Pesticide poisoned French paradise islands in Caribbean
- Published
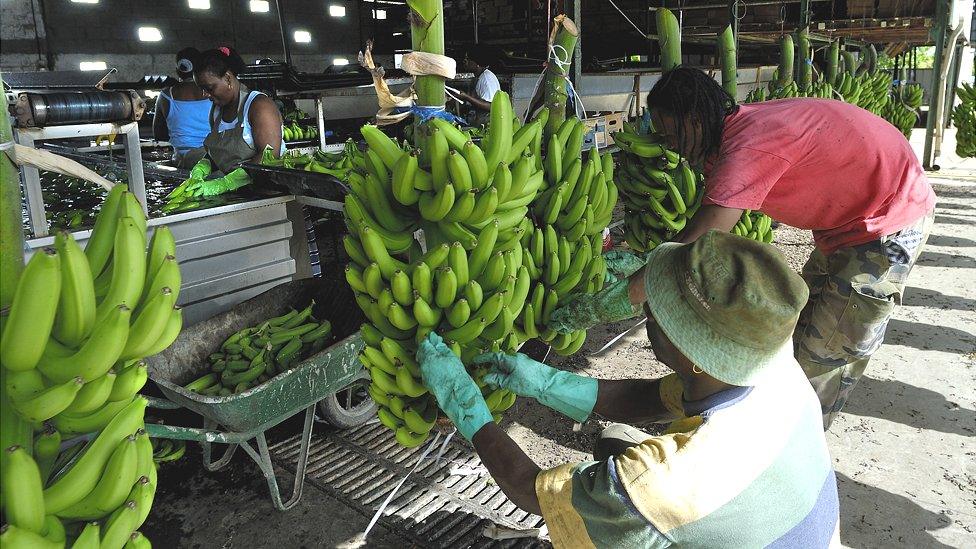

Bananas are a big export industry for Martinique and nearly all are shipped to France
The French Caribbean islands of Guadeloupe and Martinique thrive on their image as idyllic sun, sea and sand destinations for tourists.
But few visitors are aware that these lush, tropical islands have a chronic pollution problem.
A pesticide linked to cancer - chlordecone - was sprayed on banana crops on the islands for two decades and now nearly all the adult local residents have traces of it in their blood.
French President Emmanuel Macron has called it an "environmental scandal" and said the state "must take responsibility". He visited Martinique last year and was briefed on the crisis on the islands, known in France as the Antilles.
The French parliament is holding a public inquiry which will report its findings in December.
"We found anger and anxiety in the Antilles - the population feel abandoned by the republic," said Guadeloupe MP Justine Benin, who is in charge of the inquiry's report.
"They are resilient people, they've been hit by hurricanes before, but their trust needs to be restored," she told the BBC.
Large tracts of soil are contaminated, as are rivers and coastal waters. The authorities are trying to keep the chemical out of the food chain, but it is difficult, as much produce comes from smallholders, often sold at the roadside.

Grande Anse des Salines, Martinique: Tourism is the island's biggest foreign exchange earner
Drinking water is considered safe, as carbon filters are used to remove contaminants.
In the US a factory producing chlordecone - sold commercially as kepone - was shut down in 1975 after workers fell seriously ill there. But Antilles banana growers continued to use the pesticide.
What is chlordecone?
It is a chlorinated chemical similar to DDT, and an endocrine disruptor - meaning it can interfere with hormones and cause disease.
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes it as "potentially carcinogenic". It causes liver tumours in lab mice.
Banana plantations in the Antilles used it to eradicate root borers - weevils that attack banana plants.
Chlordecone was already recognised as hazardous in 1972. It was banned in the US as kepone after several hundred workers were contaminated at a factory in Hopewell, Virginia, in 1975. Their symptoms included nervous tremors, slurred speech, short-term memory loss and low sperm counts.
As French agriculture minister in 1972 Jacques Chirac, who later became president, authorised chlordecone as a pesticide.
It was not banned in the Antilles until 1993 - a delay attributed to lobbying pressure from banana growers.
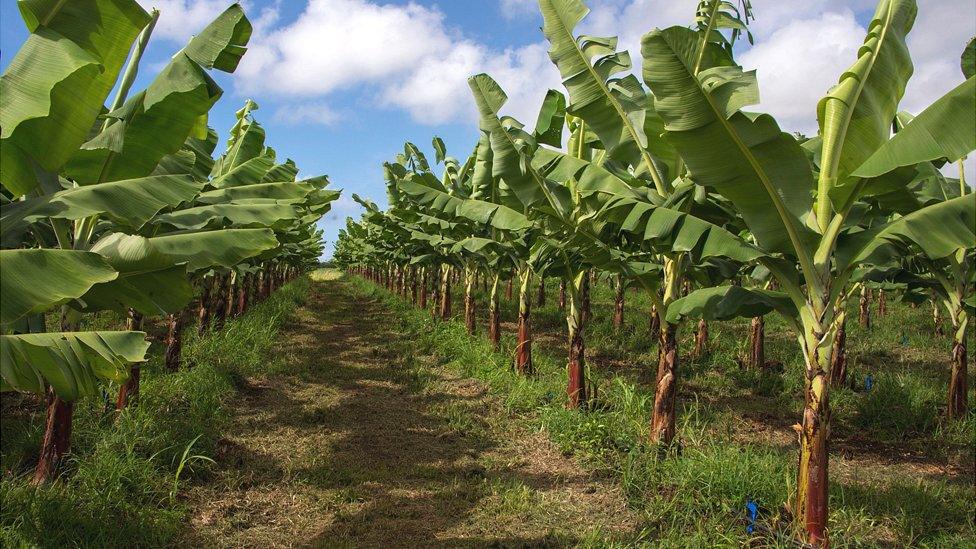

