Guam profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 27 October 2023

The US territory of Guam is a keystone of American military strategy in the Pacific. Tourism and an expanding military presence form the bedrock of its economy.
The island is an important staging post, allowing rapid access to potential flashpoints in the Koreas and in the Taiwan Strait.
The largest military installation, Andersen Air Force Base, was used by B-52 bombers during the Vietnam War in the early 1970s. Nuclear attack submarines are based on the island.
The waters off Guam are the scene of major US navy war games.
Washington plans to move thousands of troops to Guam from the Japanese island of Okinawa as part of a global realignment of its military.
This proposed build-up of US forces has brought the issue of the island's future political status to the fore in recent years.
GUAM: FACTS
Capital: Hagatna
Area: 540 sq km
Population: 168,800
Languages: English, Chamorro
Life expectancy: 77 years (men) 83 years (women)
LEADERS
Head of state: US President
Governor: Lou Leon Guerrero

Lou Leon Guerrero, a Democrat, was elected as governor in 2018.
The governor is elected to a four-year term. Although they are US citizens, residents of Guam do not vote in US national elections. Its official status is a "non-incorporated territory".
The indigenous Chamorro are a people of mixed Micronesian, Spanish and Filipino descent but the diverse population also includes Japanese, Chinese, and incomers from other Pacific islands.
MEDIA
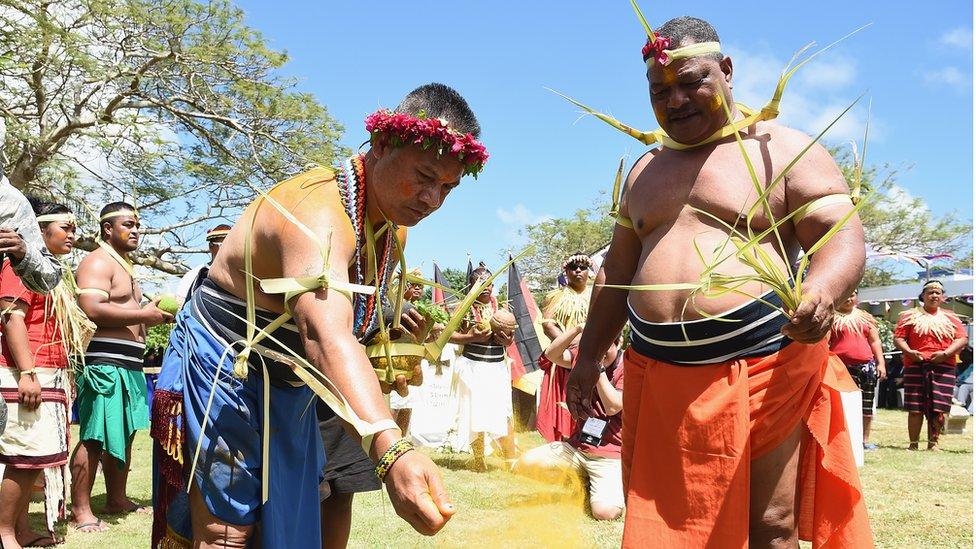

