Defaming a dog: The ways to get arrested for lese-majeste in Thailand
- Published
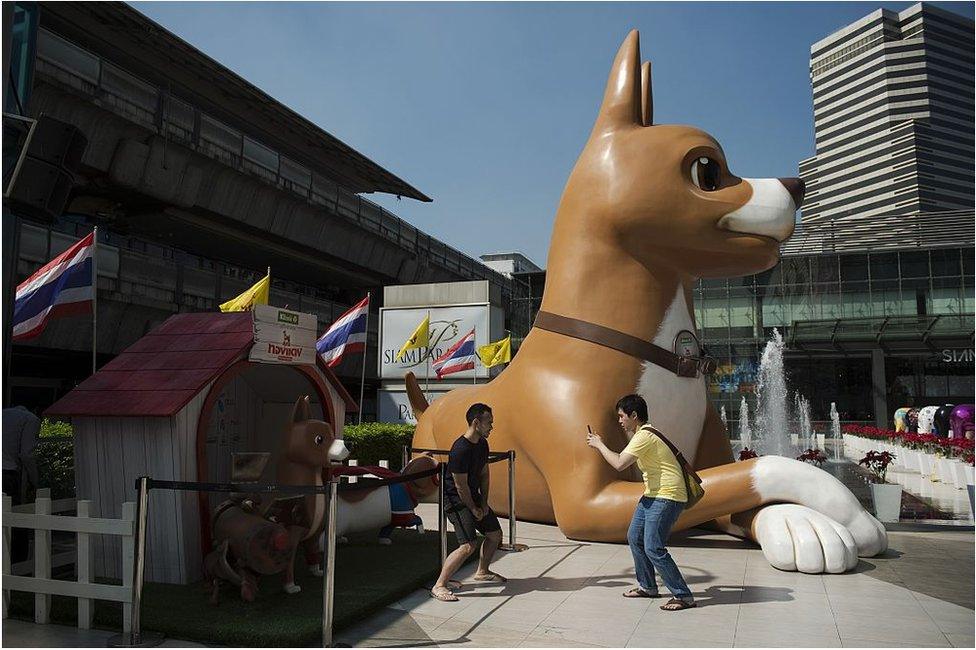

The king's favourite dog, Tongdaeng, inspired an animated movie which opened this month in Bangkok amid widespread publicity
A man in Thailand faces up to 15 years in prison for posting images on Facebook of King Bhumibol Adulyadej's favourite dog in a way that mocked the king, a prosecutor in the military court said.
He was charged under the notoriously sweeping lese-majeste law. After last year's coup, the ultra-royalist military has demanded ever tougher enforcement of it. This has led to many different and sometimes unexpected ways of falling foul of the law.
The crime of insulting the monarch dates back in Thailand to the early 19th Century, when the unlucky accused could be punished by beheading, having their ears, hands and feet cut off or, for milder infractions, be imprisoned for a month and made to cut grass for the royal elephants.

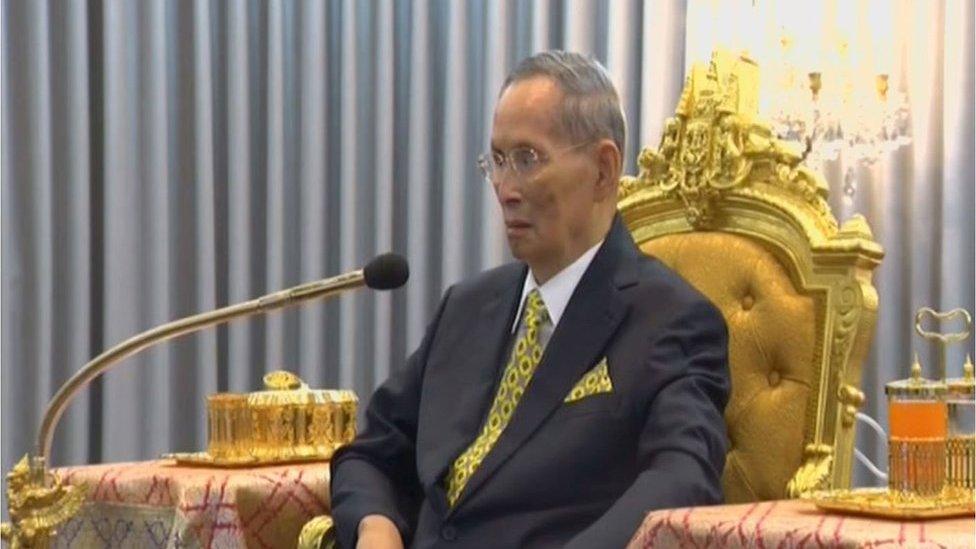
King Bhumibol Adulyadej, who made a rare public appearance earlier this week, is widely revered in Thailand
The modern concept of lese-majeste was incorporated into Thailand's first criminal code in 1908, and in its current form as the notorious Article 112, in 1956.
It states that "whoever defames, insults or threatens the king, queen, heir apparent, or regent shall be punished with imprisonment of three to 15 years."
No mention there of dogs, or any other royal pets. But ever since the start of Thailand's intractable political crisis in 2006, the number of lese-majeste prosecutions has risen sharply, as has the severity of punishments, and the breadth of interpretation of what constitutes royal defamation.
Here are a few examples:

Saying anything negative about the monarchy to passengers in a car

The taxi driver was reportedly discussing inequality in Thai society
Last August, a taxi driver was jailed for two and a half years after a passenger recorded his comments on a mobile phone and handed them to the police.

Staging a university play featuring a fictional one-eyed king
In February, two students were jailed for two and a half years for performing a play called The Wolf's Bride a year earlier, which the court judged to have parodied King Bhumibol, who lost an eye as a young man in a car accident.
The Thai government says many Thai people accept and support the law

Writing a novel featuring characters that resemble members of the Thai royal family
In August 2008, Australian Harry Nicolaides was arrested at Bangkok airport as he prepared to board a flight.
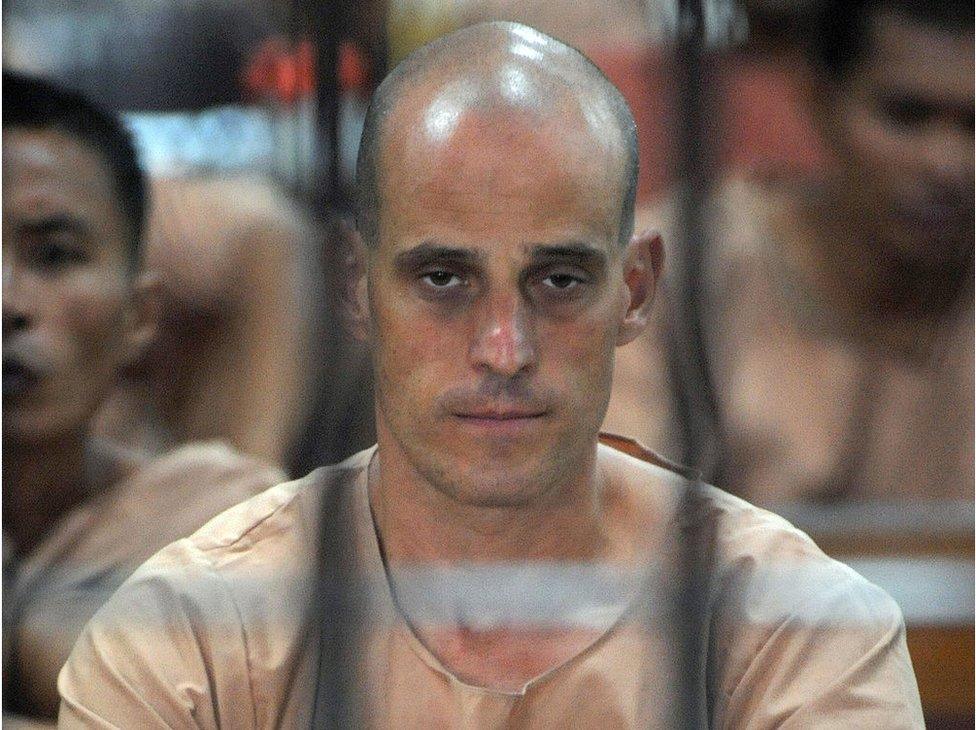

Mr Nicolaides was eventually pardoned
He was unaware of an arrest warrant issued over his self-published novel which had included a fictional crown prince with a dissolute lifestyle.
He was sentenced to three years in prison, but quickly pardoned. He says he only sold seven copies of the book. But he did send a copy to the palace to ask for approval, and when he received no reply, assumed he had got it.

Sending text messages critical of the monarchy to politicians
In November 2011, 63-year-old Ampon Tangnoppakul was jailed for 20 years over text messages sent to the secretary of then Prime Minister Abhisit Vejjajiva, despite his poor health and insistence he had not sent the offending texts.
He died the following year in prison.

