Liver cancer death rate rises by 52%
- Published
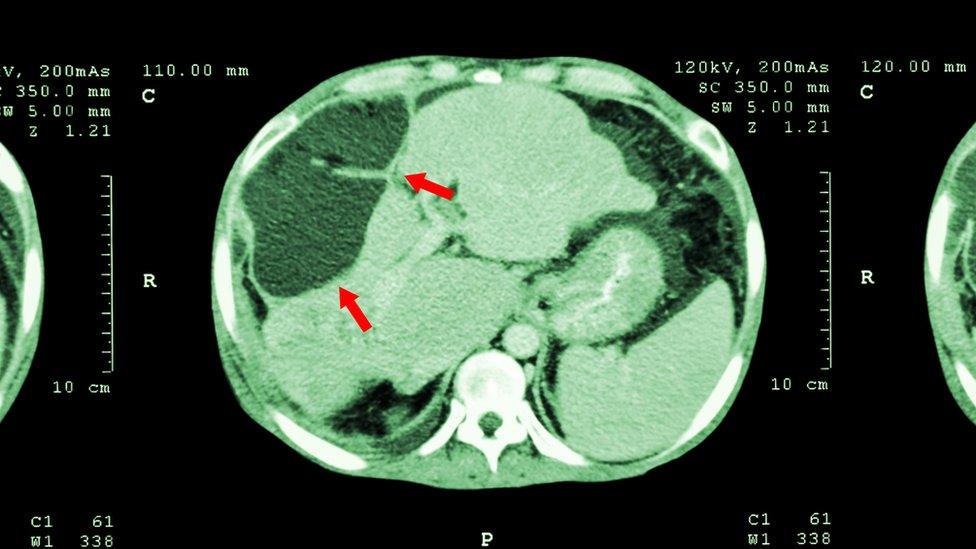
Scan showing an abnormal liver mass
Death rates from liver cancer increased by 52% in the last 10 years, with the disease killing 572 Scots last year.
But new figures from the NHS showed that the cancer mortality rate for all forms of the disease fell by 11% over the decade to 2015.
The mortality rate for breast cancer - the most commonly diagnosed cancer for women - fell by 21%
Lung cancer death rates were down by 15.1% and there was a 16.4% decrease for bowel cancer.
A total of 16,011 deaths in 2015 were caused by cancer, with the report noting that "although the rate of deaths due to cancer has decreased over this period, the actual number of deaths due to cancer has not".
This is thought to be due to the increase in older age groups within the population and the fact that cancer is a relatively common disease among the elderly.
Cancer mortality rates have fallen by 14% among men over the last 10 years. The decrease in the mortality rate for females was lower at 6%.

Most common cancers
Five types of cancer accounted for more than half of all cancer deaths in 2015:
Lung cancer - 4,047
Bowel cancer - 1,565
Breast cancer - 992
Prostate cancer - 985
Oesophageal cancer - 816
Liver cancer - 572

Deaths from liver cancer were up from 320 in 2005, with the mortality rate increasing by 45.6% in males and by 68.6% for females.
"The increase in the mortality rate of liver cancer over the last 10 years by 52% reflects the increase in incidence of this type of cancer," the report said.
"Survival from liver cancer is poor in most cases. The main risk factors for liver cancer are alcohol and infection with hepatitis B and C."
Breast cancer remains the most common form of the disease for women but mortality rates have fallen by a fifth
The figures also showed that the incidence of cancer is 31% higher in the most deprived parts of Scotland compared to the most affluent communities.
And mortality rates are almost two thirds (64%) higher in the worst-off areas than they are in the least deprived parts of Scotland.
But the report said: "There are variations in this pattern when looking at specific types of cancer.
"For example, while lung cancer incidence and mortality rates are higher in the most deprived areas of Scotland, incidence and mortality rates of malignant melanoma of the skin are higher in the least deprived areas of Scotland."
'Earlier detection'
Gregor McNie, Cancer Research UK's senior public affairs manager in Scotland, said: "These figures reflect that cancer is a stark reality for so many families in Scotland as increasing numbers of people die from the disease.
"But more people are surviving cancer and this is partly due to earlier detection of the disease.
"Treatment is more likely to be successful when cancer is found at an early stage, so people shouldn't hesitate to visit their GP if they notice any unusual or persistent changes in their body.
"Four in 10 cancers could be prevented and people can stack the odds against getting cancer in the first place by giving up smoking, being more active, drinking less alcohol and maintaining a healthy weight."
Trisha Hatt, from Macmillan Cancer Support, said: "Although the rate of death due to cancer has decreased, the actual number of deaths has not because more people are being diagnosed with cancer.
"Too often people are missing out on the right support and we want to make sure everyone with incurable cancer is offered an advance care plan outlining how and where they would like to be cared for at the end of life."