Ethiopia's Ambo city: 'From freedom to repression under Abiy Ahmed'
- Published
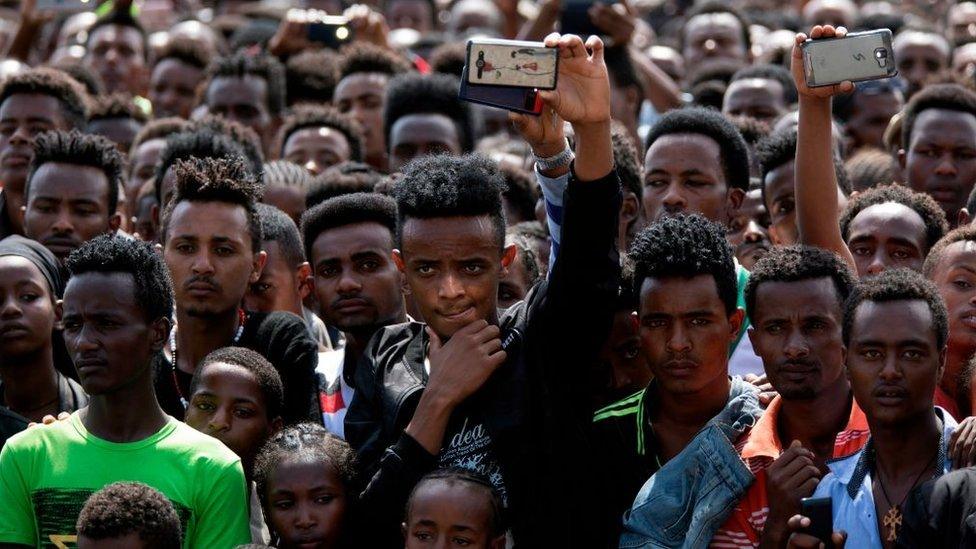

Abiy Ahmed drew a huge crowd when he visited Ambo city in his first week in office
Under Ethiopian Prime Minister and Nobel Peace Prize winner Abiy Ahmed, the city of Ambo has turned from being a symbol of freedom into a symbol of repression, as the security forces try to curb the growth of ethnically inspired rebel and opposition groups that threaten his "coming together" vision.
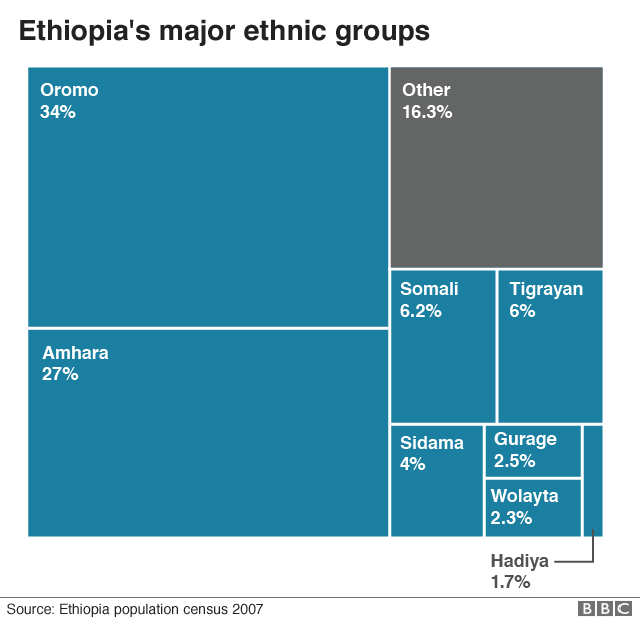
Ambo, which has a large student population because of its university, was at the centre of mass protests that saw Mr Abiy rise to power in April 2018 with a promise to end decades of authoritarian rule in a nation with more than 100 million people belonging to at least 80 ethnic groups.
Ambo is where we are going to build the statue of our liberty, our New York"

