Liberia country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 13 February 2024
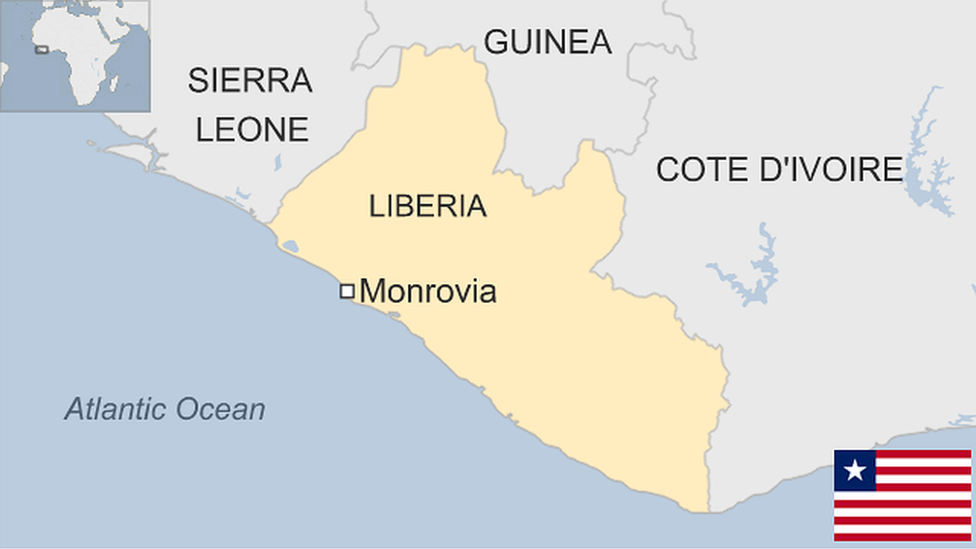
Liberia is Africa's oldest republic, but it became known in the 1990s for its long-running, ruinous civil wars and its role in a rebellion in neighbouring Sierra Leone.
Although founded by freed American and Caribbean slaves, Liberia is mostly inhabited by indigenous Africans, with the slaves' descendants comprising 5% of the population.
Around 250,000 people were killed in Liberia's civil wars, and many thousands more fled the fighting as the economy collapsed.
Big programmes are under way to address the shortage of electricity and running water.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
REPUBLIC OF LIBERIA: FACTS
Capital: Monrovia
Area: 111,370 sq km
Population: 5.3 million
Language: English
Life expectancy: 59 years (men) 62 years (women)
LEADER
President: Joseph Boakai
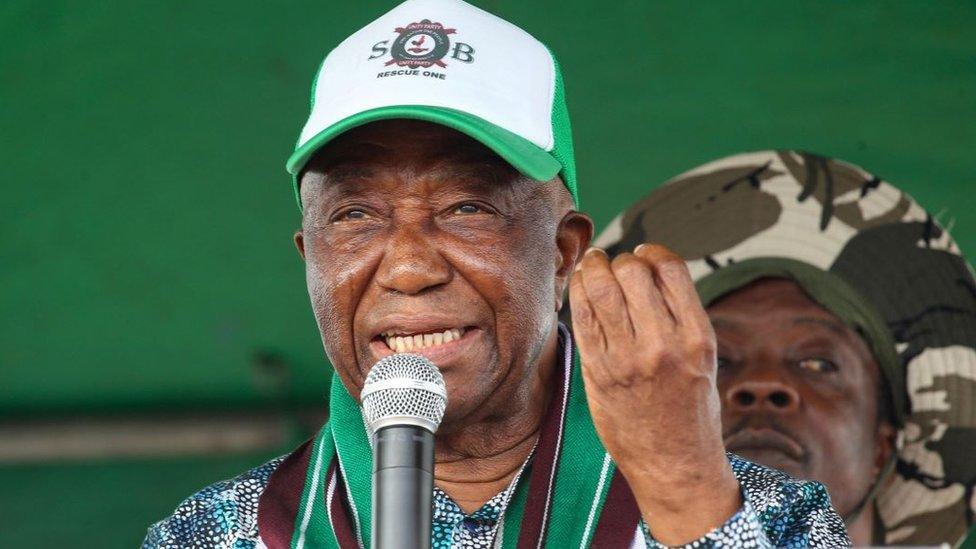

Opposition leader Joseph Boakai defeated the incumbent George Weah in the November 2023 presidential election run-off to Weah conceded defeat as the bulk of the results came in, making the final outcome clear - helping to ensure a smooth transition of power in the once-volatile African country.
