Canada country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 8 January 2025
The world's second-largest country by surface but relatively small in terms of population, Canada punches above its weight in economic terms.
A federation of former British colonies, Canada follows the British pattern of parliamentary democracy. Ties with the US are now vital, especially in terms of trade, but Canada often goes its own way.
Both English and French enjoy official status, and mainly French-speaking Quebec - where pressure for full sovereignty has abated in recent years - has wide-ranging cultural autonomy. Indigenous peoples make up around 4% of the population.
Canada is one of world's top trading nations - and one of its richest. Alongside a dominant service sector, Canada also has vast oil reserves and is a major exporter of energy, food and minerals.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
CANADA: FACTS
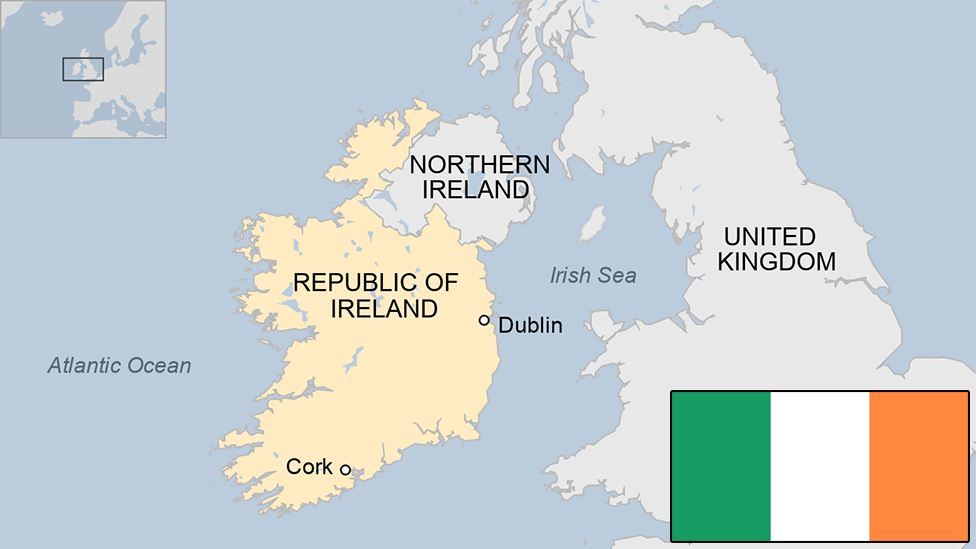
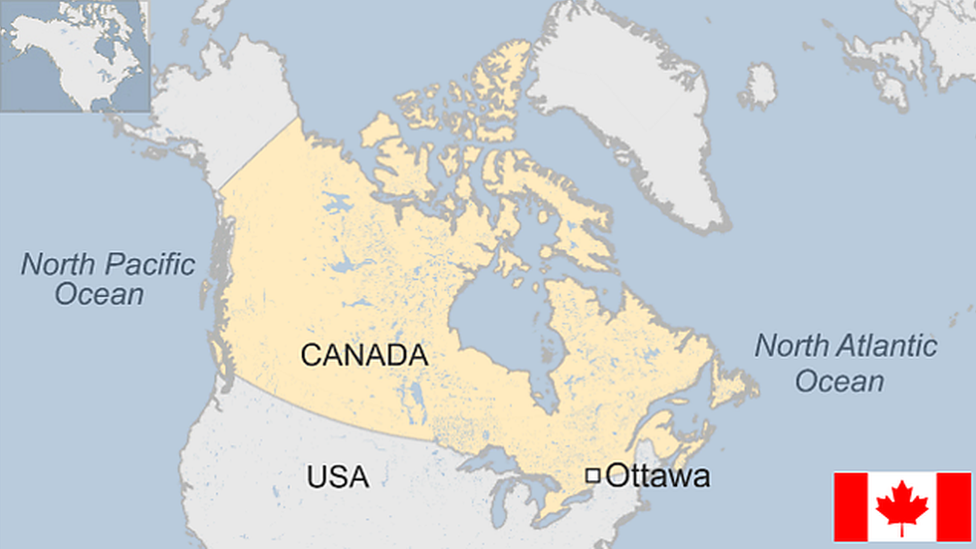
Capital: Ottawa
Area: 9,984,670 sq km
Population: 41.2 million
Languages: English, French
Life expectancy: 79 years (men) 83 years (women)
LEADERS
Head of state: King Charles III, represented by a governor general
Prime minister: Justin Trudeau (resigned)

In January 2025, under growing pressure from his own party, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced he would step down and end his nine-year stretch as leader.
