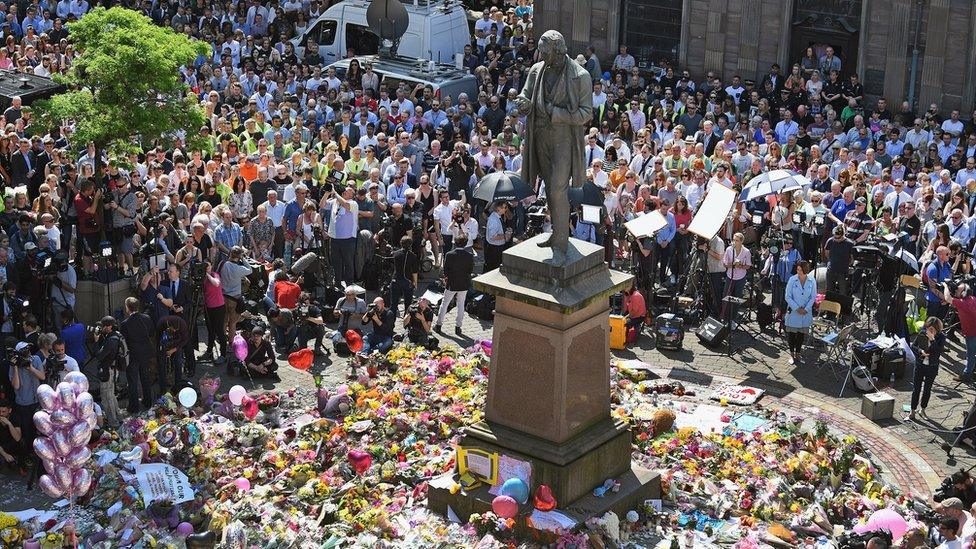

St Ann's Square in Manchester became the focus of tributes after the attack
Baroness Beverley Hughes, Mr Burnham's deputy, said the findings would "undoubtedly damage the reputation" of the fire service as an organisation.
"However, it should not tarnish the reputation of firefighters on the front line," she added.
Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service's interim chief fire officer Dawn Docx apologised "unreservedly" for her service's failures.
She said: "Firefighters were desperate on the night to help and they were let down by some of their senior colleagues."
Asked if any disciplinary action had been taken, she said: "We are very much a learning organisation.
"We are not seeking to go down the disciplining route. We are working to make sure this never happens again."
When asked whether former fire chief Peter O'Reilly - who announced his retirement last year - would have faced disciplinary action, Mr Burnham said it was not about scapegoating individuals.
Families 'hounded'
Figen Murray, whose son Martyn Hett was killed in the blast, said her daughter was told of his death by a journalist
The panel, chaired by former head of the civil service Lord Kerslake, also found:
Many key emergency personnel "exercised sound judgement"
The force duty officer from Greater Manchester Police is praised for "dynamic decision making" in allowing responders to remain in the foyer to carry out first aid
Four British Transport Police officers who had been on duty at Victoria station - which is connected to the arena - arrived at the scene within 30 seconds of the blast
However, agencies failed to share information effectively following the declaration of the incident as a terror attack
Some bereaved families felt it took too long for them to be told of their loved ones' deaths
Families felt "hounded" by the media, with reports of a "scrum" of journalists outside hospitals
Children from two families - who lost a mother and brother, respectively - were offered condolences by reporters at their homes before the deaths had been officially confirmed
Hospital staff were offered £2,000 to speak to the press by way of a note hidden in a tin of biscuits
Lord Kerslake said there was "a lot to be proud of" in the response to the attack.
"But it's also vital to learn the lessons around things that did not go so well," he added.
"It matters not just for the people of Greater Manchester and beyond who were caught up in the terrible events of that night, but also for places that might be caught up in such an attack in the future."
Andy Dark, the assistant general secretary of the Fire Brigade's Union, said the report contained "important lessons for the fire service and for all emergency services".
"A major cause of the problems encountered was the absence of any information being received by the fire service from the police," he said.
"The wider issue, of course, is that government requires only small teams of firefighters to be trained and equipped for such incidents. There is currently a dialogue with the Home Office on the issue of funding for these arrangements."
- Published27 March 2018

- Published3 November 2022

- Published12 January 2018

- Published7 November 2017
