Syria country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 7 January 2025

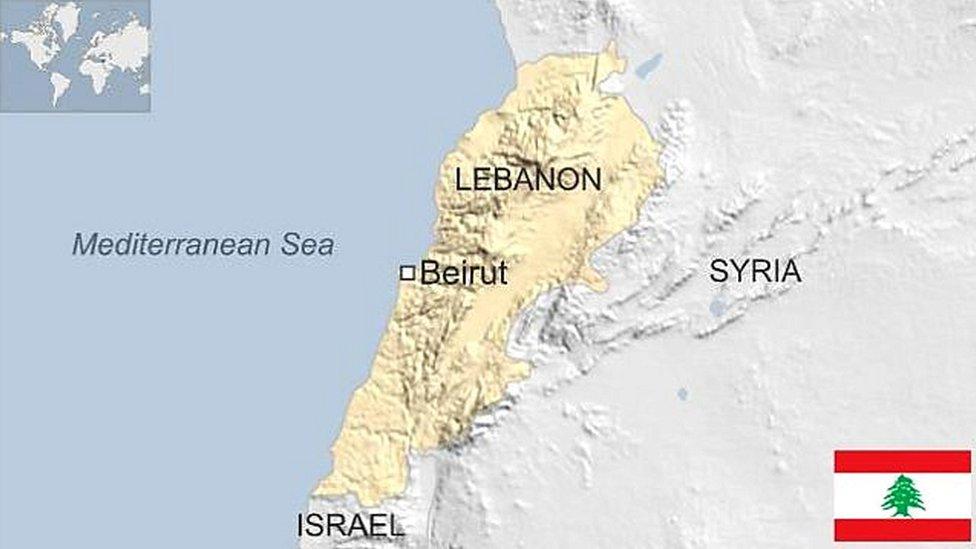
Syria covers an area that has seen invasions and occupations over the ages, from Romans and Mongols to Crusaders and Turks.
It is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including Kurds, Armenians, Assyrians, Christians, Druze, Alawites, and Shia and Sunni Arabs, the last of whom make up a majority of the Muslim population.
Modern Syria gained its independence from France in 1946, after which it saw considerable political instability with multiple military coups and coup attempts between 1949 and 1971. Between 1958 and 1961 it briefly joined with Egypt to form the United Arab Republic. Significantly, the 1963 coup saw the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party establish a one-party state.
General Hafez al-Assad seized power in 1970, setting up a repressive political system. After his death in 2000, his son Bashar al-Assad inherited the presidency.
Following the 2011 Arab Spring, Syria saw a multi-sided civil war, with involvement of different countries. More than six million Syrians fled the country.
After the defeat of Islamic State, the frontlines stabilised with the country effectively divided into cantons. In late 2024, a coalition led by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) swiftly captured several major cities, including Damascus, and toppled Assad's regime.
See more country profiles, external - Profiles compiled by BBC Monitoring, external
SYRIAN ARAB REPUBLIC: FACTS
Capital: Damascus
Area: 185,180 sq km
Population: 22.1 million
Language: Arabic
Life expectancy: 68 years (men) 75 years (women)
LEADER
Hayat Tahrir al-Sham leader: Ahmed al-Sharaa (nom de guerre: Abu Mohammed al-Jolani)
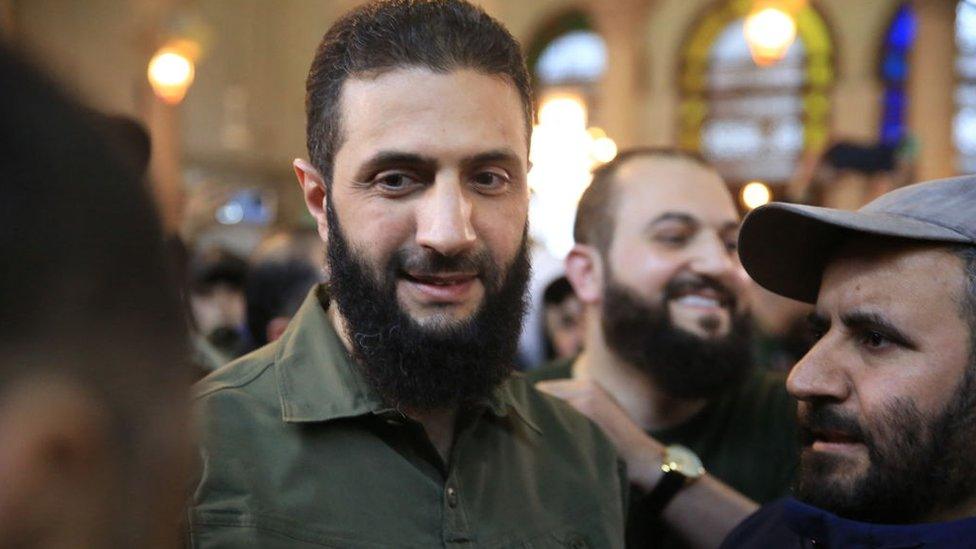