Trudeau said he would stay on in office until his Liberal Party chose a new leader.
Trudeau's personal unpopularity with Canadians had become an increasing drag on his party's fortunes in advance of federal elections later in 2025.
Trudeau faced growing calls to quit after deputy prime minister and long-time ally Chrystia Freeland resigned in December 2024, citing Trudeau's perceived failure to not take US President-elect Donald Trump's threats of tariffs on imported Canadian goods seriously.
Trump has promised to impose a tax of 25% on imported Canadian goods - which economists have warned would significantly hurt Canada's economy.
MEDIA
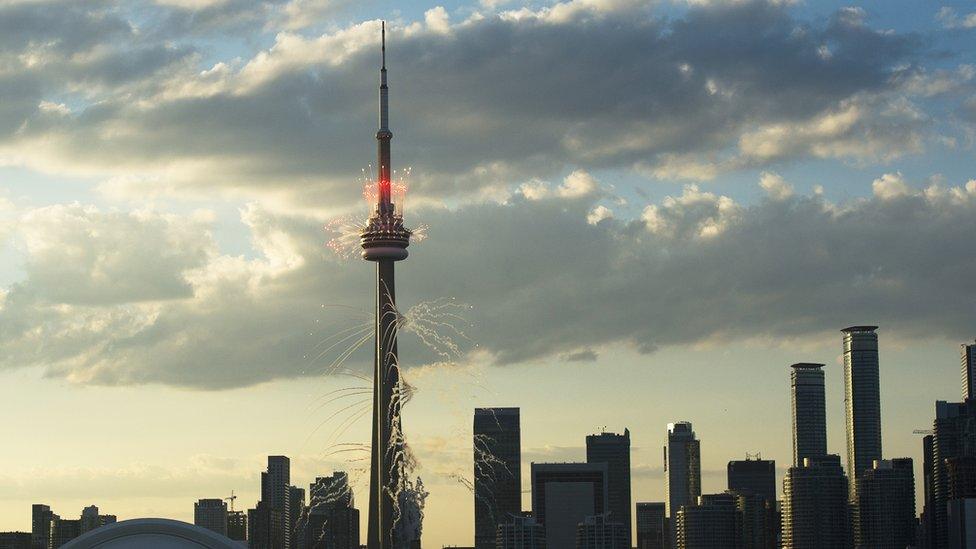

Toronto's CN Tower - used for TV and radio broadcasts - is an internationally renowned Canadian landmark
Canada has a long history of public broadcasting and a lively commercial media sector. The public Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) runs national radio and TV networks in French and English, as well as services for indigenous people in the north.
The Canadian media are free to present a wide range of views and opinions. Quotas exist for broadcasts of Canadian material.
TIMELINE

After lengthy debate, Ottawa was chosen as Canada's capital by Queen Victoria in 1857
Key dates in the history of Canada:
15,000-20,000 before present - North America's first humans migrate from Asia.
500BC onwards - First Nations people settle and establish trade routes across what is now Canada.
11th Century - Norse explorers reach North America, establishing the first known European settlement in the Americas on Newfoundland.
1497 - Italian-born navigator John Cabot reaches the coasts of Newfoundland and Cape Breton.
Late-15th Century - First Nations population is estimated to be between 200,000 and two million. This falls by 40-80% after European colonization, due to repeated outbreaks of European infectious diseases, conflicts, loss of land and a subsequent loss of self-sufficiency.
1534 - Jacques Cartier explores the St Lawrence river and claims the Gulf of St Lawrence for France.
1583 - Newfoundland becomes England's first overseas colony.
1600s - Fur trade rivalry between the French, English and Dutch; the Europeans exploit existing rivalries between local peoples to form alliances.
1627 - Company of New France established to govern and exploit "New France" - France's North American colonies.
