Uruguay country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 25 November 2024

Uruguay has traditionally been more affluent than other countries in South America, and is known for its advanced education and social security systems and liberal social laws.
It was the first nation in Latin America to establish a welfare state, maintained through relatively high taxes on industry, and developed a democratic tradition that earned it the sobriquet "the Switzerland of South America".
But economic and political turmoil, in particular left-wing urban guerrilla attacks in the early 1970s, led the government of the day to suspend the constitution and launch a period of repressive military rule that lasted until 1985.
Since the restoration of democratic government, successive governments have liberalised the economy. Colonial towns, beach resorts and a year-round mild climate have contributed to a growing tourist industry.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
ORIENTAL REPUBLIC OF URUGUAY: FACTS
Capital: Montevideo
Area: 181,034 sq km
Population: 3.4 million
Language: Spanish
Life expectancy: 74 years (men) 81 years (women)
LEADERS
President-elect: Yamandú Orsi
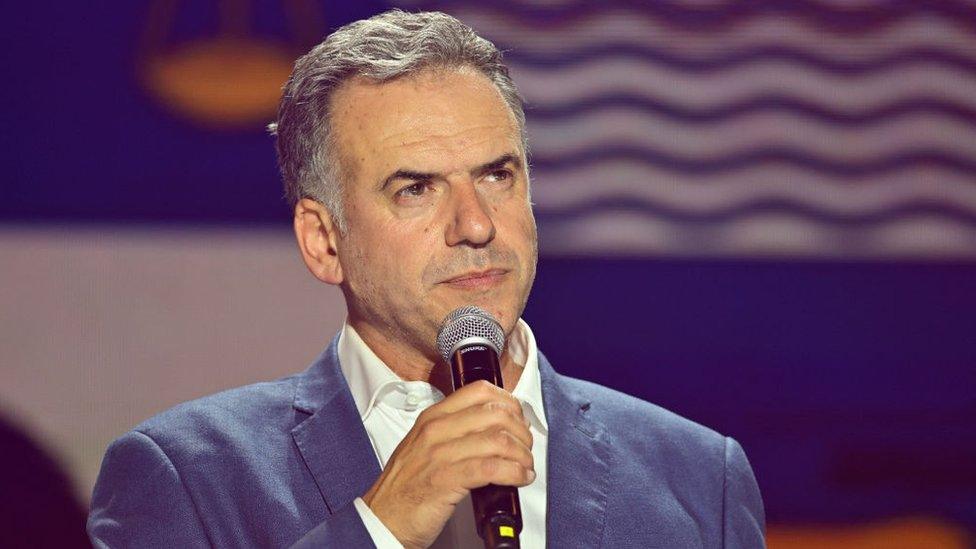

Centre-left Yamandú Orsi was elected president after winning the second-round runoff in November 2024, beating Álvaro Delgado, the candidate of the governing conservative coalition.
Orsi struck a business-friendly note in his campaign, saying that he planned to avoid raising taxes that could scare off investors.
After his victory, he stressed he wanted to be a president for all Uruguayans, saying he would "call for a national dialogue again and again" and that he would listen to those who had voted for his rival.
"I'm going to be the president who builds a more integrated country, where we set aside our differences and nobody is left behind, neither economically, socially or politically."
Uruguay's election - which pitted two moderates against each other - bucked the trend seen in other countries in the Western Hemisphere, such as Argentina, Brazil and the US, where deep divisions came to the fore.