Shortly before his forces captured Damascus, Abu Mohammed al-Jolani dropped that nom de guerre associated with his jihadist past, and started using his real name, Ahmed al-Sharaa, in official communiques.
The move is part of Jolani's effort to bolster his legitimacy in a new context, now that his Islamist militant group, Hayat Tahrir al-Sham, leading other factions, has captured the Syrian capital, Damascus, solidifying its control over much of the country.
Jolani's transformation is not recent, but has been carefully cultivated over the years, evident not only in his public statements and interviews with international outlets but also in his evolving appearance.
Once clad in traditional jihadist militant attire, he has adopted a more Western-style wardrobe in recent. During the rebel offensive, he donned military fatigues, symbolising his role as military commander.
MEDIA

Syria has three distinct media environments - pro-government, opposition and Kurdish - reflecting its territorial divisions after more than a decade of war.
It as yet unclear how the media landscape will change with the fall of the Assad regime.
Journalists have faced clear red lines on reporting, and media workers have been targeted by all parties to the conflict.
Read full media profile
TIMELINE
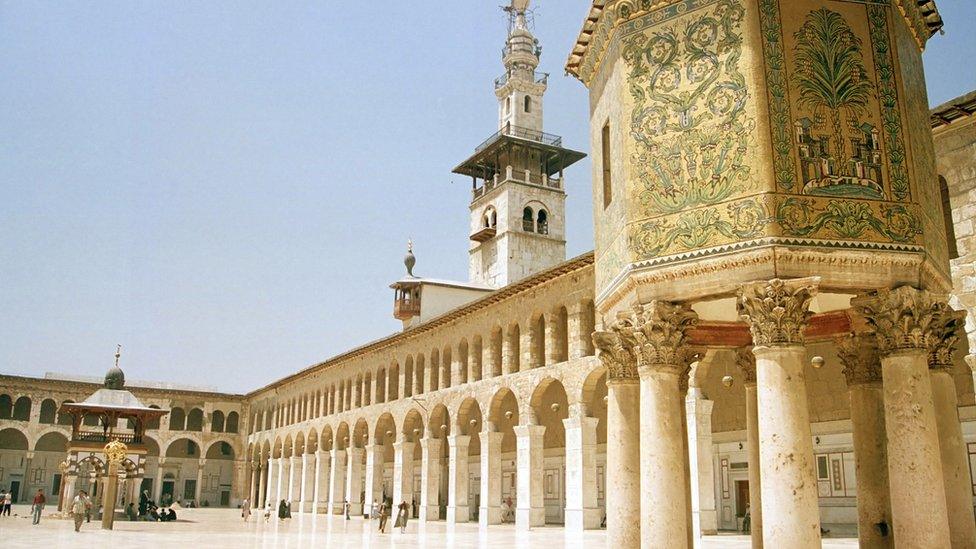