1670 - Hudson's Bay Company established by London traders. The company holds trading rights for regions whose rivers drain into Hudson Bay.
1756-63 - Seven Years' War between New France and the larger and economically-stronger British colonies. After early French successes, Quebec falls in 1759 and the British advance on Montreal.
1763 - Under the Treaty of Paris, Britain acquires all French colonies east of the Mississippi including New France, which becomes the colony of Quebec.
1774 - The Quebec Act recognises the French language and Roman Catholicism in the colony.
1776 onwards - Loyalist refugees from the American War of Independence settle in Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec and Ontario.
1800s - Increased European immigration.
1812-14 - War of 1812 between the US and Britain, largely over the effects on the US of British blockades of French ports. Naval battles on the Great Lakes and a US attack on York, now Toronto. But the US fails to realise its plans to invade Canada.
1837-38 - Armed rebellions in Upper and Lower Canada, caused by disaffection with the ruling elites, poverty and social divisions.
1867 - British North America Act unites Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick in the Dominion of Canada.
1867-1914 - Canadian West, the provinces of British Colombia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, becomes home to millions of immigrant settlers. Their resettlement in the region is underpinned by the displacement of indigenous peoples.
1885 - Canadian Pacific railroad is completed.
1896-99 - Klondike Gold Rush: Some 100,000 prospectors migrate to the Klondike region of Yukon, in north-western Canada.

The promise of gold lured tens of thousands to the Yukon in northwest Canada
1914-18 - World War One: Canadian forces play a key role in the fighting in France, particularly in the Battle of Vimy Ridge in 1917.
1931 - Statute of Westminster limits the legislative authority of the British parliament over Canada, though the British parliament retains the power to amend the constitution at the request of Canada. This remains in effect until the Constitution Act, 1982, which transfers it to Canada.
1939-45 - World War Two: Canadian forces are active in Italy, Europe, the Atlantic and elsewhere. Canadian troops play important roles in many key battles including the 1942 Dieppe Raid, 1943 Allied invasion of Italy, the Normandy landings and Battle of Normandy, and Battle of the Scheldt in 1944.
1947 - Canada is declared to be of equal status with Great Britain within the Commonwealth.
1949 - Canada becomes a founder member of Nato. Newfoundland, until then a British dominion, becomes a province of Canada.
1950-53 - Korean War: Canadian forces participate in the United Nations war effort.
1963 - Front de Liberation du Quebec (FLQ), a militant Quebec separatist group established. It carries out a sustained bombing campaign between 1963-70 in its bid to create an independent, socialist Quebec.
1965 - New Canadian flag is adopted, replacing one incorporating the British flag.
1967 - Expo 67 in Montreal provides impetus to Canadian national identity. French President Charles de Gaulle visits and causes diplomatic incident when he declares "Vive le Quebec libre" - Long live free Quebec.
1968 - Pierre Trudeau of the Liberal party wins elections and governs until 1984, with the exception of a nine months in 1979-80. Parti Quebecois (PQ) is formed to push for complete independence for Quebec.
1969 - FLQ militants bomb the Montreal Stock Exchange, injuring 27 people.