Most of Ambo's residents are Oromos - and the protests were largely driven by anger that despite being Ethiopia's largest ethnic group, they were marginalised from political and economic power, with no Oromo ever serving as prime minister.
Acknowledging Ambo's role in bringing about change during a visit to the city within days of becoming the first Oromo to hold the prime minister's post, Mr Abiy said: "Ambo is where we are going to build the statue of our liberty, our New York."
At a fund-raising event in February 2019, the prime minister sold his watch for 5m birr (about $155,000, £120,000) to kick-start development in the city.
It was a further indication of the huge political significance he attached to Ambo, traditionally regarded as a stronghold of the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF), a former rebel group which laid down arms following peace talks with Mr Abiy.
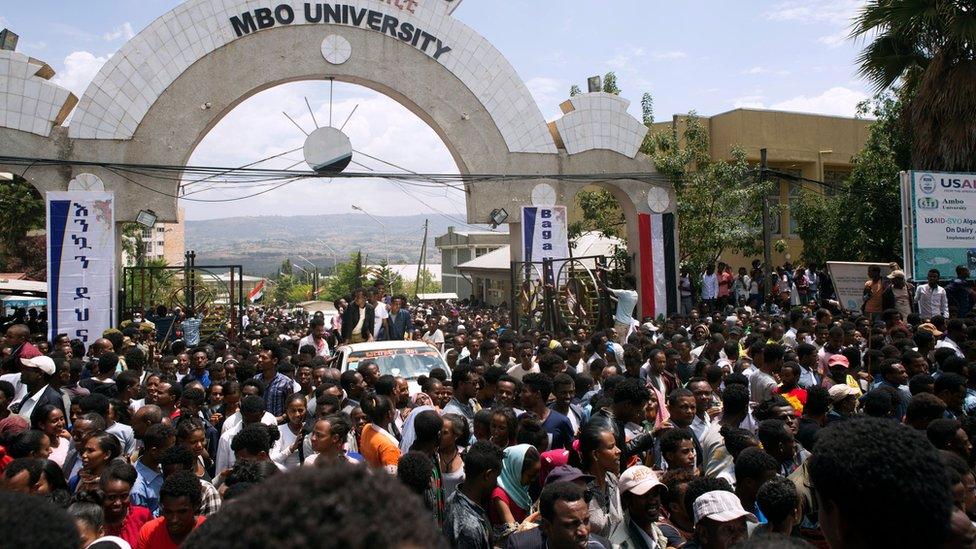
Students were at the forefront of demands for change
But a year later, there are few signs of development in Ambo, which is about 100km (60 miles) west of the capital Addis Ababa. Instead, residents are once again complaining of a return of police brutality, with young men being randomly beaten up or detained as they go about their daily lives.
'I was lucky'
I witnessed some of this during a visit to Ambo.
In one instance about six policemen forced two young men to kneel in front of pedestrians, before kicking them and hitting them with sticks.
In another instance, two young men were forcibly taken to a police station. Their elbows were tied behind their backs. One of them pleaded, in vain, with the officers to untie him.
No-one dared to intervene for fear that the police would assault them too.
I saw policemen walk around with scissors, giving haircuts to young men perceived to have long hair or afros"

The policemen were from the regional force - and their numbers were swelled last Sunday when hundreds more graduated, raising fears that the crackdown will intensify ahead of the general election slated for August. That is the first time that Mr Abiy will face the voters since the ruling coalition chose him as prime minister to order to quell the nationwide protests.
I also saw policemen walking around Ambo with scissors, giving haircuts on the spot to young men whom they perceive to have long hair or afros.
They considered my hair to be an afro but I was lucky - they let me off with a warning to chop it off myself, which I did not do as I was going to leave Ambo in two days' time.
'I was unable to access the internet'
Police just assume that men with such looks are troublemakers and supporters of rebel leader Kumsa Diriba, who they see as a major threat to western Oromia's stability and Mr Abiy's vision of forcing a new sense of national unity, known as "coming together" .

Rebel commander Kumsa Diriba refuses to make peace with the government
Having spurned Mr Abiy's peace overtures in 2018, Mr Kumsa, who is also known as Jaal Maro, is continuing to push for the "liberation" of Oromia from his forest hideout in the remote west.
He split from the OLF, the biggest Oromo rebel group, after it decided to turn into a political party, taking with him an unspecified number of fighters under his command.
The government suspects that Mr Kumsa's rebels have infiltrated Ambo, and were responsible for the bomb blast at a pro-Abiy rally held last month to show that the prime minister still commands significant support in the city.
The rebels, via their supporters and anonymous accounts, have also been slowly gaining a profile on social media in an attempt to raise discontent against the government, especially through the circulation of the names of victims of alleged brutality by the security forces.
The government's attempt to keep a lid on dissent has led to frequent internet shutdowns in much of western Oromia since January, and in some areas people cannot even make or receive phone calls. This is despite the fact that Mr Abiy has promised to liberalise the telecom sector and end the monopoly of state-owned Ethio Telecom.

Read more about Ethiopia:

In an interview with BBC Afaan Oromoo, the deputy chief of staff of Ethiopia's Defence Force, Gen Berhanu Jula, hinted that the shutdowns were linked to military operations to dismantle camps under Mr Kumsa's control, while a senior official of Mr Abiy's newly formed Prosperity Party (PP), Taye Dendea, denied that innocent people were victims of the security force operation.
"The government has no reason to target civilians, we care about our people more than anyone else," Mr Taye told BBC Afaan Oromoo.