Following the Arab conquest of Syria in the 7th Century, the Umayyad caliphs made Damascus the capital of their empire
Some key dates in Syria's history:
3500-2300BC - Kingdom of Ebla, the earliest recorded indigenous civilization in the region.
c. 2300BC - Part of the Akkadian Empire under Sargon the Great and his grandson Naram-Sin.
1800-1200BC - Rise of the coastal kingdom of Ugarit.
During the Bronze Age, Syria becomes a battleground between the competing empires of the Hittites, Egyptians, Assyrians, Mitanni and Babylonia.
1274BC - Battle of Kadesh between the Egyptians under Ramesses II and the Hittites under Muwatalli II - the best-documented battle of the ancient Near East including records of the world's first surviving peace treaty.
c. 1200BC - Canaanites come to dominate the area after the Bronze Age collapse of civilisations in the Eastern Mediterranean.
911-605BC - Area part of the Neo-Assyrian Empire.
605-539BC - Becomes part of the Neo-Babylonian Empire under Nebuchadnezzar the Great.
539-330BC - Becomes part of the Persian Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great and his successors.
330BC - Greeks under Alexander the Great conquer the area, on his death it subsequently becomes part of the succeeding Seleucid Empire.
63BC - Roman general Pompey the Great annexes Syria - which becomes a Roman province.
5th Century AD - Syria becomes part surviving eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire following the fall of the western half of the empire.
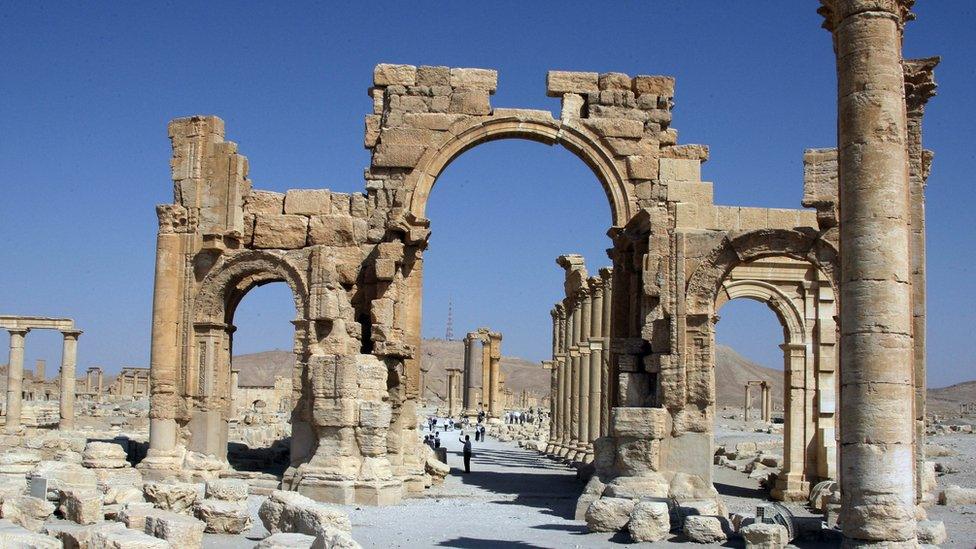

