Gangs tighten grip as Haiti spirals to collapse
- Published

Haiti is fast descending into anarchy.
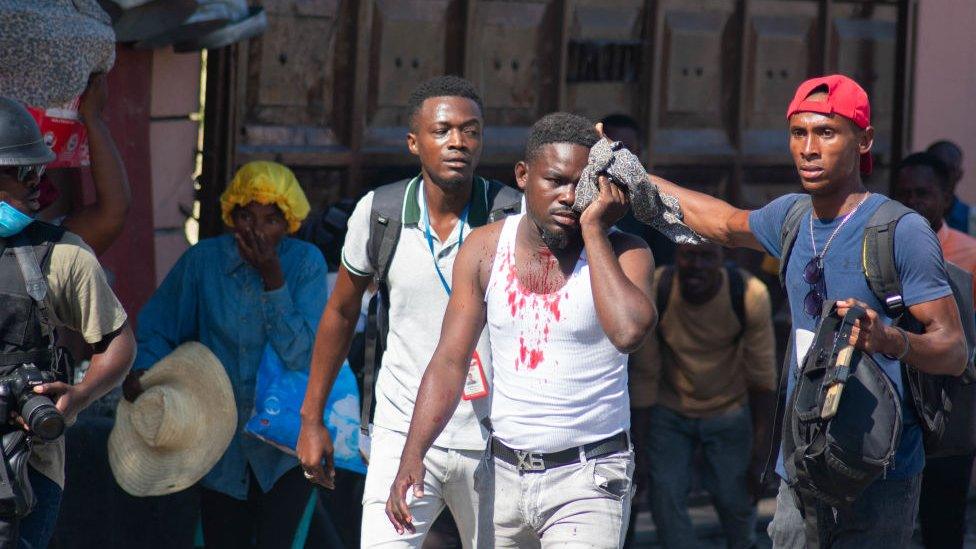
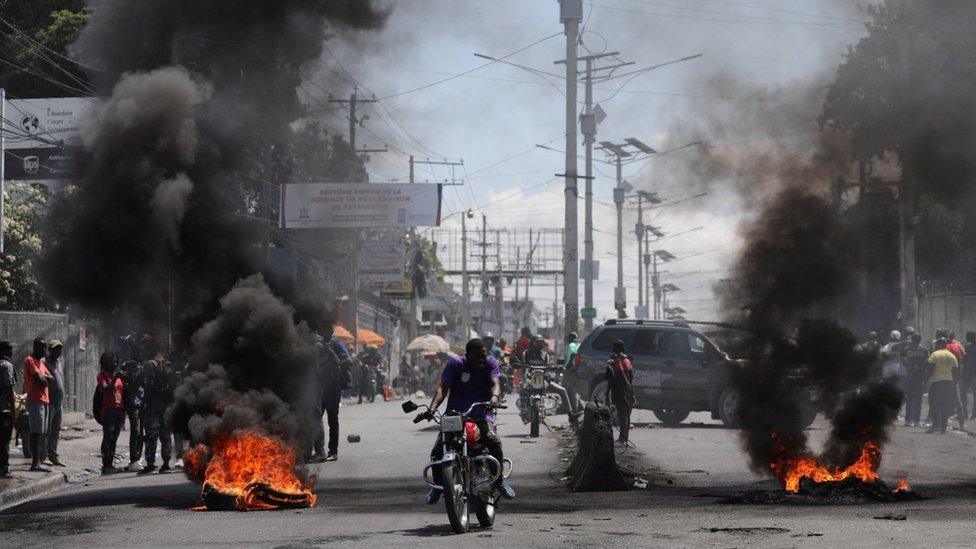
Over the weekend, the violence in the capital Port-au-Prince ramped up once again. Heavily armed gangs attacked the National Palace and set part of the Interior Ministry on fire with petrol bombs.
It comes after a sustained attack on the international airport, which remains closed to all flights - including one carrying Prime Minister Ariel Henry.
He tried to fly back to Haiti from the United States last week, but his plane was refused permission to land. He was then turned away from the neighbouring Dominican Republic too.