The 2023 result was a marked change from the 2017 election. In that earlier election, the former football star Weah had secured a stunning victory against Boakai. But since then, many Liberians had become disillusioned with a lack of progress on the challenges of poverty, joblessness, food insecurity and power shortages.
President Boakai has promised to restore hope in Liberia and prevent the country "from falling over the cliff".
Having served for 12 years as vice-president under Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, the first elected female African head of state, he is familiar with running a country.
MEDIA

Liberia has seen a growth in the media sector since the mid-2000s, helped by the country's political stability that flourished in the aftermath of its civil wars.
However, Reporters Without Borders (RSF) says that attacks on journalists continue. While the constitution provides for freedom of speech and the press, these rights are sometimes restricted in practice.
TIMELINE
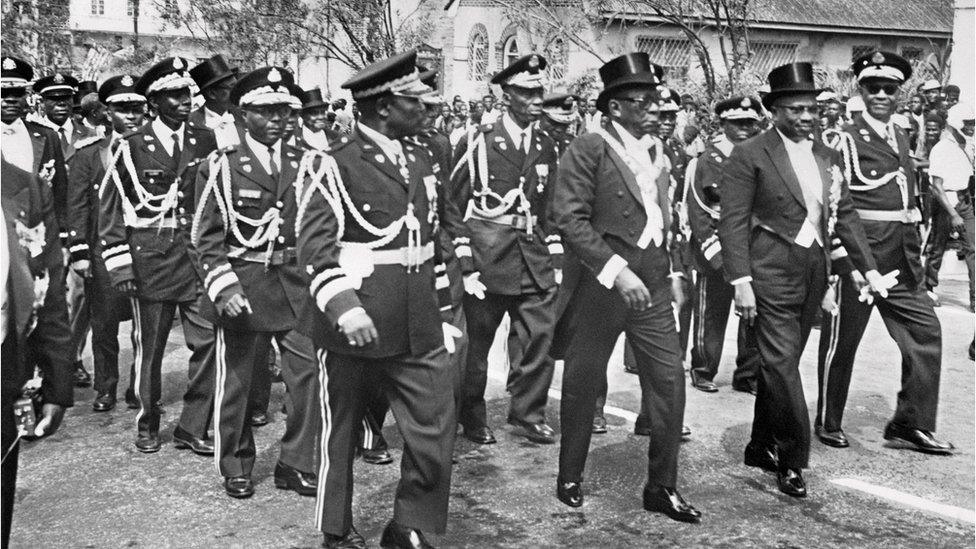

President William Tubman, centre, served from 1944 until his death in 1971. He introduced numerous reforms, including the vote for women
Some key events in Liberia's history:
14th-16th Centuries - Decline of the Mali and then the Songhai empires, compounded with inland desertification, sees increased settlement in coastal areas.
15th-17th Centuries - Portuguese, Dutch, and British establish trading posts along the coast.
1816 - American Colonization Society (ACS) is formed with the aim of resettling former slaves in Africa. It believes "repatriation" is preferable to having emancipated slaves remain in the US.
1822 - ACS begins sending freed slaves voluntarily to establish a colony.
1847 - Constitution modelled on that of the US is drawn up, and Liberia becomes independent. It is politically dominated by the newly-settled incomers.
1917 - Liberia declares war on Germany, giving the Allies a base in West Africa.
1926 - Rubber production becomes backbone of Liberia's economy after Firestone Tyre and Rubber Company opens rubber plantation on land granted by government.
