Ebola crisis: Rwanda reopens border with DR Congo amid outbreak
- Published
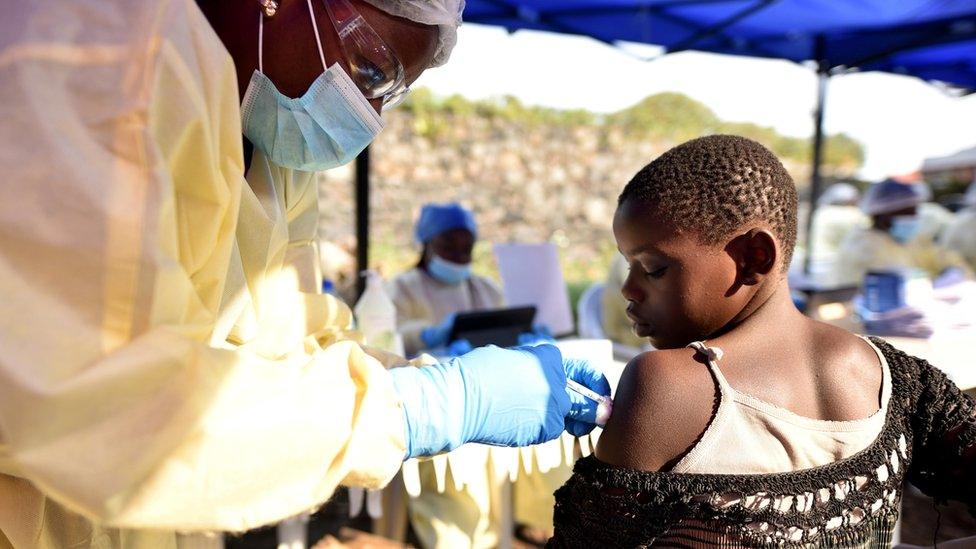
A year since an Ebola outbreak was declared in DR Congo, medics are still trying to control the disease
Rwanda has reopened its border with DR Congo, where an Ebola outbreak has killed more than 1,800 people in the past year.
The border was closed for several hours after the confirmation of a third death from Ebola in the Congolese city of Goma.
At least 2,700 people have been infected in the worst Ebola outbreak in the country's history.
Tackling the disease has been complicated by conflict in the region.
About 12 new cases are being reported every day in Democratic Republic of Congo, the World Health Organization (WHO) reports.
Last week, the WHO designated the outbreak of Ebola a global health emergency, its highest level of alarm, but warned against trying to contain the virus by closing borders or restricting travel or trade.
What is the situation on the ground?
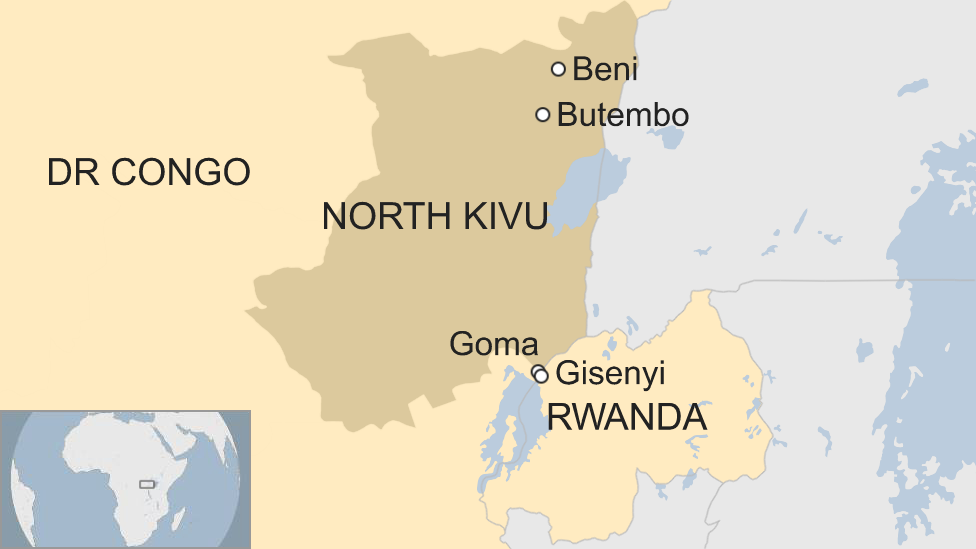
Goma, home to two million people, is the capital of North Kivu, one of the two provinces in DR Congo which have borne the brunt of the epidemic.
The city lies just across the border from the Rwandan city of Gisenyi, which has a population of around 85,000. Many residents cross the frontier for work and other activities - although illegal routes are also used.
The border had been closed "to avoid unnecessary crossings" to Goma, Gilbert Habayarimana, mayor of Rubavu district in western Rwanda which borders Goma, said earlier.
The Congolese presidency had criticised the decision to close the border, and people on the Rwandan side rejoiced after it was reopened.
Rwanda's government has intensified cross-border monitoring, advising citizens to avoid unnecessary travel to Goma, according to Health Minister Diane Gashumba.

