Norway country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 28 March 2023

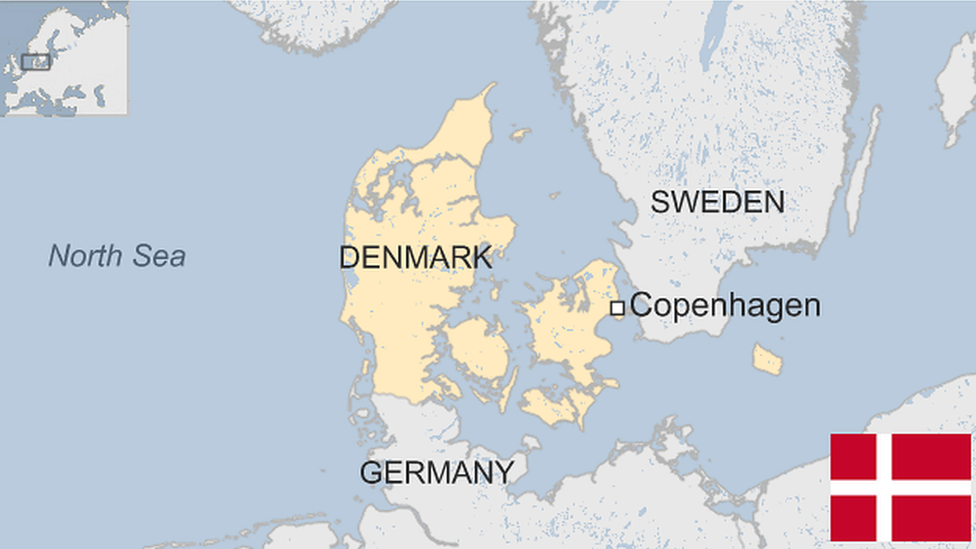
Europe's northernmost country, the Kingdom of Norway is famed for its mountains and spectacular fjord coastline, as well as its history as a seafaring power.
It also enjoys one of the world's highest standards of living, in large part due to the discovery in the late 1960s of offshore oil and gas.
It is a major oil exporter and has resisted the temptation to splurge its windfall, choosing instead to deposit the surplus wealth into its oil fund - now the world's largest sovereign wealth fund.
What to do with the money is a hot political issue: whether to use more of it to improve infrastructure or keep it for a rainy day and future generations.
Norway plays an active international role. It has mediated between Israel and the Palestinians as well as in the Sri Lankan conflict, and has participated in military action in Afghanistan and Libya. Ex-premier Jens Stoltenberg is Nato's secretary general.
It defies a global ban on commercial whaling, along with Japan and Iceland.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
KINGDOM OF NORWAY: FACTS
Capital: Oslo
Area: 385,207 sq km
Population: 5.4 million
Languages: Norwegian, Sami plus Kven, Romani, Scandoromani
Life expectancy: 81 years (men) 84 years (women)
LEADERS
King: Harald V
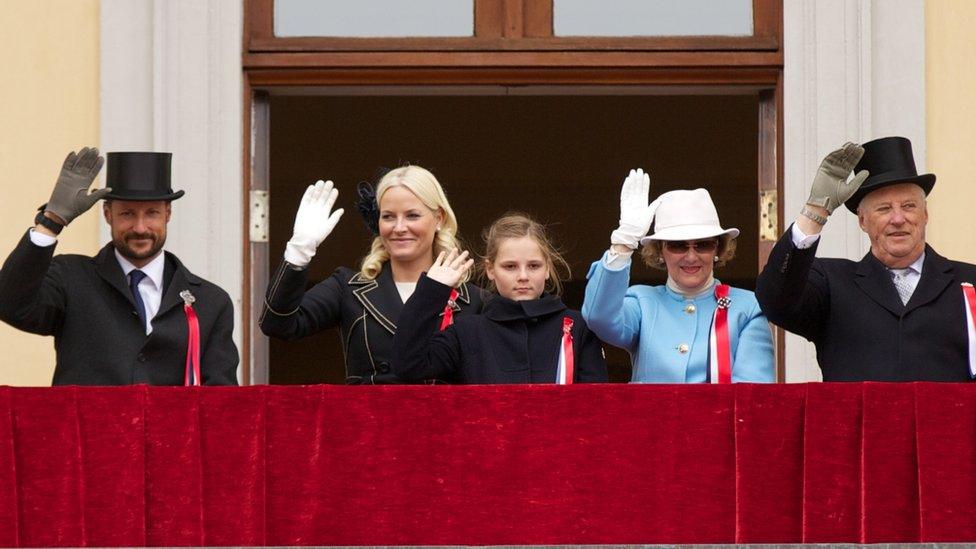