A Guadeloupe banana plantation - the fruit itself is not contaminated
The chemical is very slow to break down in the environment: contamination can persist for centuries, experts say.
It was restricted globally under the Stockholm Convention in 2016, along with 25 other "Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)".
Read more on pesticide risks:
How big is the problem?
"The economic impact is enormous," says Prof Luc Multigner, head of research at Inserm, the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research.
Prof Multigner has investigated the chlordecone crisis and says Antilles residents are very anxious and feel the French state is not doing enough.
"The authorities have banned fishing near the coast, but small-scale fishermen get by from day to day, so they are out of work," he told the BBC.
"One-third of coastal waters are contaminated, all the rivers are - fishing is banned there. Agricultural land is 30-50% contaminated, so some cultivation has to stop."
However, he notes that the chemical does not contaminate bananas.
Last year the official unemployment rate in Guadeloupe was 23% and in Martinique 18%, compared with 9% in mainland France. The Antilles rely heavily on French state subsidies.

Serge Letchimy, a Martinique MP leading the French parliamentary inquiry, said half of the island's 24,000 hectares (59,305 acres) of agricultural land had some chlordecone contamination, and 4,000 ha of that was totally polluted.
Ms Benin said compensation claims would follow the inquiry, but "the priority is more research, we need soil analysis and impact assessments for the affected farmers".
Determining responsibility was proving hard because the pesticide's licensing and distribution was complicated, she said.
"The kepone licence was resold several times," she said, adding that so far the inquiry had been unable to speak to the producers.
What is the health impact?
A study in 2013-2014 found that among adults in Martinique, 95% had chlordecone in their blood, while the figure for Guadeloupe was 93%. That corresponds to about 750,000 people.
In 2010 Prof Multigner and colleagues found a link between higher chlordecone concentrations in the blood and prostate cancer. Their conclusion was based on a study, external of 623 men in Guadeloupe with newly diagnosed prostate cancer and a control group of 671.
The World Cancer Research Fund reports that prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide., external
In 2018, the highest rates in the world were in Guadeloupe (189 per 100,000) and Martinique (158 per 100,000). The rate for mainland France was 99.
"Chlordecone contributes to the higher rate [in the Antilles], but it is not the only factor," Prof Multigner said. Ethnicity and lifestyle are also factors in hormone-dependent cancers.
Prostate cancer is more common among Afro-Caribbean and Afro-American men than among white Europeans or Asians. But testicular cancer rates are higher among white European men.
Inserm's research also found a link between chlordecone exposure and "adverse effects on cognitive and motor skills development in infants", external.
Another scientific study in the Antilles suggested that the chemical was a factor in premature births.
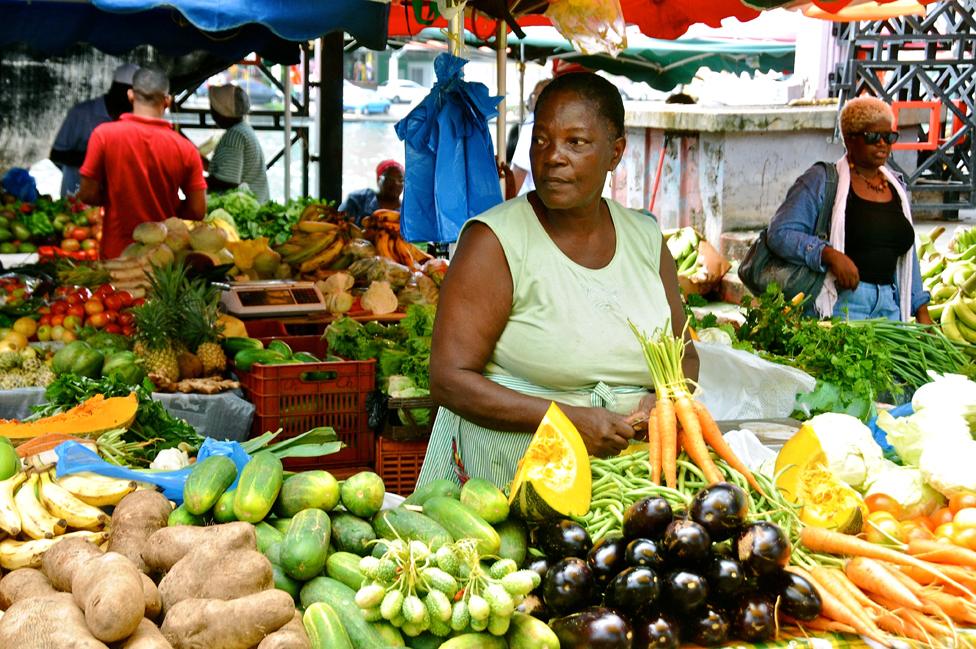

A Guadeloupe market: There are fears about produce grown on contaminated soil
What is France doing about it?
Since 2008 France has conducted public awareness campaigns in the Antilles, warning of the chlordecone risk.
The islands' authorities are monitoring local fruit and vegetables, as well as meat and fish.
The French ministers of health, overseas territories, research and agriculture have been questioned at the parliamentary inquiry.
But MP Serge Letchimy said just 16% of the polluted land had been mapped and "the measures adopted to deal with this drama bear no relation to its gravity".
- Published13 May 2019

- Published23 January 2019

- Published15 August 2018

- Published6 March 2015

- Published20 March 2019

- Published9 November 2012

- Published15 November 2016