1936 - Forced-labour practices abolished.
1943 - William Tubman elected president.
1951 - Women and indigenous property owners vote in the presidential election for the first time.
1958 - Racial discrimination outlawed.
1971 - Tubman dies and is succeeded by William Tolbert Jr.
1980 - Master Sergeant Samuel Doe carries out a military coup, ousting and publicly executing President Tolbert and 13 aides. Doe assumes full powers.
1984 - Doe's regime allows return of political parties following pressure from the United States and other creditors.
1985 - Doe wins presidential election.
1989-97 - First Liberian civil war.
1989 - National Patriotic Front of Liberia (NPFL) led by Charles Taylor begins an uprising against the government.
1990 - Doe is executed by a splinter group of the NPFL.
1996 - Peace agreement between the rival factions. Some 200,000 people are killed in the civil war.
1997 - Charles Taylor wins presidential election. He sets up a totalitarian regime, supporting rebel groups in Guinea and Sierra Leone. In return, both countries start backing anti-Taylor dissidents.
1999-2003 - Second Liberian civil war.
1999 - An anti-Charles Taylor rebel group backed by Guinea, invades northern Liberia.
2003 - Second rebel group invades southern Liberia. Major fighting for the capital, Monrovia which is besieged for two months. Taylor goes into exile. Interim government and rebels sign peace accord. Some 50,000 people die in the war, which sees the widespread use of child soldiers.
2005 - Ellen Johnson Sirleaf becomes the first woman to be elected as an African head of state.
2007 - Charles Taylor goers on trial at The Hague, accused of instigating atrocities in Sierra Leone.
2012 - Energy companies report discovery of oil off the coasts of Liberia and Sierra Leone.
2012 - Charles Taylor is found guilty of war crimes for aiding and directing rebels in Sierra Leone. He is sentenced to 50 years in jail, to be served in Britain.
2013-2016 - Outbreak of Ebola virus in Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone, killing 11,300 people, almost half in Liberia.
2017 - George Weah wins presidential election, marking first peaceful transfer of power in decades.
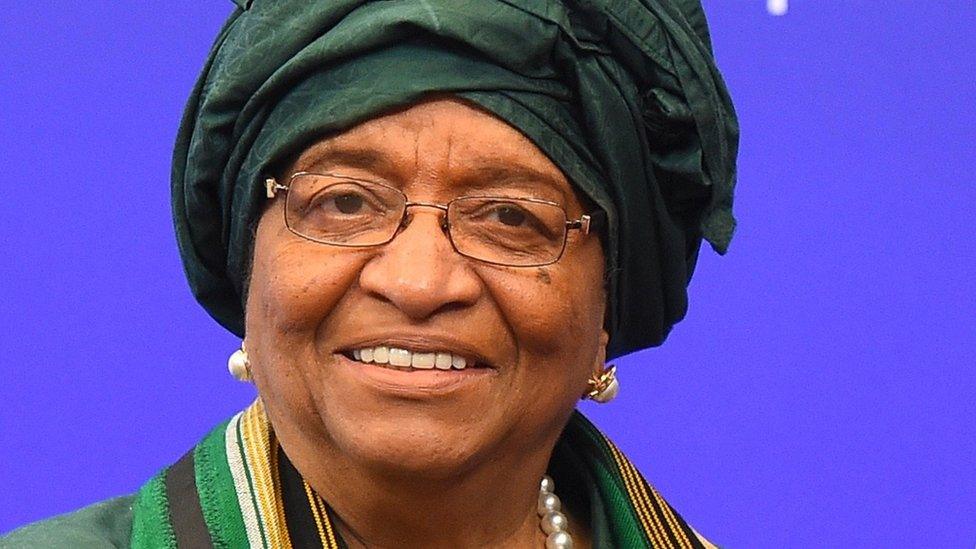

Ellen Johnson Sirleaf was elected as the first female president in Africa in 2005
- Published26 February 2024
- Published27 November 2023
- Published14 April 2023
- Published24 July 2023
- Published7 January