Syria conflict: UN welcomes Russia-Turkey truce efforts
- Published

Children in the rebel-held Damascus suburb of Jobar released balloons during the truce
The UN Security Council has voted to back efforts by Russia and Turkey to end fighting in Syria and plans for fresh peace talks next month.
The resolution, drafted by Russia, also calls for rapid access for humanitarian aid to be delivered across the country.
Turkey and Russia led a ceasefire deal that has mostly held since Thursday.
The resolution helps pave the way for talks in Kazakhstan between the Syrian government and opposition, which have the backing of Russia, Iran and Turkey.
Earlier Syria's main rebel alliance threatened to abandon the truce by 18:00 GMT if the government continued to attack areas under its control.
The Free Syrian Army (FSA) issued the ultimatum to Russia - Syria's key ally - amid reports of intense bombardment by government forces on the rebel-held Wadi Barada area of Damascus.
But shelling on the area concerned ceased just minutes before the deadline, the group's legal adviser, Osama Abu Zeid, said.
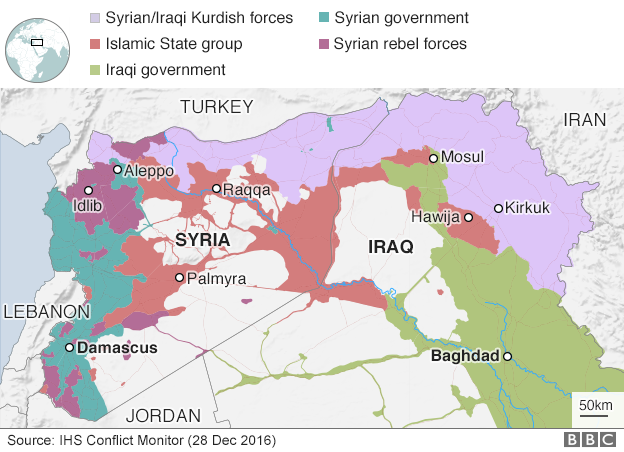
The new ceasefire deal applies across Syria but excludes the jihadists of so-called Islamic State (IS) and Jabhat Fateh al-Sham (JFS), and the Kurdish YPG militia.
Questions over resolution text
A final text of the UN resolution dropped the word "endorsed", stating, instead, that the Security Council "welcomes and supports" efforts by Russia and Turkey to end the crisis in Syria.
It said it had taken note of the documents issued by the two countries, but the French Ambassador to the UN later said the council had not seen any documents signed by the rebel groups and the Syrian government.

"In these conditions, the level of commitment of the parties to this truce remains somewhat uncertain and its implementation rather fragile," Alexis Lamek said.
Some of the rebel signatories have alleged that they were made to sign a version that may differ from that of the Syrian government.
Who backs who at the UN?
The resolution comes against a backdrop of deadlock among the veto-wielding members of the council, with Russia supporting Syrian President Bashar al-Assad and the US, UK and France insisting he must step down as part of any deal to end the war.

Russia drafted the new UN Security Council resolution
Russia and Turkey also back opposite sides in the conflict, with Turkey supporting the rebellion against Mr Assad.
Russia's Ambassador to the UN, Vitaly Churkin, appealed to council members to give the latest ceasefire efforts a chance, saying: "Don't just keep repeating outdated cliches."
"Let us work very seriously on this and ensure that in 2017 we achieve a political settlement of the Syria crisis," he added.
Why is Wadi Barada so important?
On Thursday, the UN expressed concern, external about the fighting in the town, saying fighters were deliberately targeting and damaging springs used to supply some four million people in the Damascus area with drinking water.
Wadi Barada is held by opposition forces, including JFS, which was known as al-Nusra Front until it formally broke ties with al-Qaeda in July.
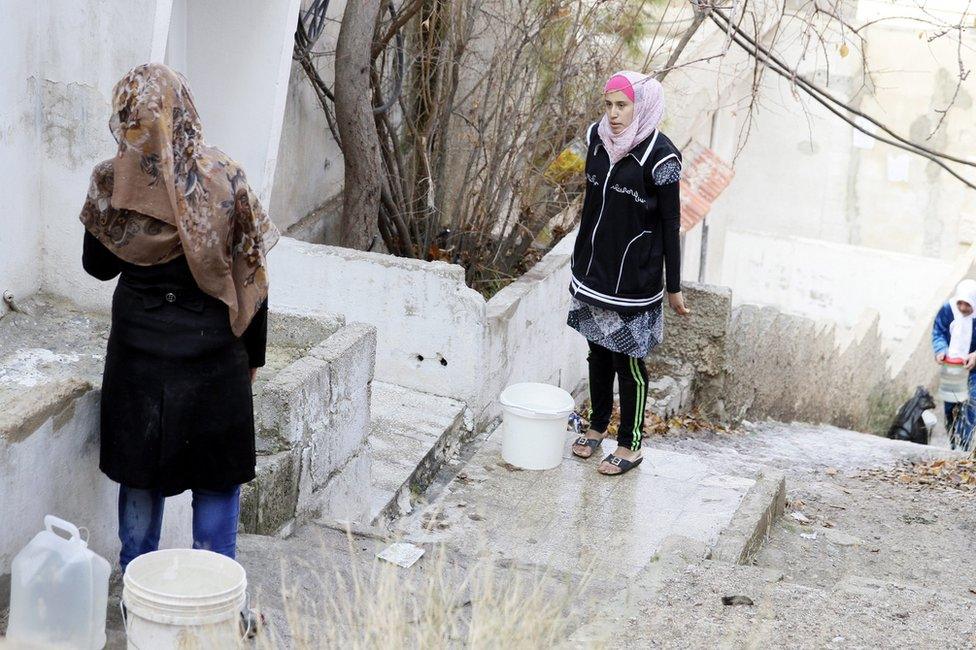

Damascus residents have reportedly been suffering a water shortage
On Saturday, the FSA accused the government and Iranian militias of "brazen violations" in the town and planning a "massacre" which would "lead to an immediate end" of the truce.
"We call on Russia which signed the agreement as a guarantor for the regime and its allies to bear its responsibility," the rebels said.
The FSA added that it was "fully committed to the ceasefire in accordance with a comprehensive truce which does not exclude any area or faction present in opposition areas".

Who is included in the truce agreement?
On the one side, Syrian government forces, allied militias and the Russian military.
On the other, the FSA plus several other groups.

Rebel fighters in al-Rai, in northern Aleppo province
The Russian defence ministry named, external seven "moderate opposition formations" included in the truce as Faylaq al-Sham, Ahrar al-Sham, Jaysh al-Islam, Thuwwar Ahl al-Sham, Jaysh al-Mujahidin, Jaysh Idlib and Jabhah al-Shamiya.
Ahrar al-Sham, which said it had "reservations" about the deal, and Jaysh al-Islam are Islamist groups that Russia has previously described as terrorist organisations.

Who is not included?
IS and JFS and the groups affiliated to them", are not part of the agreement, according to the Syrian army.
JFS said on Friday it would continue to fight President Assad, with a spokesman saying the political solution under the truce would "reproduce the criminal regime".
Members of the group are currently operating as part of a rebel alliance that controls Idlib province.

What will happen to Kurdish YPG fighters?
The FSA also said the deal did not include the Kurdish Popular Protection Units (YPG).
The militia, which has captured large swathes of north-eastern Syria from IS with US support, is designated a terrorist organisation by Turkey.
The truce is nominally nationwide, although that really only covers the areas where the sides who have signed up have a presence - western Syria.