Mr Henry is now stuck in Puerto Rico, unable to set foot in the nation he ostensibly leads.
Among those who did manage to get into the stricken Caribbean nation, though, was a group of US military personnel.
Following a request from the US State Department, the Pentagon confirmed it had carried out an operation to, as it put it, "augment the security" of the US embassy in Port-au-Prince and airlift all non-essential staff to safety.
Soon after, the EU said it had evacuated all of its diplomats, fleeing a nation mired in violence and facing its biggest humanitarian crisis since the 2010 earthquake.
Millions of Haitians, however, simply don't have that luxury. They're trapped, no matter how bad things get.
Haiti: The basics
The Caribbean country shares a border with the Dominican Republic and has an estimated population of 11.5 million
It has a land area of 27,800 sq km, which is slightly smaller than Belgium and about the same size as the US state of Maryland
Chronic instability, dictatorships and natural disasters in recent decades have left Haiti the poorest nation in the Americas
An earthquake in 2010 killed more than 200,000 people and caused extensive damage to infrastructure and the economy
A UN peacekeeping force was put in place in 2004 to help stabilise the country and only withdrew in 2017
In July 2021, President Jovenel Moïse was assassinated by unidentified gunmen in Port-au-Prince. Amid political stalemate, the country continues to be wracked by unrest and gang violence
The situation is dire at the State University of Haiti Hospital, known as the general hospital, in downtown Port-au-Prince. There is no sign of any medical staff at all.
A dead body, covered by a sheet and swarming with flies, lies in a bed next to patients waiting in vain for treatment.
Despite the overpowering stench, no-one has come to remove the body. It is rapidly decomposing in the Caribbean heat.
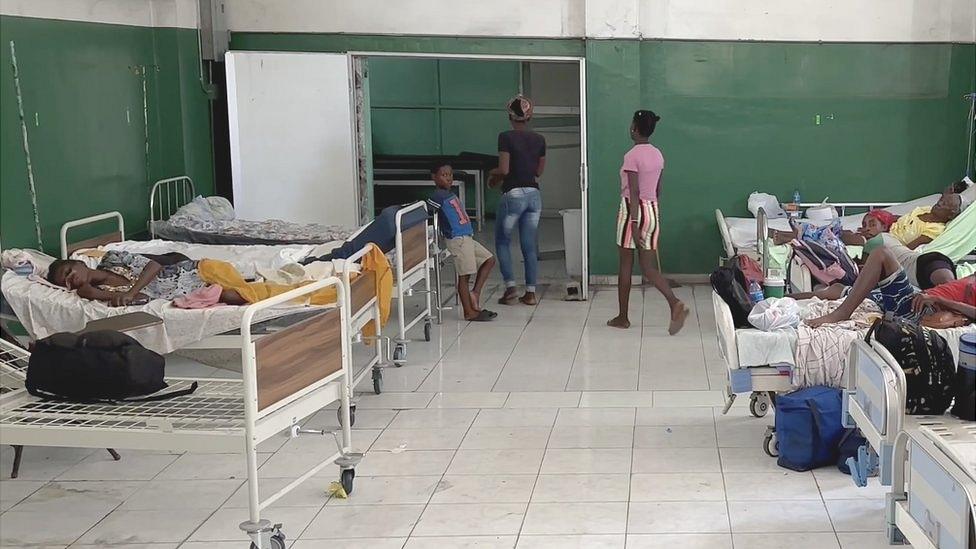

The situation at the general hospital in Port-au-Prince is particularly dire
"There are no doctors, they all fled last week," said Philippe a patient who didn't want to give his real name.
"We can't go outside. We hear the explosions and gunfire. So, we must have courage and stay here, we can't go anywhere."
With no prime minister and a government in disarray, the gangs' power over the capital is near absolute.
They control more than 80% of Port-au-Prince and the country's most notorious gang leader, Jimmy "Barbecue" Chérizier has again told the prime minister to resign.
"If Ariel Henry doesn't step down and the international community continues to support him," he said last week, "they will lead us directly to a civil war which will end in genocide."