In Ambo, I was unable to access the internet over my mobile phone throughout my three-week stay. On the two occasions I went to an internet cafe, it had poor broadband connection and I had to wait for a long time before I could check my emails and social media accounts.
Residents suspect that apart from government concerns about the rebels, the shutdowns are intended to limit political campaigning and starve young people of news ahead of the general election.
Residents point out that Jawar Mohammed - who is probably the most prominent and controversial Ethiopian social media activist - is now also making life difficult for the prime minister.
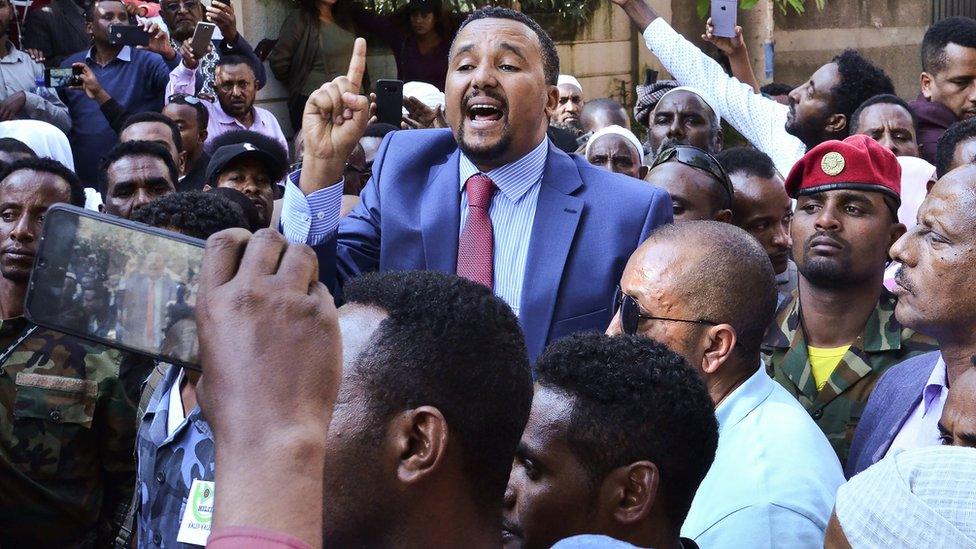
Social media activist Jawar Mohammed has joined an opposition party
When exiled in the US, Mr Jawar used Facebook effectively to get Oromos on to the streets to rise against the former government.
Having returned to Ethiopia after Mr Abiy took power, he briefly became a supporter of the prime minister but is now a fierce opponent.
Nobel laureate booed
Mr Jawar put out a video on Facebook soon after Mr Abiy was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in October, accusing the government of trying to remove his guards from his home in Addis Ababa as part of a ploy to orchestrate an attack on him.
Despite government denials of any such plan, Mr Jawar's supporters staged protests against Mr Abiy in parts of Oromia - in one instance, burning copies of the prime minister's newly published book, which outlines his "coming together" vision.
When Mr Abiy subsequently visited Ambo for a meeting with selected guests in a hotel, pro-Jawar youths staged a protest and booed the prime minister, who had been awarded the Nobel prize for his "decisive initiative" to end the border conflict with Eritrea, and for the "important reforms" he had initiated in Ethiopia with a pledge to "strengthen democracy".
Bornto a Muslim father and a Christian mother on 15 August 1976
Joinedthe armed struggle against the Marxist Derg regime in 1990
Served as a UN peacekeeper in Rwanda in 1995
Enteredpolitics in 2010
Becameprime minister in 2018
Wonthe Nobel Peace Prize in 2019

Mr Jawar has joined the Oromo Federalist Congress (OFC), which has formed an alliance with the OLF and the Oromo National Party (ONP) to contest the election on what is expected to be a strong ethno-nationalist ticket.
In Oromia, it is likely to pose the biggest electoral challenge to Mr Abiy's PP, which was launched in December after a merger of eight of the nine regional parties which make up Ethiopia's ruling coalition.
Mr Abiy hopes that the PP will foster national unity and keep ethnic nationalism in check.
But he has taken a huge risk as the mass protests that propelled him to power were not just about political freedom - but also about the right of each group to express their ethnic identities more freely and to have greater autonomy for their regions.
So, as far as ethno-nationalists in Ambo and elsewhere in Oromia are concerned, Mr Abiy has sold out.
Worrying for the Nobel laureate, Defence Minister Lemma Megersa, a fellow Oromo with political clout, also expressed doubts about the PP's formation in November, though party officials say he and Mr Abiy have been ironing out their differences since then.
"The merger is not right and timely, as we are in transition, we are on borrowed time. Dissolving the regional party to which the public entrusted their demands is betraying them," Mr Lemma said at the time.
For Mr Abiy's supporters, he offers the best hope of getting Ethiopia's myriad ethnic groups to work together, and avoid the country's disintegration.
They are confident that he will demonstrate his popularity by leading the PP to victory in the election, though its legitimacy is bound to be questioned if the crackdown in Ambo continues.

You may also want to watch:
What was Ethiopia's PM like as a child?