Under Queen Zenobia, the rich trading city of Palmyra became a key regional player in the 3rd Century AD
636 - Arab armies defeat Byzantine forces at the Battle of Yarmuk and conquer Syria.
c. 650 - Umayyad dynasty make Damascus the capital of their empire.
750 - Abbasids overthrow the Umayyads and move their capital to Baghdad.
887-1100s - Egypt-based rulers annex Syria, and are later replaced by the Aleppo-based Hamdanids.
1098-1189 - Areas of Syria held by various Crusader states, primarily the Principality of Antioch.
1175-1185 - Syria largely conquered by the Kurdish leader Salah ad-Din, founder of the Ayyubid dynasty.
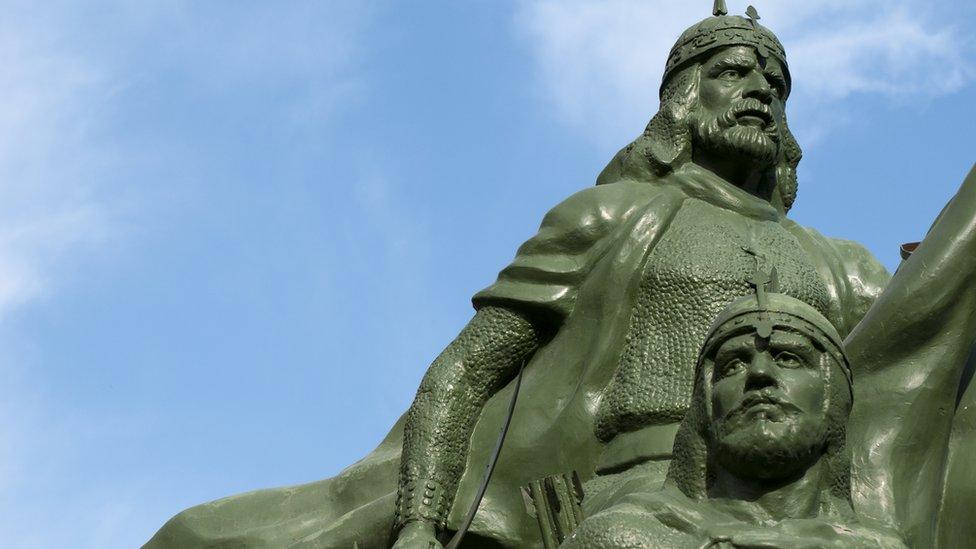

A statue of Saladin, or Salah ad-Din, outside the old city in Damascus
1260 - Mongol invasion; Mongols defeated by Egyptian Mamluk forces at the Battle of Ain Jalut.
1400 - Turco-Mongol leader Tamurlane sacks Aleppo and Damascus.
1516 - Ottomans invade the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt, conquering Syria, and incorporating it into their empire.
1914-1918 - Ottoman Empire fights on the side of Germany and Austria-Hungary. It ultimately suffers defeat and loss of control of the entire Near East to the British and French.
1918 - Arab and British forces capture Damascus, ending 400 years of Ottoman rule.
1920 - San Remo conference splits up newly-created Arab kingdom by placing Syria-Lebanon under a French mandate, and Palestine under British control.
1925-27 - Great Syrian revolt; led by Sultan al-Atrash against French rule.
1940 - Fall of France in World War Two sees Syria under the control of Vichy France until British and Free French forces invade in the 1941 Syria-Lebanon campaign.
1946 - France evacuates its troops and Syria becomes independent. Syrian politics are characterised by instability and periodic coups from independence until the late 1960s.
1958-61 - Egypt and Syria form the short-lived United Arab Republic
1967 - Egypt, Jordan, and Syria are defeated in the Six-Day War with Israel. Israel seizes the Golan Heights.