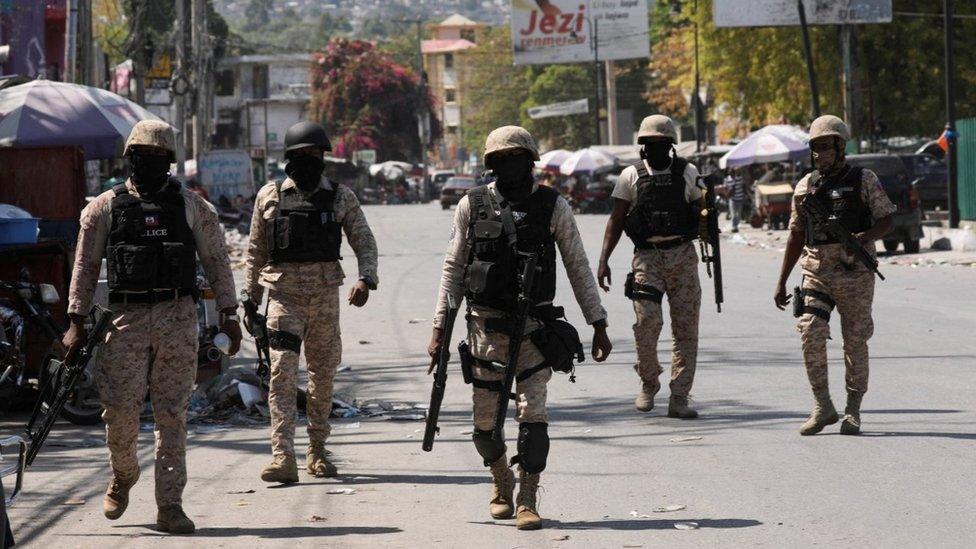
Meanwhile, the police, outnumbered and demoralised, are struggling to keep looters at bay. The Salomon police station in Port-au-Prince was attacked and burnt out, and charred police vehicles lie outside the still-smouldering building.
Nevertheless, even in the face of the total collapse of law and order, people must still venture out to make a living.
At a nearby market, several street hawkers told the BBC they had no other option but to leave their homes, even with gunmen roaming the streets.
"I have three kids, and I'm all they have - I'm their mother and their father," said Jocelyn, a market trader who also didn't want to give her real name.
"So, I'm obliged to take to the streets. Yesterday gunmen came here and stole all our money. A lot of vendors lost all their money. But there's no way to stay at home when you have three mouths to feed."
"The anxiety is killing me when I'm in the street," echoed an older woman selling fruit. "I keep thinking what if I get shot dead? Who will take care of my children then? I have no family to support me."
To the west, in one of Haiti's nearest neighbours, Jamaica, the dignitaries, diplomats and heads of state of the Caricom regional group are gathering for an emergency summit.
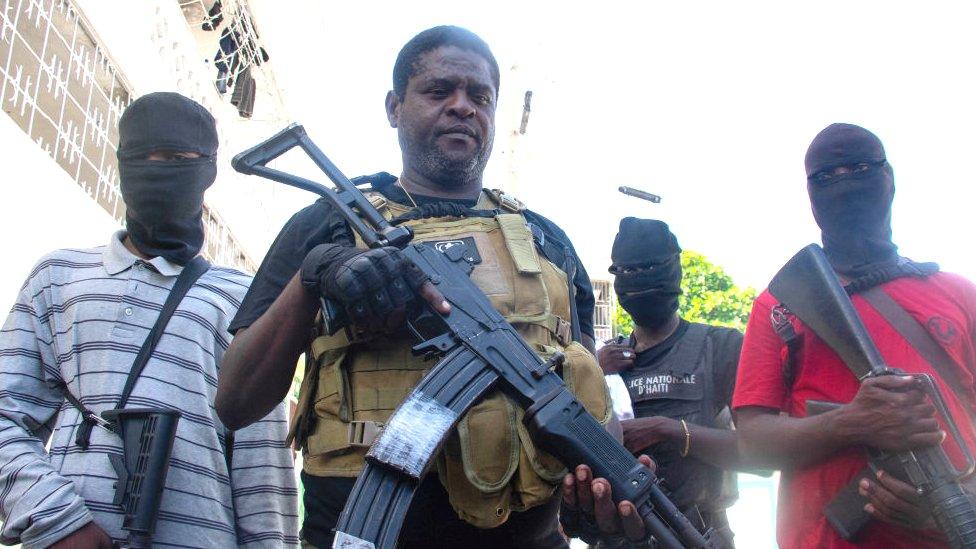

Armed gang leader Jimmy "Barbecue" Cherizier and his men are seen in Port-au-Prince, on March 5,2024
The instability in Haiti is a problem for the entire Caribbean community, and for Washington too. The idea of a nation of some 11 million people being run by gangs is of huge concern, particularly the potential impact on outward migration during an election year in the US.