The royal family symbolises Norway's strong sense of national identity
Crown Prince Harald became king on the death of his father Olav V in 1991. Born in 1937, he fled with his mother and siblings to the United States after the German invasion in 1940, while his father and grandfather, the then King Haakon VII, joined the government in exile in London.
King Harald is a keen sportsman, and represented Norway with distinction as a yachtsman at the Tokyo, Mexico and Munich Olympics. He caused some controversy by marrying a commoner, rather than a royal princess.
The king has clearly defined constitutional duties. Apart from being head of the armed forces and Church of Norway, he chairs the Council of State once a week. He appoints the government according to which party commands the largest number of seats in parliament, or else on the advice of the head of parliament and the prime minister of the day.
King Harald has continued the royal family's tradition of unpretentious public duty, and serves as a symbol of the country's strong sense of national identity.
Prime minister: Jonas Gahr Store
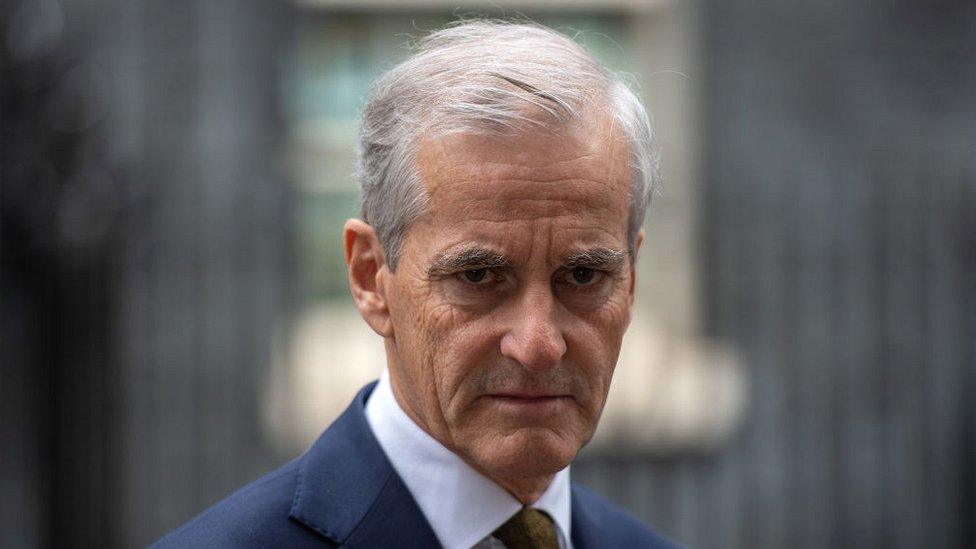

Jonas Gahr Store's centre-left Labour Party won the greatest number of seats in the September 2021 general election, but not enough to form a majority government.
In alliance with the agrarian Centre Party, he leads a minority coalition government, which are common in Nordic countries..
Erna Solberg, who had been prime minister since 2013 resigned after her Conservative party ended up with the second-largest number of seats.
Store, like his political mentors Gro Harlem Brundtland and Jens Stoltenberg, is associated with the business-friendly right wing of the Labour Party.
MEDIA

Public broadcaster NRK operates alongside major privately-owned TV and and radio networks
The media are free and journalists do not face censorship or political pressure, says Reporters Without Borders.
TIMELINE

Sailors on a replica Viking boat recall an era when their forebears traded and raided across Europe
Some key dates in Norway's history:
Circa 800-1050 - Viking Age, in which Scandinavians go on plundering expeditions abroad. Some Norwegians settle at their destinations, including Scotland and Greenland.
1030 - Christianity adopted.
1536 - Norway becomes a dependency of Denmark.
1814-1905 - Union with Sweden.
1905 - Norwegian parliament, the Storting, proclaims independence from Sweden. Prince Carl of Denmark becomes King.
1913 - Universal suffrage for women introduced.
1940 - German forces invade Norway in April, attacking important ports. fighting lasts for two months.
The Royal Family and the government flee to Britain in June. A government-in-exile is set up in London. Vidkun Quisling proclaims himself head of government in Norway.
1941 - Quisling introduces martial law due to widespread resistance and acts of sabotage by the Norwegian people.
1945 - German forces in Norway surrender in May. The King returns to Norway in June. Quisling is tried and executed for treason. Norway becomes a charter member of the United Nations.
1949 - Norway joins the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (Nato).
1959 - Norway becomes founder member of the European Free Trade Association (Efta).
Late 1960s - Oil and gas deposits discovered in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea. By the early 1980s they constitute nearly one-third of Norway's annual export earnings.
1970s - Exploitation of oil and gas deposits begins. By the early 1980s they constitute nearly one-third of Norway's annual export earnings.
1972 - Norwegian voters reject the Labour government's recommendation on EEC membership.
1973 - Norway signs a free trade agreement with the EEC.
1994 - Norwegians for the second time reject membership of the European Union in a referendum, by a margin of about 5%.
2011 - Extreme right-winger Anders Behring Breivik carries out a bomb attack and mass shooting, killing more than 70 people in the worst massacre in Norway's modern history.
2016 - The Lutheran Church - to which three-quarters of Norwegians belong - adopts a new liturgy allowing gay couples to marry in church weddings.