MEDIA
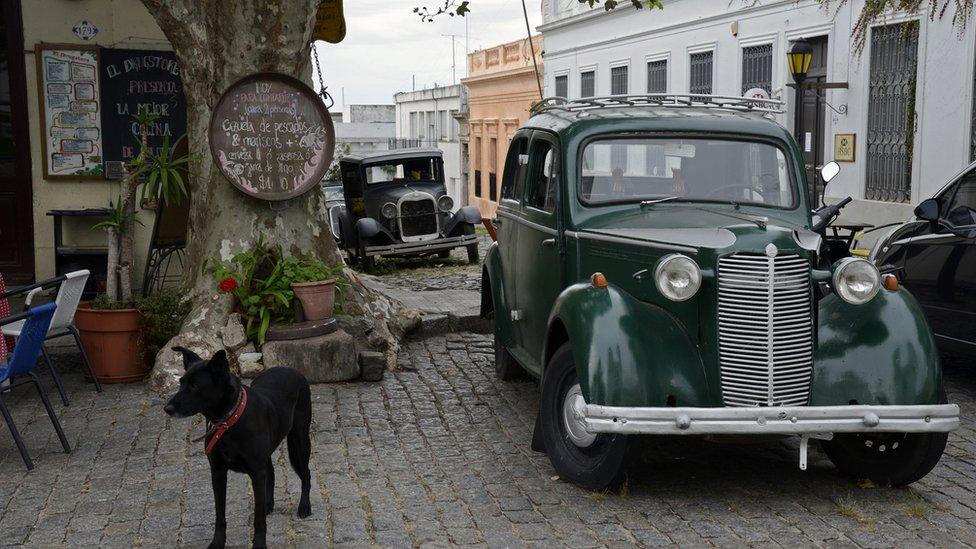
The historic quarter of Colonia del Sacramento, Uruguay's oldest town, has been designated a Unesco World Heritage Site
Uruguayans can access a wide range of views via hundreds of privately-owned media outlets.
The state of media freedom is healthy and Uruguay has been praised for setting up an independent broadcasting regulator.
TIMELINE
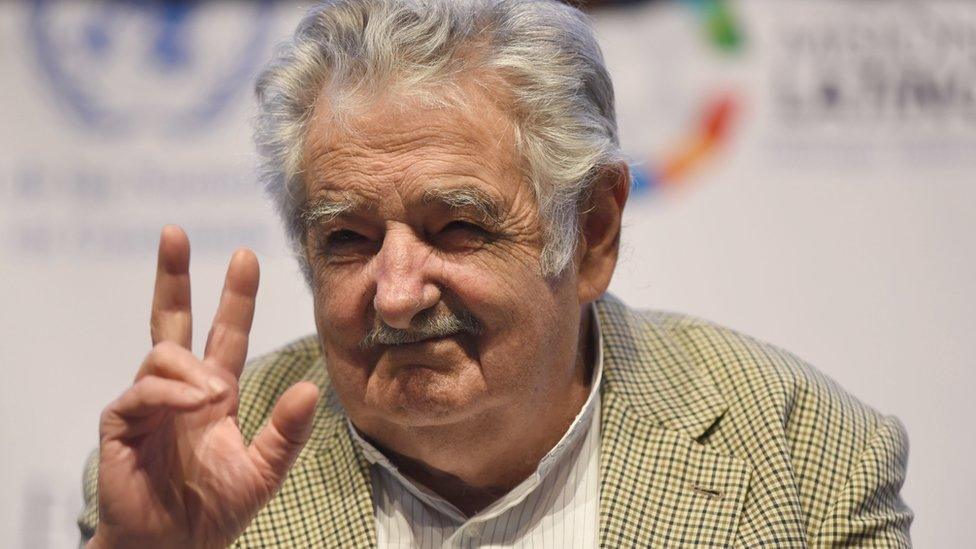

Jose Mujica was imprisoned by the military dictatorship as an urban guerrilla and later served as president
Some key dates in Uruguay's history:
1516 - Spanish navigator Juan Diaz de Solis is killed while exploring the Rio de la Plata, his death discourages European colonisation for more than 100 years.
1726 - Spanish found Montevideo and take over Uruguay from the Portuguese; many of the indigenous people are killed.
1776 - Uruguay becomes part of the Vice-royalty of La Plata, which has its capital at Buenos Aires.
1808 - Uruguay rebels against the Vice-royalty of La Plata following the overthrow of the Spanish monarchy by Napoleon Bonaparte.