It's clear Caricom favours seeing Mr Henry resign as soon as possible, from outside of the country if necessary.
The Biden administration in the US has publicly said the unelected prime minister - who had promised to hold an election in February - should return to Haiti, but only in order to stand down and begin a transition to a new government.
Privately, though, US diplomats are increasingly aware that it might now be impossible for him to return, and that even attempting to do so could further destabilise Haiti.
A UN-backed plan for a Kenyan-led rapid reaction force to tackle the gangs is still far from becoming a reality.
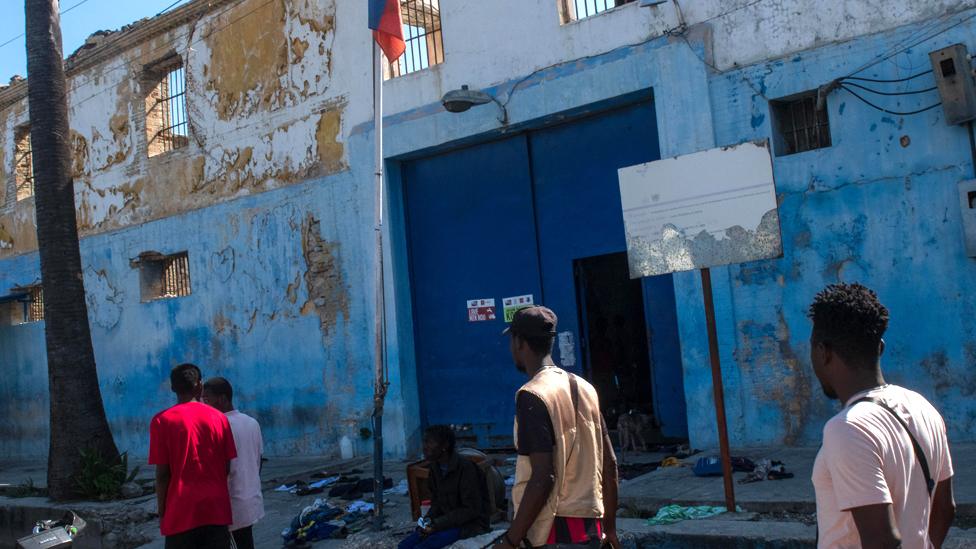
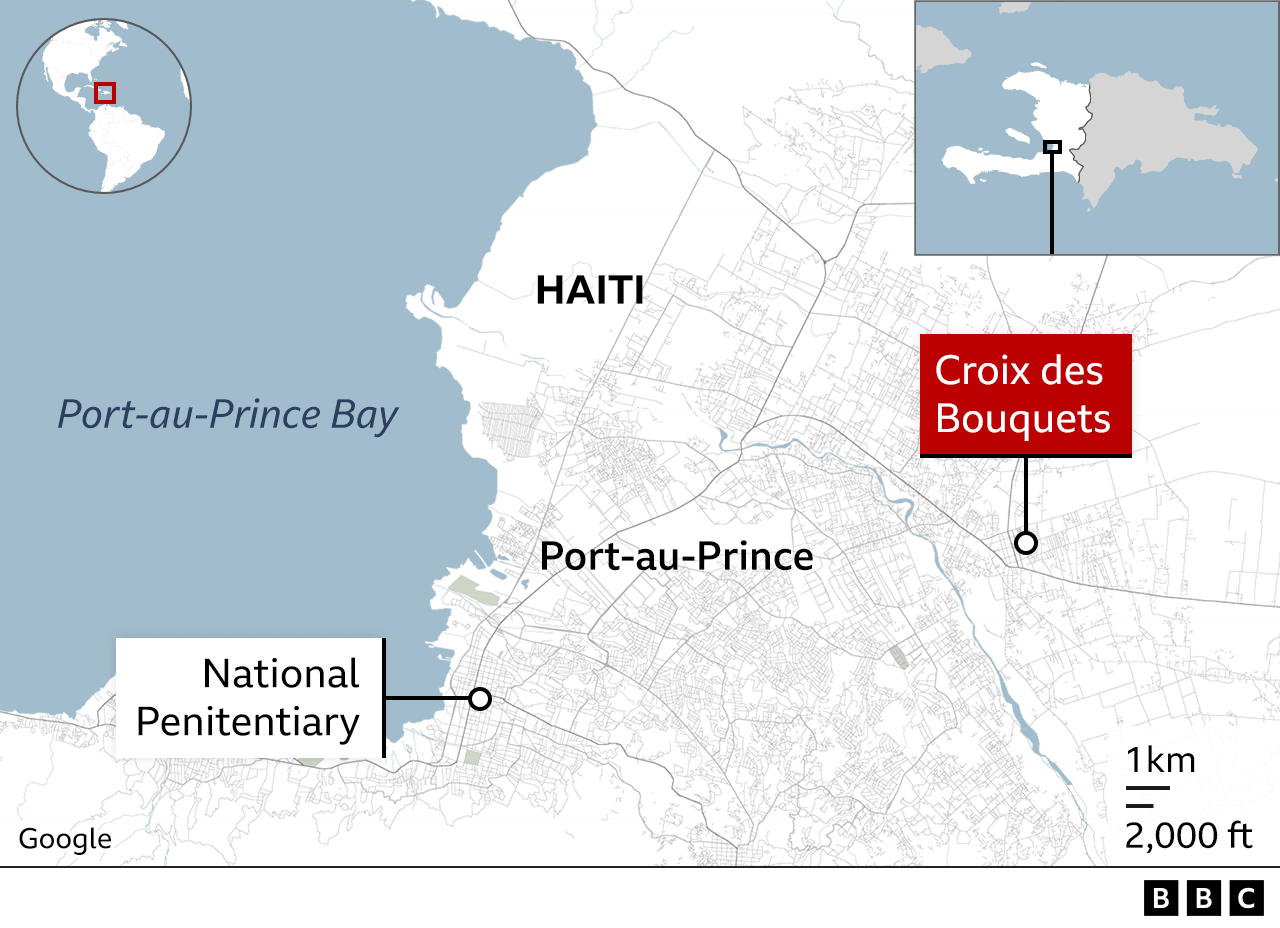
To add to the lawlessness, a week ago, around 4,000 inmates escaped after the gangs attacked the main prison in Port-au-Prince.
Those prisoners are now back on the streets and bolstering the ranks of their gangs.
In the aftermath, the cell doors are now wide open, the facility is virtually abandoned and there are blood stains on the ground after gunmen overpowered the guards.
A prime minister unable to return, violent gangs in control of the capital and dead bodies piling up on the streets: Haiti is currently a nation about as close to a failed state as it's possible to be.

Are you in the region? If it is safe to do so, email haveyoursay@bbc.co.uk, external.
Please include a contact number if you are willing to speak to a BBC journalist. You can also get in touch in the following ways:
WhatsApp: +44 7756 165803
Tweet: @BBC_HaveYourSay, external
Please read our terms & conditions and privacy policy
If you are reading this page and can't see the form you will need to visit the mobile version of the BBC website to submit your question or comment or you can email us at HaveYourSay@bbc.co.uk, external. Please include your name, age and location with any submission.
Related topics
- Published10 March 2024

- Published7 March 2024

- Published4 March 2024