'Liking' anything critical of the monarchy on Facebook

An online thumbs-up could prove troublesome in Thailand
Last week, 27-year-old factory worker Thanakorn Siripaiboon - the man who was arrested for mocking the king's dog - was also charged under Article 112 for another alleged offence: clicking the 'like' button on Facebook next to a doctored photo of King Bhumibol.

Referring to anything from Thailand's history that could be construed as damaging the monarchy's image
In 2007, a local politician was sentenced to two years in prison for talking on a radio programme about slavery during the reign of King Mongkut (1851-1868).
In May last year, the Supreme Court upheld the verdict, stating that defaming past monarchs also damaged the present king, despite the fact that slavery did exist in Thailand then.
Truth is no defence in Thai defamation cases.

Questioning an elephant battle
In October last year, two retired military officers filed a complaint of lese-majeste against renowned social critic Sulak Sivaraksa because he cited academic research which questioned whether a famous elephant battle, led by the 16th Century King Naresuan, had actually taken place.
Activist Sulak Sivaraksa: "If you have enough courage, you should abolish the law"
The police investigating Sulak have said they believe he has defamed the monarchy. This is the fifth time he has faced a lese-majeste charge.

Having a row with your brother
In 2012, Yuthapoom Martnok was charged with lese-majeste and jailed after his brother filed a complaint.
He was released nearly a year later when it was discovered there were no grounds for the charge, and that the brothers had in fact fallen out over fights between their dogs.

Bone to pick: The two brothers had quarrelled over their dogs
This case illustrated two problematic aspects of Article 112.
First, that anyone can file a complaint against anyone else, and the police have to start a formal, and often secretive, investigation, no matter how flimsy the evidence.
Second, that defendants rarely get bail, so they are jailed awaiting trial, which can take years in Thailand.
Many cases are heard in camera, so no reporting of proceedings is possible. Since the coup, most lese-majeste cases are heard in military courts, whose verdicts allow no appeal.

Failing to take down offending messages from a website
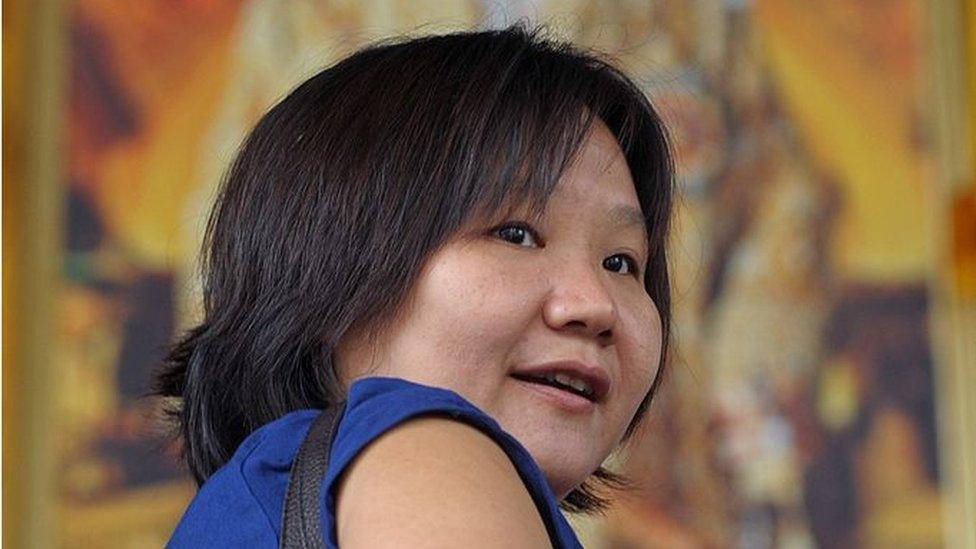

Ms Chiranuch narrowly escaped jail
In May 2012, Chiranuch Premchaiporn, editor of the news website Prachathai, was given an eight-month suspended sentence for failing to remove comments from the site quickly enough.
She had removed some after 10 days, but others had stayed up for 20.