The Northern lights over Tromso in northern Norway
- Published25 October 2024
- Published11 February
- Published25 March 2024
- Published29 March 2023
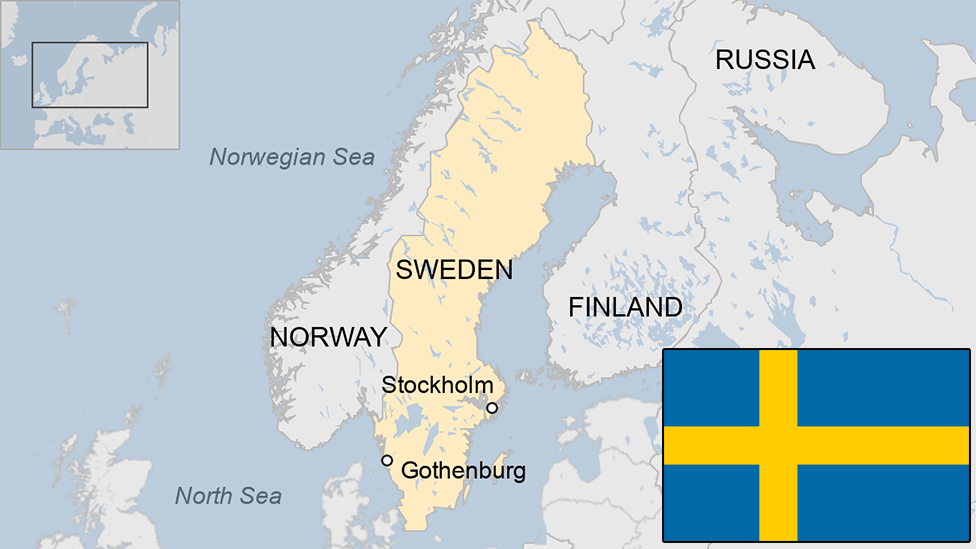
- Published13 February 2024
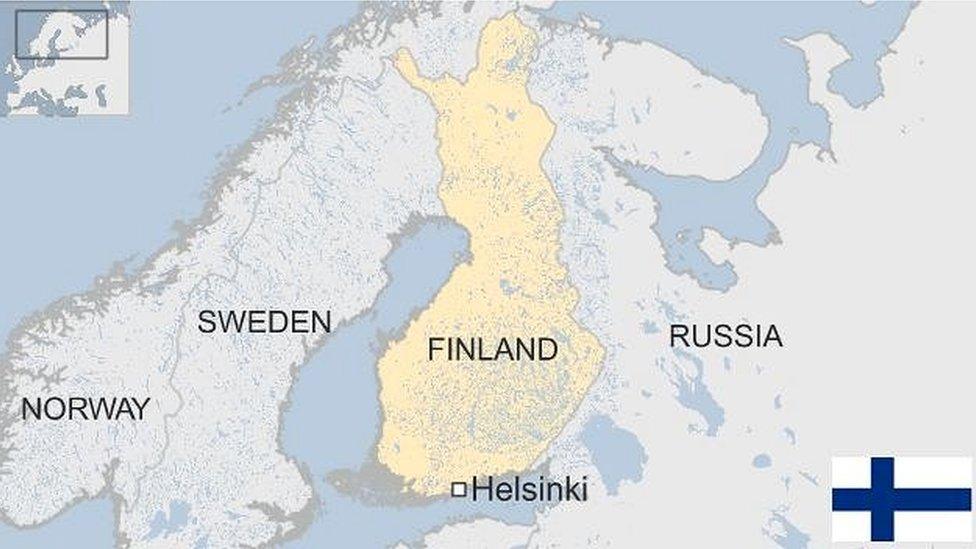
- Published8 January