Ebola: How a disease is prevented from spreading
- Published
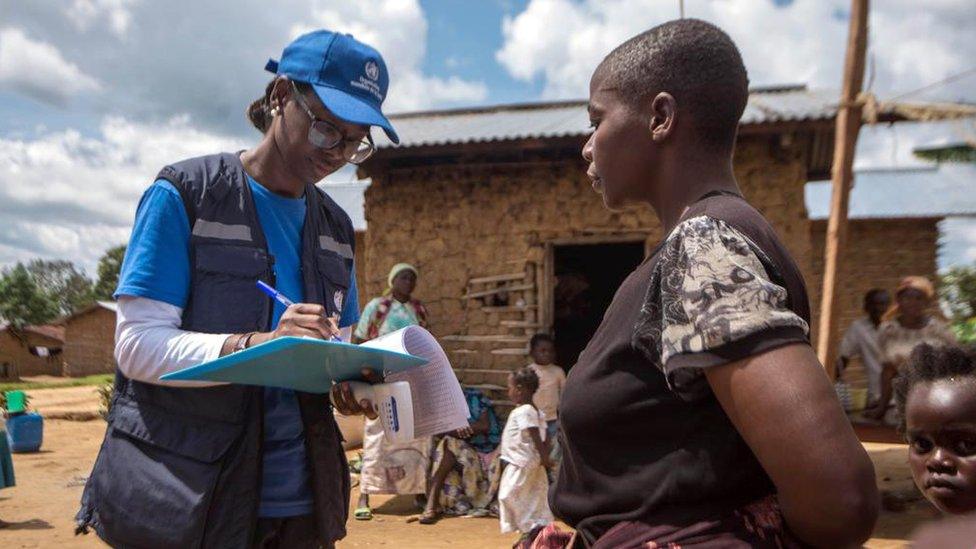

Marie Roseline Darnycka Belizaire (L) helps to lead WHO efforts to tackle Ebola in the Democratic Republic of Congo
For health workers on the frontlines of the battle against Ebola, time means everything.
Earlier this month, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared an international health emergency in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) after an outbreak of Ebola. The second-deadliest Ebola epidemic in history, it has killed more than 1,600 people so far and the numbers are rising.
Haitian doctor Marie Roseline Darnycka Belizaire is helping lead the WHO's efforts to tackle the disease in the DRC, where additional challenges include armed conflict, tough terrain and widespread fear and suspicion.
Here, Marie Roseline talks us though the process of trying to contain Ebola.
Step one: The first case
One case of Ebola is an epidemic. When someone is suspected to have the virus, we must quickly get samples to check and confirm that.
The symptoms are very, very similar to lots of other diseases, like malaria for example. It can begin with abdominal aches, headaches, sore throats, fevers. After two days, there will be an exacerbation of these symptoms and others may be exposed. For example, you can have diarrhoea, you can also have a higher fever. After five to seven days, we can begin to see haemorrhagic symptoms. When we get into the last stages of symptoms, we have very pronounced asthenia, when the person becomes very weak.
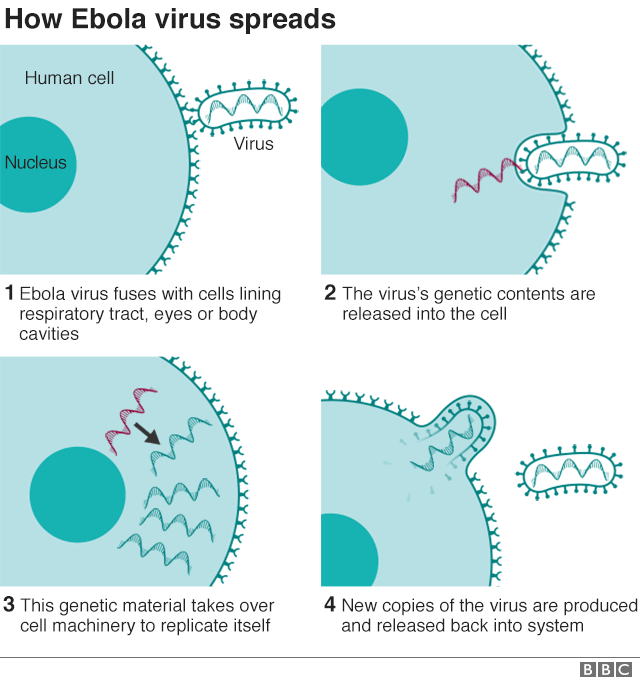

