The men who feel left out of US abortion debate
- Published

The fiercely-contested debate over US abortion focuses on the rights of the mother and foetus. But a lawsuit in Alabama by a man who says his girlfriend had an abortion against his wishes adds a third voice to the conversation, writes James Jeffrey.
After the rage has dissipated, after overcoming alcoholism as a coping mechanism, even after a new and beautiful family comes on the scene, a great sadness still persists - and likely always will.
That's the message from men talking about their experiences of abortion, a voice rarely heard among the passionate multitudes in the US abortion debate, though abortion rights supporters argue that this group is an outlier and does not speak for the majority of men involved in an abortion. Currently, the usual male perspectives that feature are legislators pushing to restrict abortion procedures, drawing the ire of pro-choice supporters accusing them of trying to legislate women's bodies. But now would-be fathers denied by abortion are speaking out.
An Alabama abortion clinic is being sued by a man after his girlfriend had an abortion at the six-week stage, against his will in 2017. The case is the first of its kind because the court recognised the foetus as the plaintiff and the father as the representative of his baby's estate. "I'm here for the men who actually want to have their baby," the man told a local news agency in February. "I just tried to plead with her and plead with her and just talk to her about it and see what I could do. But in the end, there was nothing I could do to change her mind."
Currently in the US, fathers have no legal rights to hinder the abortion of a pregnancy for which they are responsible. State laws requiring that a father be given a say in, or even notified of, an abortion have been struck down by the US Supreme Court.
"I was in my 30s living the good single life in Dallas," says 65-year-old Karl Locker. When a woman he was seeing told him she was pregnant, he says he felt "like one of those wolves with its leg caught in a trap".
Nevertheless, he decided he had to support her - and the pregnancy. "I tried everything, I offered to marry her, to take the baby myself, or to offer it up for adoption," Mr Locker says, explaining that he felt keeping the child would be the right thing to do. "She said she could never give her child up for adoption - it didn't make cognitive sense."

Other voices in abortion debate

In the end he drove the woman to the clinic and paid for the abortion. Afterwards he says he moved to California as he couldn't bear the knowledge of what he'd done.
"I didn't know how I was going to survive; I wasn't going to jump off a bridge, but I probably would have drank myself to death," says Mr Locker, who believes that reconnecting with his faith and starting a family with another woman saved him. "I've thought about what happened every day for the last 32 years."
Men are usually involved in an abortion in one of four ways, all of which can leave men traumatised when they come to reflect afterwards on their roles, say those running counselling groups for post-abortive men. Sometimes men coerce a woman into having an abortion against her will; others say they will support the woman's decision either way, while steering that decision towards abortion. Some men find out about the abortion for the first time after the fact, or the abortion goes ahead against their wishes.
What polling has occurred indicates a majority of women say they do not regret having an abortion, external, but fewer studies have been done on men's reactions. What data there is for men comes from post-abortive support groups, which is dependent on men seeking them out, making it difficult to make any broad statistical observations. But the accounts include commonalities such as feelings of anger, guilt, shame and deep sadness on anniversary dates.
"Men are meant to be protectors, so there is a sense of failure - failing to protect the mother and the unborn child, failing to be responsible," says 61-year-old Chuck Raymond, whose 18-year-old girlfriend had an abortion in the late '70s when he was a teenager. "There is incredible guilt and shame about having not done that."
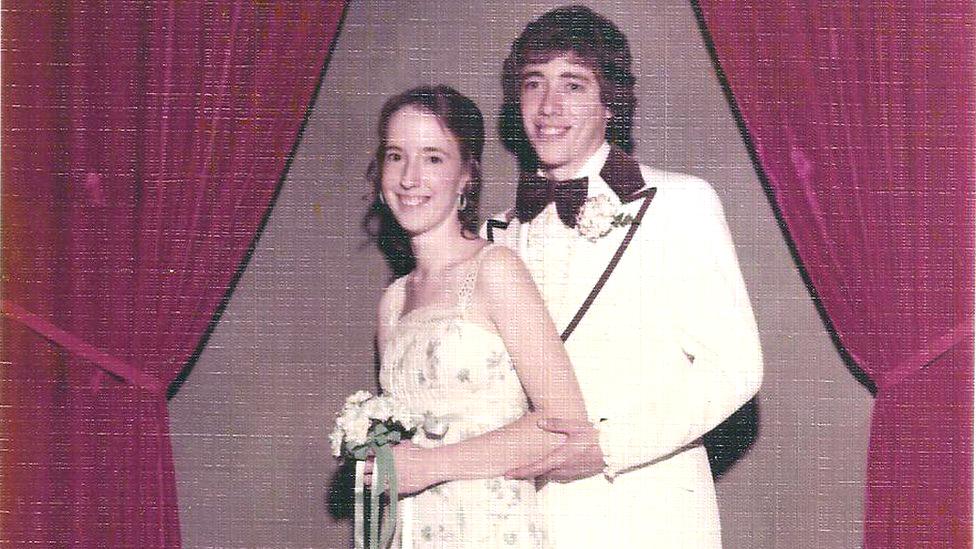

Chuck Raymond and his then-girlfriend Linda in 1976. They are still married
Mr Raymond says he thought a child would have interfered with educational plans and his military training at West Point military academy, where cadets are not allowed to be married or be raising children. "Once I was involved in training, I got caught up in everything and suppressed the event, keeping it out of my consciousness. Years later though, I realised that a tragedy had occurred, and we had made a tragic choice."
He likens the mental and emotional anguish that can follow an abortion to battlefield post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).