Still shaking hands
By Ley Uwera, BBC Afrique, Goma
Life goes on pretty much as normal in both Goma and Gisenyi, although some got worried when the two official border crossings were closed earlier on Thursday. And soldiers and police were also deployed to the many unofficial crossing points which people often use.
Thursday is a public holiday in DR Congo, Parents' Day. People clean up the graves and pay respects to their deceased relatives in the morning before taking gifts to their parents. Most people were still shaking hands and embracing when meeting. Only a few have stopped since Ebola was confirmed in the city.
The only major change is that water taps have been set up in public buildings, where people have to wash their hands before entering, and at the two official border crossings.
There are still quite a few in Goma who still do not believe that Ebola exists but this might change now that another person has died.

What is happening in Goma?
A third case of Ebola has been confirmed in Goma, raising fears the virus could spread in the densely populated city.
The patient is the daughter of an artisanal miner who died on Wednesday. He had come from Ituri, the other province where many cases have been confirmed.
The other victim in Goma was a priest who died last month.

The border crossing was closed after more cases were reported in Goma, eastern DR Congo
Efforts to control the outbreak have been hampered by violence against healthcare workers or Ebola treatment facilities. Seven people have been killed and 58 injured in 198 attacks this year.
Another major problem has been distrust of healthcare workers. As a result, about a third of deaths have not been at specialist treatment centres, but in the community, where there is a greater risk of the disease spreading to neighbours and relatives.
The designation has only been used four times previously, including during the Ebola epidemic that killed more than 11,000 people in West Africa between 2014 and 2016.
The WHO has also said it has insufficient money to tackle the problem. It had estimated that it needed $98m (£81m) to tackle the outbreak between February and July, but it faced a shortfall of $54m.
What is Ebola?
Ebola is a virus that initially causes sudden fever, intense weakness, muscle pain and a sore throat
It progresses to vomiting, diarrhoea, and both internal and external bleeding
People are infected when they have direct contact through broken skin, or the mouth and nose, with the blood, vomit, faeces or bodily fluids of someone with Ebola
Patients tend to die from dehydration and multiple organ failure
Is there no vaccine?
Yes, there is. It is 99% effective and more than 161,000 people have received it.
However, not everybody is vaccinated - only those who come into direct contact with an Ebola patient, and people who come into contact with them. And some of those people refuse to take it.
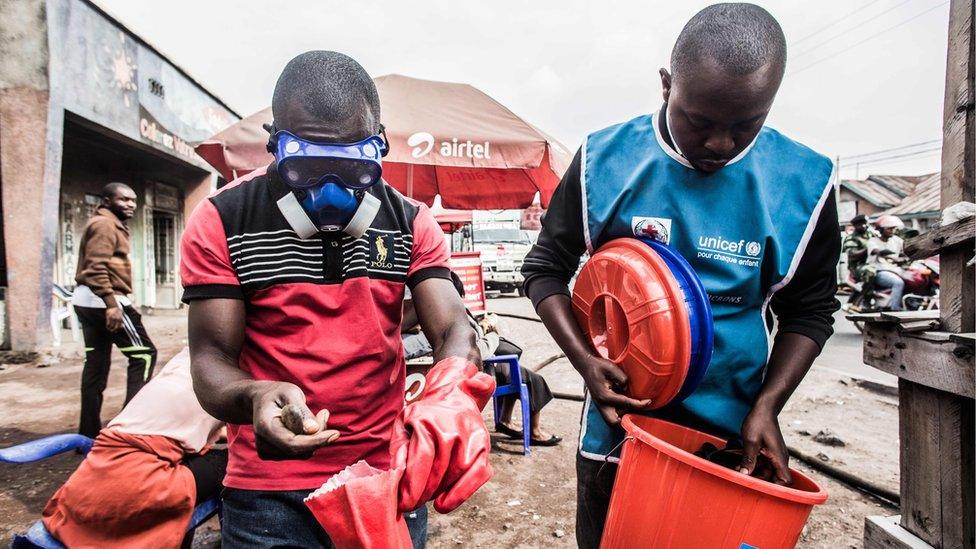

Health workers wear protective gear to mix water and chlorine in Goma, where two people have died
People give a variety of reasons for not taking the vaccine, including:
They may have religious beliefs that do not permit them to take vaccines
They may think they do not need it
They may not believe in Ebola
The vaccine, made by Merck, was developed during the epidemic in West Africa and has been available throughout the latest outbreak.
It has proven effective but is in relatively short supply, so the WHO recommended a second vaccine made by Johnson & Johnson to complement it.
But DR Congo's Health Minister Oly Ilunga complained that the Congolese were being treated as "subjects of experimentation", according to Reuters news agency, and he resigned over the issue.
- Published17 July 2019

- Published18 July 2019