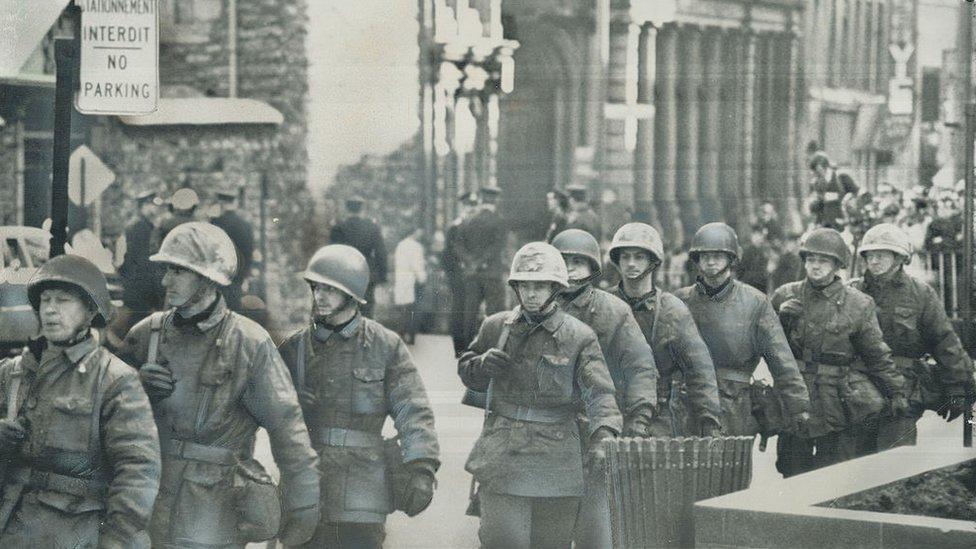

Montreal 1970: Canadian soldiers are sent in as part of the security crackdown against the FLQ militant separatist group
1970 - October Crisis: FLQ separatists kidnap British Trade Commissioner James Cross, external. Canadian armed forces are deployed across Quebec. Cross is freed but during talks, Quebec Labour Minister Pierre Laporte is kidnapped and murdered by the FLQ, leading to a drastic loss of support for the group.
1980 - A referendum on the separation of Quebec is defeated.
1982 - The UK transfers remaining final legal powers over Canada to Canada.
1991 - Canadian forces participate in the Gulf War following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait.
1992 - Canada, US and Mexico finalise the terms of the North American Free Trade Agreement (Nafta).
1995 - A referendum in Quebec narrowly rejects independence by a margin of only 1%.
1999 - Territory of Nunavut is created in northern Canada - the first Canadian territory to have a majority Inuit population.
2002 - Canada sends first contingent of regular troops to Afghanistan as part of the post-Taliban stabilising mission.
2003 - Canada opts not to join the US-led coalition against Iraq, sparking fierce domestic political debate.
2006 - Parliament agrees that the Quebecois should be considered a "nation" within Canada.
2010 - Canada hosts Winter Olympics.