1812-20 - Orientales, or Uruguayans from the eastern side of the River Plata, fight against Argentinian and Brazilian invaders.
1828 - Brazil, Argentina renounce claims to territories which become the Eastern Republic of Uruguay.
1830 - Constitution approved.
1838-65 - Civil war between Blancos, or Whites - the future conservative party - and Colorados, or Reds - the future liberals.
1865-70 - War of the Triple Alliance. Uruguay joins Argentina and Brazil in war against Paraguay, which is defeated.
1903-15 - Reformist Jose Batlle y Ordonez (Colorado Party) gives women the franchise and establishes a welfare state, disestablishes the church and abolishes the death penalty during two successive terms as president.
1933 - Opposition groups excluded from politics following military coup.
1933 - Gabriel Terra abolishes National Council.
1960s - Emergence of the leftist Tupamaros group, which stages guerrilla attacks. The military launches a brutal counterinsurgency.
1973-85 - Military rule characterised by extreme repression.
1985 - Army and political leaders agree on return to constitutional government and the release of political prisoners; law grants amnesty to members of the armed forces accused of human rights violations.
2007 - A new parliament of South America's leading trading bloc Mercosur is inaugurated in Montevideo.
2009 - The Supreme Court rules that a law shielding officials of the last military government from prosecution for human rights abuses is unconstitutional.
Former military ruler Gregorio Alvarez is sentenced to 25 years in prison for murder and human rights violations.
2010 - Former president Juan Maria Bordaberry is sentenced to 30 years in prison for murder and violation of the constitution in the wake of the 1973 military coup.
2011 - Congress revokes an amnesty law that protected military officers from prosecution for crimes committed under military rule in 1975-1983.
2012 - Uruguay becomes the first country in Latin America after Cuba to legalise abortion for all women.
2013 - Uruguay legalises same-sex marriage.
2013 - Uruguay becomes the first country to legalise the cultivation, sale and consumption of marijuana for recreational use, as a measure to counter drug cartels.
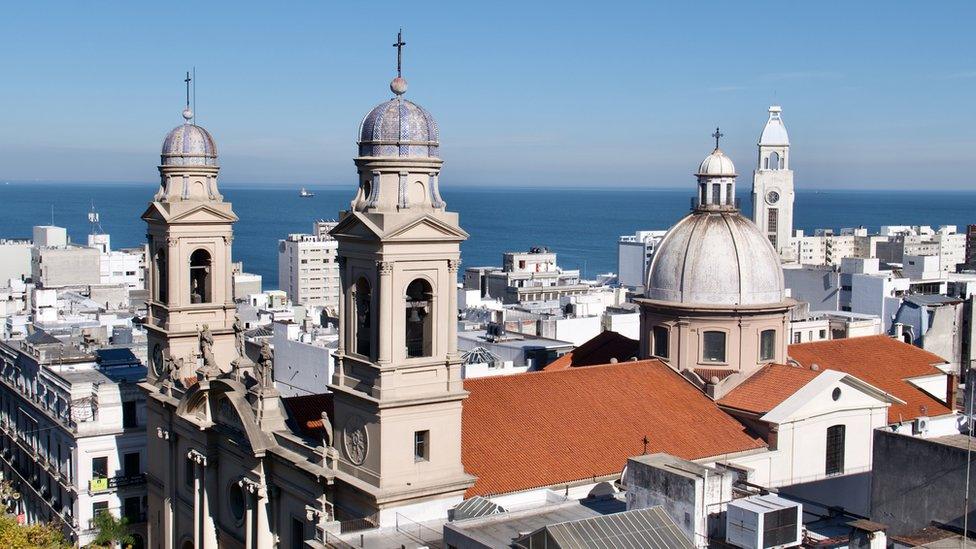

Montevideo is the seat of the administrative headquarters of Latin America's leading trade blocs, Mercosur and ALADI
Related topics
- Published8 January 2024
- Published11 December 2023
- Published7 February 2023
- Published22 August 2023
- Published2 June 2023