US health experts confirm that Zika causes birth defects
- Published
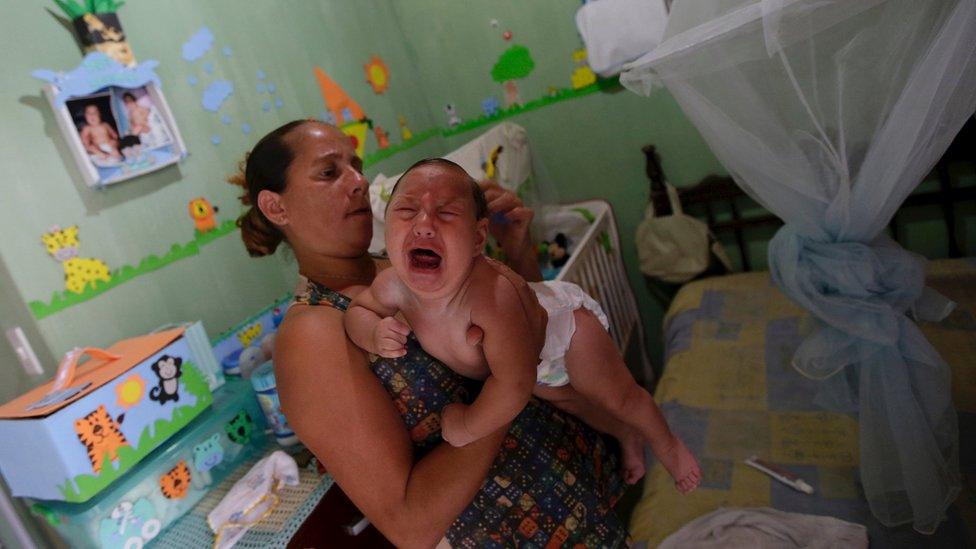

Brazil has seen a growing number of cases of microcephaly in recent months
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has confirmed that the Zika virus causes severe birth defects, including microcephaly.
Hundreds of babies were born in Brazil last year with microcephaly, a syndrome where children are born with unusually small heads.
The defects coincided with a spike in Zika infections, leading experts to suspect the mosquito-borne virus.
Research has now affirmed those experts' suspicions, the CDC said.
"This study marks a turning point in the Zika outbreak. It is now clear that the virus causes microcephaly," said Dr Tom Frieden, the head of the CDC.

More on the Zika crisis:

Microcephaly: Why it is not the end of the world
What you need to know Key questions answered about the virus and its spread
Travel advice Countries affected and what you should do
The mosquito behind spread of virus What we know about the insect
Abortion dilemma Laws and practices in Catholic Latin America

On Monday, US health officials warned the Zika outbreak could have more of an effect on the United States and called for additional funding to combat the virus.
"Everything we know about this virus seems to be scarier than we initially thought," said Dr Anne Schuchat of the CDC.
Zika virus was first diagnosed in 1947 in Uganda, but symptoms have typically been mild, including rash, joint pain and fever.
The current outbreak started in 2015 in Brazil and the symptoms have been much more severe. Nearly 200 babies have died as result of the virus.
Researchers are interesting learning why some cases of the virus result in birth defects while others do not.
Some women who were infected with Zika while pregnant gave birth to apparently healthy children.
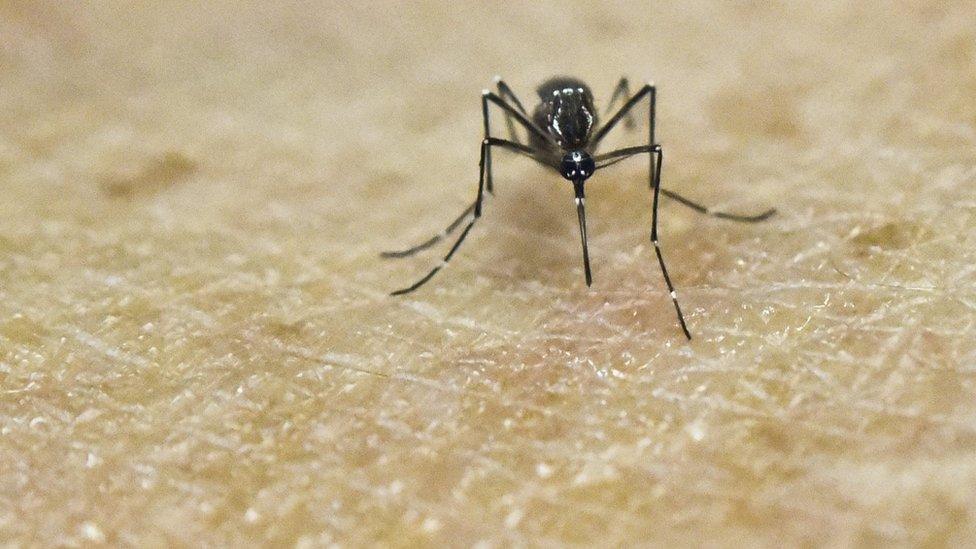

The Zika virus can be transmitted via mosquito
There have been 346 confirmed cases of Zika in the continental United States, according to the CDC, all associated with travel.
CDC officials said the findings do not change the agency's earlier guidance to pregnant women.
The CDC has discouraged pregnant women from travelling to places where the Zika virus is spreading, mostly in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Dr Frieden said intensive research was under way to find out much more about the mosquito-borne virus and to develop a vaccine for it, although he warned that that could still be years away.
This is the first time that mosquito bites have caused birth defects, Dr Frieden said. The virus can be transmitted by sexual contact as well.
- Published14 April 2016