Suspected ringleader of Islamic extremist group is jailed for life for plot to bomb Toronto stock exchange.
2014 - Canada launches a mission to map the Arctic seabed, to support its 1925 claim to the North Pole and its sector of the Arctic Ocean.
2016 - Canada signs a free trade agreement with EU.
2017 - French-Canadian student Alexandre Bissonnette is charged over the shooting of six Muslims at a Quebec mosque.
Government says it will pay compensation to thousands of indigenous people who were taken from their families as children to be brought up by primarily white middle-class families decades ago.
2018 - US, Canada and Mexico reach a new trade deal - the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) - to replace Nafta.
2021 - After decades of advocacy by First Nations people, the Canadian parliament passes the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act.
2023 - Canada sees its worst wildfire season on record, with thousands evacuated from threatened towns and about 15m hectares (37m acres) of land burnt.

Founded by the French in 1608, Quebec City is one of North America's oldest European settlements
Related topics
- Published21 January
- Published25 March 2024
- Published11 September 2023
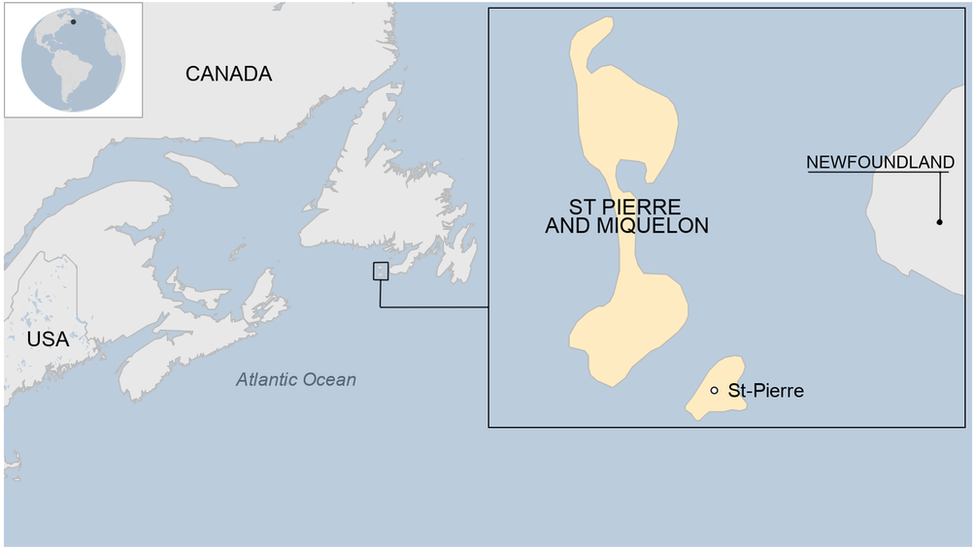
- Published10 January
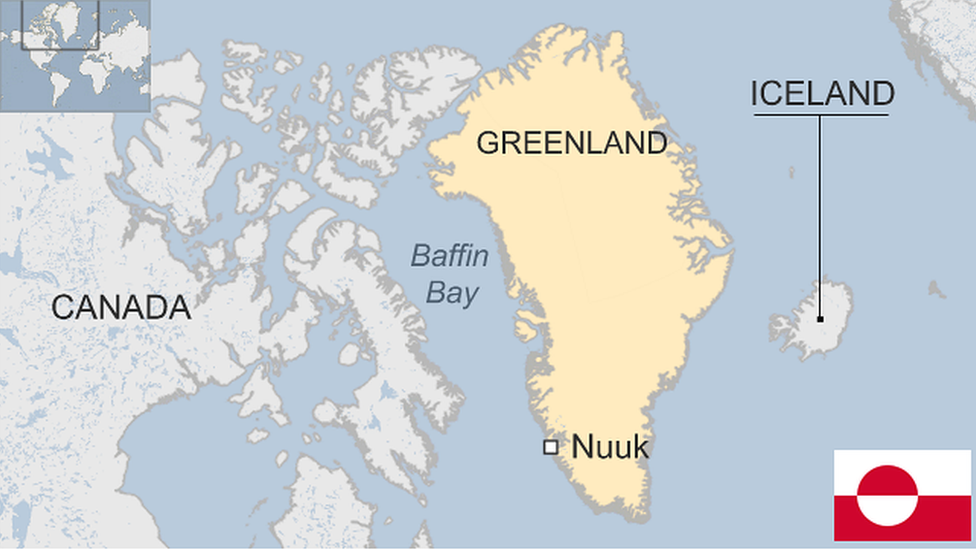
- Published25 October 2024
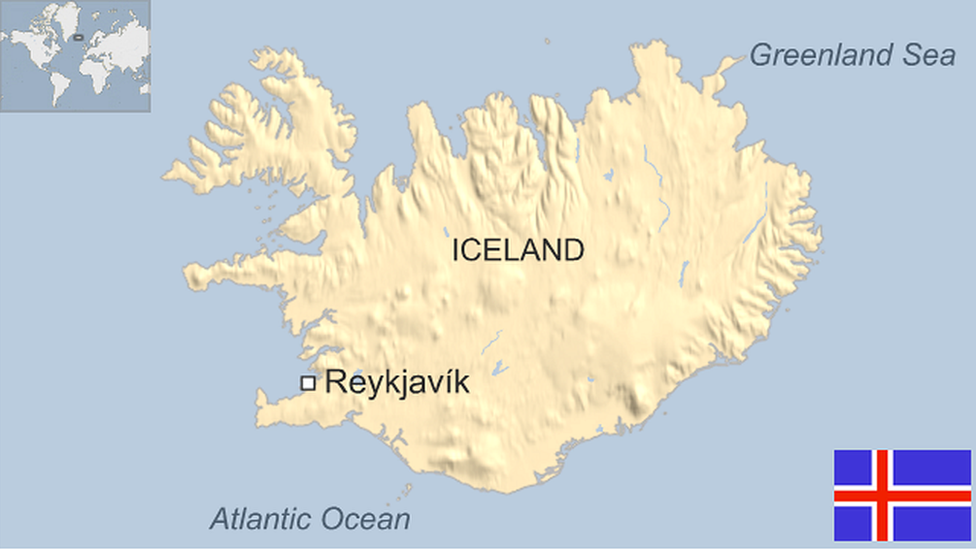
- Published7 February