Using the name of Crown Prince Vajiralongkorn to raise funds

The king's successor is Crown Prince Maha Vajiralongkorn
Over the past year, a slew of lese-majeste charges has been filed against people formerly linked to the heir to the Thai throne.
Nine family members of the prince's estranged wife were charged last year with citing his name to extort money, and given long prison sentences.
One police officer also involved died mysteriously in custody after apparently falling from a high window.
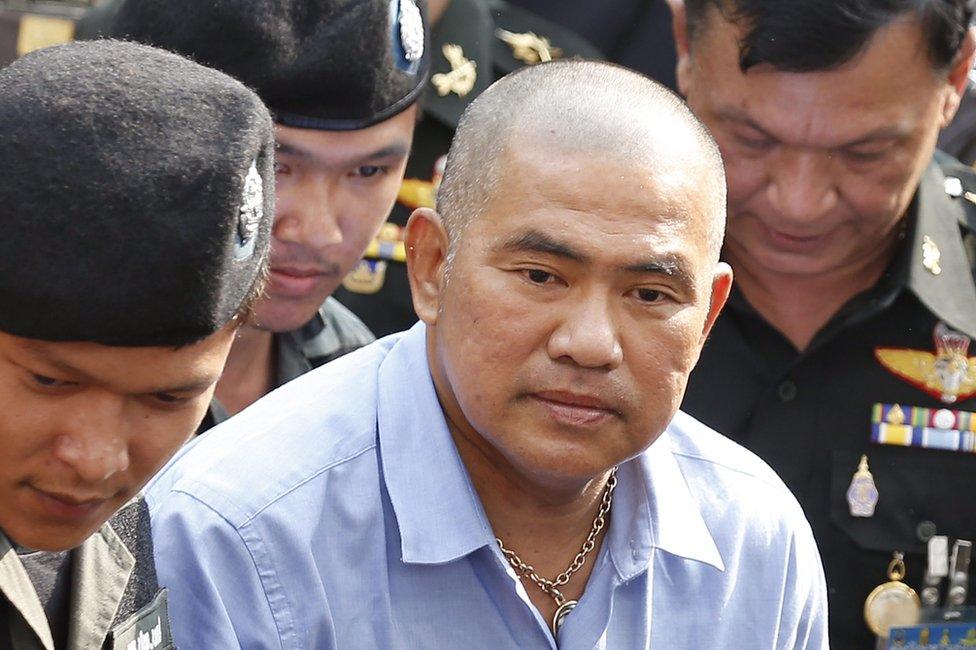

The fortune-teller, known as Mor Yong, died in custody
In October this year, three men, including a famous fortune-teller, were charged under Article 112 for using the prince's name to persuade donors to pay for promotional products tied to a bicycle ride honouring the royal family.
Two of the three died in custody.

Singing satirical songs about the royal family
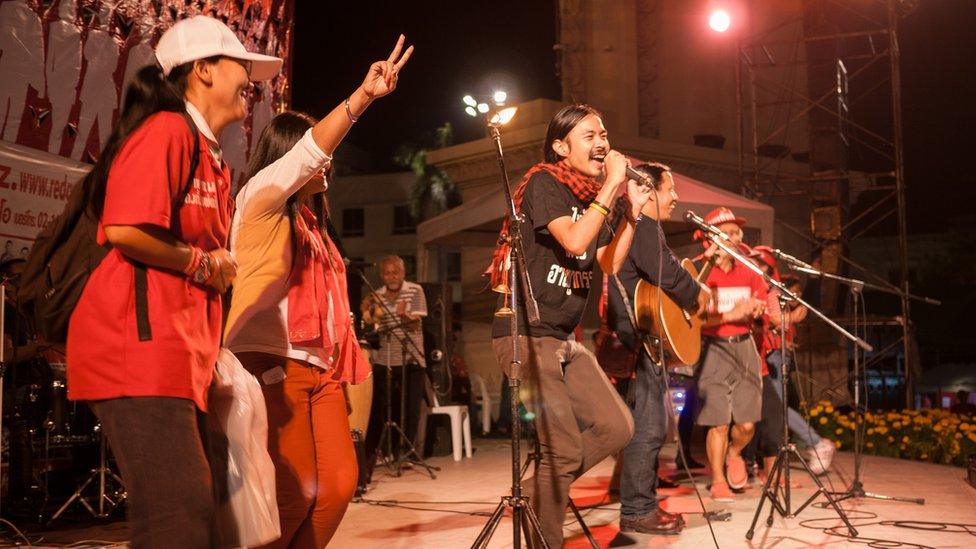
Nithiwat Wannasiri (centre), of Fai Yen, is currently living in exile
Nithiwat Wannasiri was once a follower of the royalist yellow-shirt movement, but switched to the red-shirt side in 2010, forming a band called Fai Yen, or Cool Fire. They specialised in songs that mocked the lese-majeste law and members of the royal family, performing openly around Bangkok until the coup. Nithiwat has since been charged under article 112, and is living in exile, along with hundreds of other Thais fleeing military rule.
- Published16 December 2015

- Published16 December 2015

- Published16 December 2015

- Published11 December 2015

- Published9 November 2015

- Published6 October 2017