Guam has a diverse population, including indigenous Chamorro, a people of mixed Micronesian, Spanish and Filipino descent
Broadcasting on Guam is regulated by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
There were 181,000 internet users by July 2022, comprising more than the total population of the territory (Internetworldstats.com).
Press
Television
KUAM, external - commercial
KTGM, external - commercial
PBS Guam, external - public
Radio
PNC Guam, external - commercial, news, talk
KPRG, external - public
TIMELINE
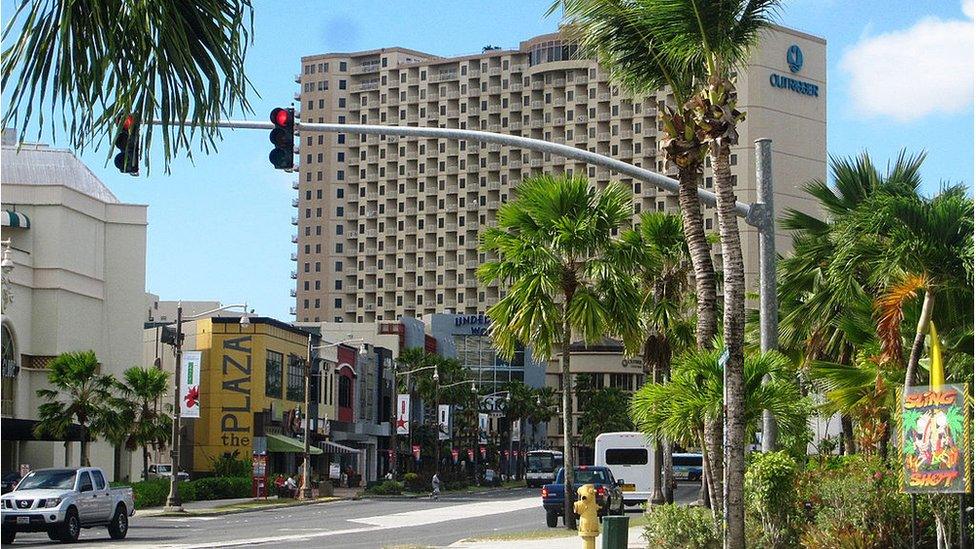

Tourism makes a major contribution to the economy
Some key dates in Guam's history:
2000BC - Guam settled by Indonesian-Filipino people.
Circa 1521 - Explorer Ferdinand Magellan, sailing for the King of Spain, lands on Guam.
1565 - Spain claims the island.
1898 - Guam is ceded to the United States in the Spanish-American War.
1941 - Japan seizes Guam after the Pearl Harbor attack during World War Two.
1944 - Allied forces retake the island, which becomes an important base from which to attack Japan towards the end of the war.
1950 - Guam Organic Act establishes Guam as an unincorporated organised territory of the United States, granted islanders US citizenship.
1969 - Islanders reject the idea of unification with the Northern Mariana Islands in a referendum.
1980s and 1990s - Movement in favour of Guam becoming a commonwealth, giving it a level of self-government similar to Puerto Rico and the Northern Mariana Islands.
1997 - A decolonisation commission is set up to educate islanders about the various political options in the territory's relationship with the US.
2020 - Guam joins the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization (UNPO).
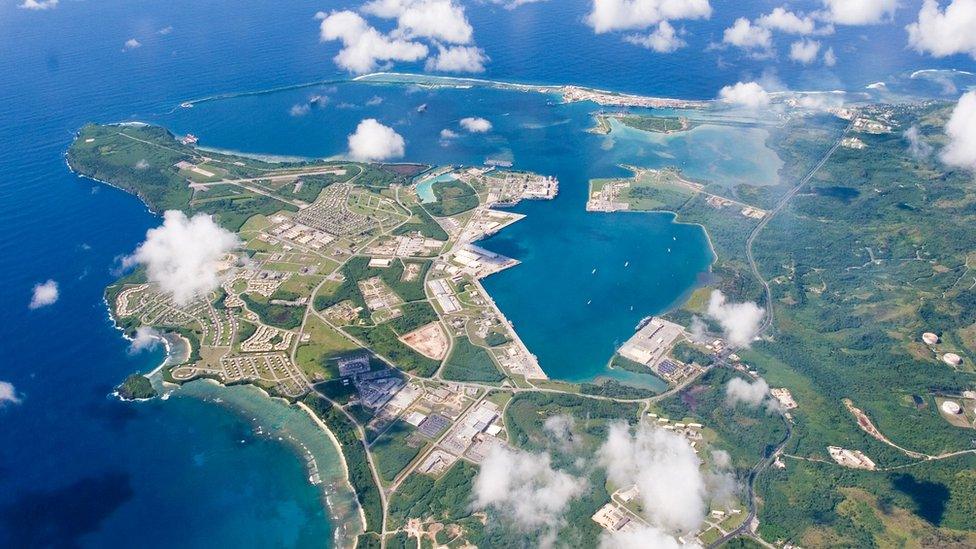

The US military has various facilities on the island including a naval base, an air force base as well as a hospital
Related topics
- Published4 June 2024
- Published5 July 2023
- Published27 October 2023
- Published27 October 2023
- Published26 January 2024
- Published27 October 2023
- Published27 October 2023