Ebola patients look like any person who is sick. When you are very accustomed to seeing people with Ebola, you can distinguish an Ebola sufferer with the most severe symptoms. It's like someone who is very ill with a lot of pain in his body. He's looking at you with some anxiety, some fear of dying. We have found people who have escaped and have gone to hide themselves to die.
We have put in place what we call a surveillance system. Members of the community go between houses to detect if someone is sick. If this is the case, they will refer this person to a health centre where the health worker has to refer this person to the Ebola team if the symptoms are the same as those seen in Ebola. At that point, we will receive an alert.
To distinguish a case of Ebola we have to make a sample. When we suspect a case, only a laboratory can say it is or it is not.
The person is then transferred to an Ebola treatment centre for the sample to be collected and analysed. Throughout this time, the patient will be receiving psychological support. This is important because it is a deadly disease that can kill several family members at the same time, people are often stigmatised when they have it, and some people think they have Ebola because they have done something wrong.
Step 2: The diagnosis
If the sample is positive, we now know we have an Ebola case. At this point, we put all pillars of our response plan into action.
Ebola is not killing you spontaneously, there is time to go for help.
If you get to a treatment centre in the first two days of symptoms, you have a 95% chance of being healed. But if you go 10 days after symptoms begin, you have a 95% chance of dying.
One of the main difficulties we're having is when a doctor within the local health structure suspects someone of having Ebola they are not calling quickly. The problem that we have is that 90-95% of the health structure is private. So when they refer the patient quickly, they say that they are not earning anything. Sometimes they keep the patient and then the patient infects other people in the health structure.
After the patient is informed of a positive result, the team will go to the family to tell them and offer psychological support.
In the Ebola treatment centre, we make sure that every treatment is available to the patient. We make some laboratory analyses to see if the kidneys are OK, if the heart is OK. Once we check all the biological functions of the person, the committee dealing with the treatment meet and decide what the best option available is.


If the person comes early, if they come late, they are treated at the same level. All of the patients are receiving the treatment. All of those patients are receiving the vital support. All the patients are receiving psychological support, and all the patients have the right to have a family member there, although direct contact is not allowed.
We are some times also called after a community death. In this case we arrange a safe and dignified burial.
Step 3: 'Mapping'
Once the psychological support is in place and the family is accepting of the result and understands what it means, our surveillance team will go deeper into an investigation we launched when we validated the case as suspected.
We do what we call "mapping". The mapping is to find where and with whom this person has been, not only in the period since symptoms began but also 21 days before this.
If someone has been in a church, we have to go to the church and try to find all the people that have been around this person. If this person went to prayer, then the pastor may have put his hand under the person. So then we have to find all the people that have been in the same room praying as this person.
How many people are affected completely depends on the movements of this person.
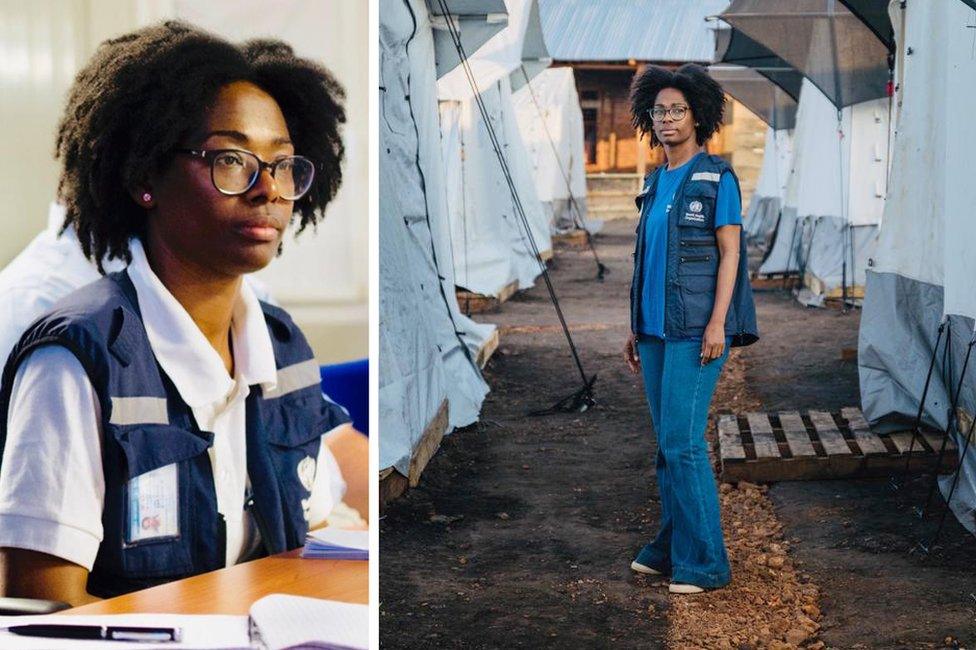