Hafez al-Assad ruled Syria repressively for 30 years until his death in 2000
1970 - Hafez al-Assad comes to power in a coup. His rule is characterised by repression and a major arms build-up.
1973 - Syria and Egypt initiate the Yom Kippur War against Israel. The Israeli army reverses initial Syrian gains and pushes deeper into Syria.
1976 - Syria intervenes in the Lebanese civil war. It maintains military presence there for next three decades, and exerts significant influence on Lebanese politics.
1982 - Muslim Brotherhood uprising in Hama is suppressed in a month-long siege by the military, who kill an estimated 10-40,000 civilians.
2000 - Hafez al-Assad dies and is succeeded by his son, Bashar al-Assad.
2005 - Syrian forces withdraw from Lebanon under international pressure following assassination of Lebanese premier Rafiq al-Hariri.
2011 - Outbreak of the Syrian civil war. Inspired by the "Arab Spring" uprisings, confrontation between the government and opposition soon develops into a multi-sided fight involving Islamists and rebels that draws in world powers. Some 600,000 people are estimated to have died.
2024 - President Asad is toppled after a swift rebel offensive led by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) captures the capital Damascus.
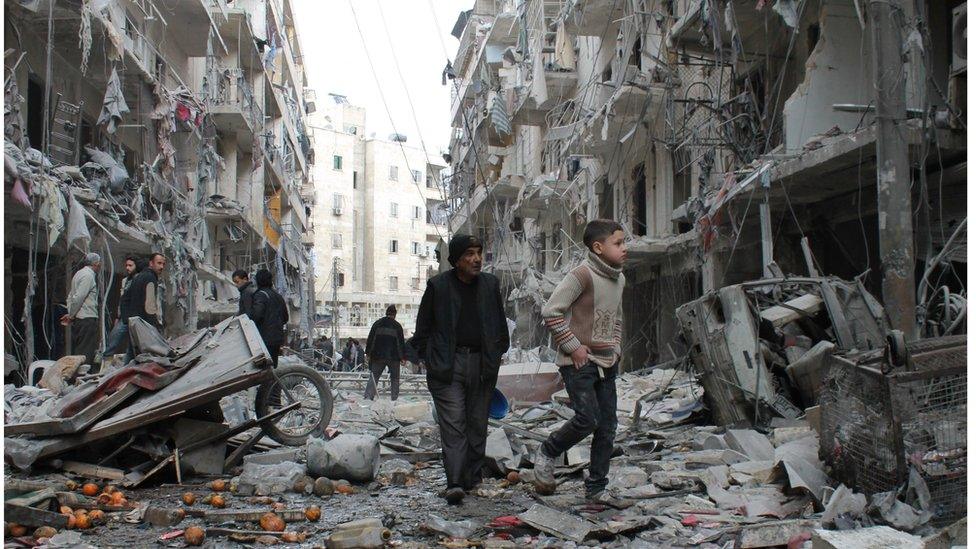

Shell-damaged buildings in Aleppo: Many areas have seen huge destruction in the country's civil war
Related topics
- Published7 April 2023
- Published22 August 2023

- Published13 September 2023
- Published19 April 2023
- Published13 October 2023
- Published29 August 2023
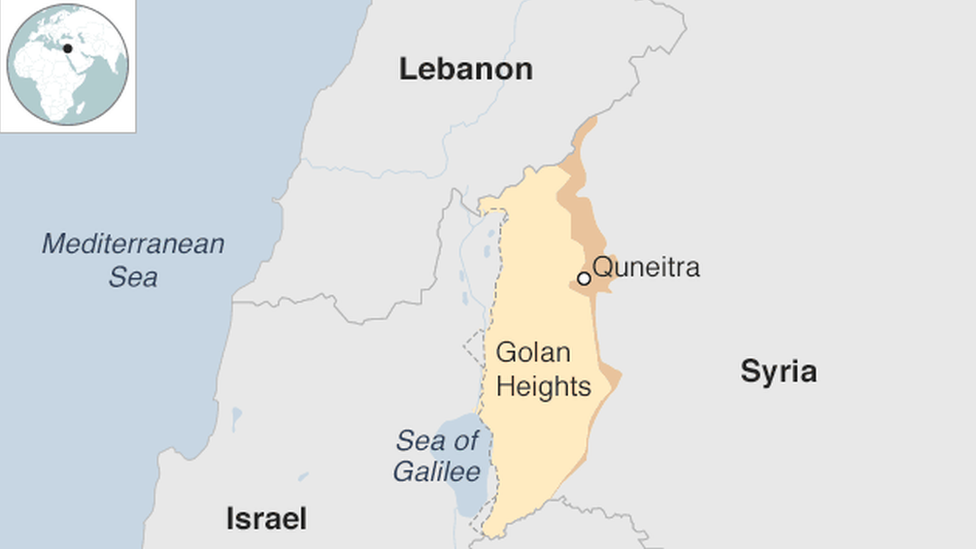
- Published10 January