Marie Roseline Darnycka Belizaire says 'mapping' is a central part of the fight against Ebola
Sometimes we find that families are the main contacts, but we find also friends who are visiting, and in the community we find neighbours who have been visiting after hearing that this person has been sick in their house. When the person has been in hospital, this means all the co-patients are also contacts, workers in this hospital who have been dealing with the person are also contacts and people who have been visiting patients in the same room as the confirmed case are also contacts. You can understand how difficult it is after listing all those contacts to identify them and find them.
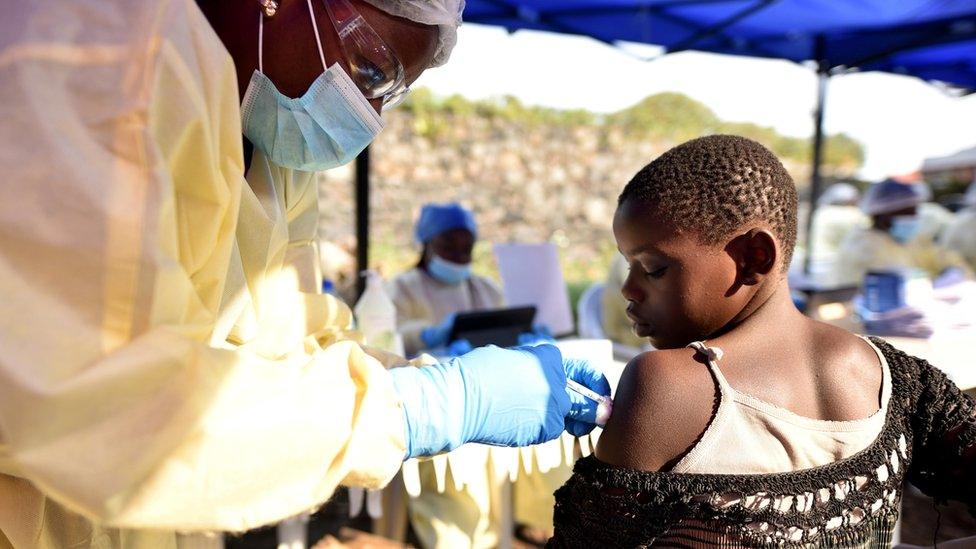
When we have identified each direct contact in the case one by one, we follow all of them for 21 days. While we are monitoring them, we also offer them vaccinations.
We also offer vaccinations to contacts of contacts. Those are people who have been in contact with someone who has been in direct contact with the confirmed case. Contacts of contacts of contacts are offered vaccines too.
We call these groups the first, second and third generation of contacts. There is a median number of contacts we have established of between 50 and 150 people, which helps to guide us when we are looking for them.
We have had a case that generated 356 contacts because he was a singer. It all depends on the mapping of the person.
Step 4: Vaccinations
The first, second and third generation of contacts are all offered the vaccine, but the vaccine is not mandatory.
Before offering them the vaccine, we explain why we are proposing it and why it would be good for them to take it. We also explain to them what will happen to them once they take it, because there are some symptoms they can have afterwards. After all this, they decide if they want it.
When they decide not to take the vaccine, we try to convince them. But in the end, it is a personal decision.
It is normally not so difficult to get people to take the vaccine but sometimes we have issues.
We have found people who don't want to take the vaccine because they don't want to put any external liquid in their body. We have those that have refused because they have a religion that doesn't want them to take vaccines. We have people who refuse just because they don't believe in Ebola. And we have people refuse because they think they are protected against all the bad things in the world. We have faced all of those things when people refuse them.
The vaccine has been invaluable for those who want to take it.
Some simple techniques can help prevent spread of Ebola.
We do not vaccinate everyone in the country because the vaccine is still under investigation, the number of vaccines that are available now is not enough, and by vaccinating the third ring of contacts, we create what we call community immunisation anyway. This means that the entire population is not in need of the vaccine.
We are working in very remote places, so sometimes we are carrying the vaccine on our heads. We had a team who had to walk more than five hours to a place because no cars, no motorcycles could get there so they had to go by foot.
With very remote places in the forest, we can also have insecurity because there are armed groups operating there.
Sometimes you think you might not survive. One of our colleagues has been killed and there are also people in the community who have been killed in their houses because they are working with us in the response.
Step 5: Cross-border co-ordination

We also support bordering countries with their preparedness and response plan.
When someone - a contact - is displaced to another place, we rapidly contact the other country. We have contacts who have travelled to Uganda but we have informed Uganda quickly and those contacts have been identified and come back to the DRC.
So far, the recommendation of WHO is not to close the borders. We should reinforce checks on the borders, screenings at the point of entry - this is the recommendation.
At the points of entry, if someone is sick and trying to get to another country, you can detect them there.
Step 6: Epidemic over
To declare that an epidemic is over, we have to have 42 days without any cases. Forty-two days is double the incubation period.
After the Ebola is declared finished, we begin with a surveillance phase. This is 90 days during which the team is still in the field. We train local people to try to make the system sustainable. We also actively search the community to find any cases that have been hiding somehow.
After an outbreak, we want to help local health systems to become more reliable.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
- Published18 July 2019
- Published2 August 2019

- Published9 July 2019