Abortion in US - how we got here
The abortion battle explained in three minutes

The Supreme Court's landmark Roe v Wade decision issued on 22 January, 1973, is the best-known case on abortion, for having legalised the procedure across the United States. But two later cases had more of an impact on men, says Allen Parker, president of The Justice Foundation, a conservative law centre in Texas.
After the 1976 Supreme Court decision in Planned Parenthood v Danforth, the father's consent to an abortion was no longer required. In its 1992 Planned Parenthood v Casey decision, the court went further, saying fathers are not entitled to be notified about an abortion.
"There's so many contradictions around all this - it's abortion first, and be damned if otherwise," says the Reverend Stephen Imbarrato, a Catholic priest and anti-abortion activist. Before entering the priesthood, Father Imbarrato got his girlfriend pregnant in 1975 and steered her toward having an abortion, finding out decades later she had been carrying twins. "Men regret lost fatherhood, as men are inherently called to be fathers."
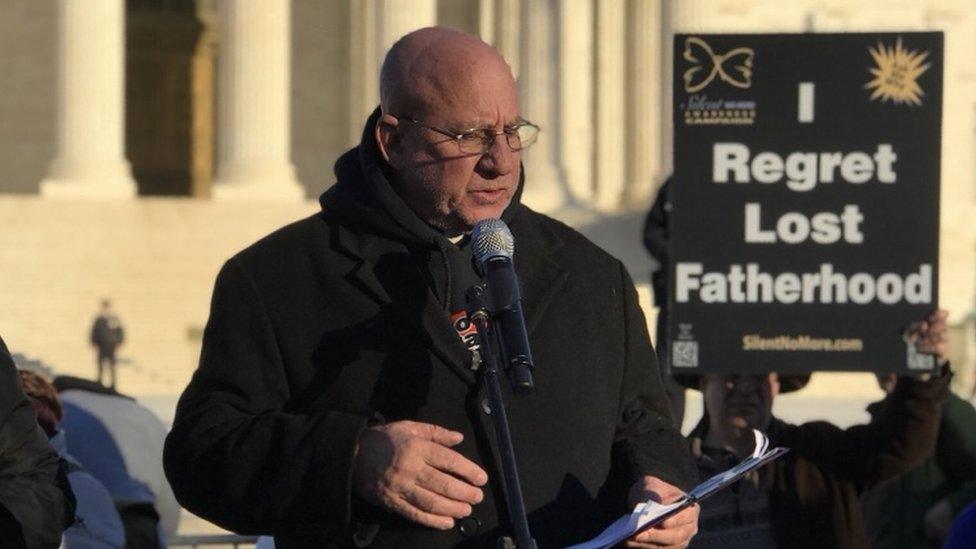

Father Stephen Imbarrato campaigning outside the Supreme Court
But others argue that the number of men traumatised by abortions are outliers.
Gillian Frank, a historian of sexuality at the University of Virginia, says that the 1992 Planned Parenthood v Casey decision found that "in most contexts, where there was a stable and loving relationship, men and women made the decision together". "And when men are absent from the decisions, it is often because there is a risk of violence or coercion in the relationship. These decisions [by the courts] rested on the fact it is not a child, so the situation is not analogous to child custody."
There is disagreement on the ratio of women who have abortions without telling men, or in spite of them, or because of them. According to the Guttmacher Institute, a research and policy organisation that analyses abortion in the US, half of women getting abortions in 2014 said they did not want to be a single parent or were having problems with their husband or partner.
"It has been recognised time and again that when people say they are arguing for men's voices to be heard it is actually more about being able to control women and to regulate their decisions," Mr Frank says. "And I don't see it as men have been absent, quite the opposite, men have always been vocal about women's ability to control their reproductive destiny."
Before Roe v Wade, he notes, this took the form of women having to go in front of a panel of usually male doctors to plead their cases for an abortion, and it continues today with "the men controlling pharmaceuticals and the men behind desks making decisions".
Voices from the abortion frontline
"Outside our clinics, it's typically men who are leading the protests and clambering on to cars to yell over the fence with bullhorns," says Sarah Wheat who works for Planned Parenthood in Austin, the Texas state capital and a major battleground over Texas legislation on abortion. Planned Parenthood is an organisation that provides sexual health care services, of which about 6% involves abortion, Ms Wheat says.
"It's usually loud and intimidating, designed to shame, stigmatise and intimidate. And when we go to the Capitol it feels very similar with the legislators. From our perspective, it feels men are still overrepresented."
Indeed, much of the pushback against men's involvement in abortion is steeped in the historical context of a patriarchy telling women what to do.
"There is a disconnect," Mr Locker says. "Men have a responsibility - as they should do - hence their wages get docked with child support if a baby is born, but at the same time they get no rights on an abortion going ahead."
"People don't see it, they keep men out of it," says Theo Purington, 34, whose pregnant girlfriend got an abortion in 2006 against his wishes, leaving him "depressed and a mess". The experience led to him becoming involved in pro-life advocacy and counselling post-abortive men enduring similar struggles.
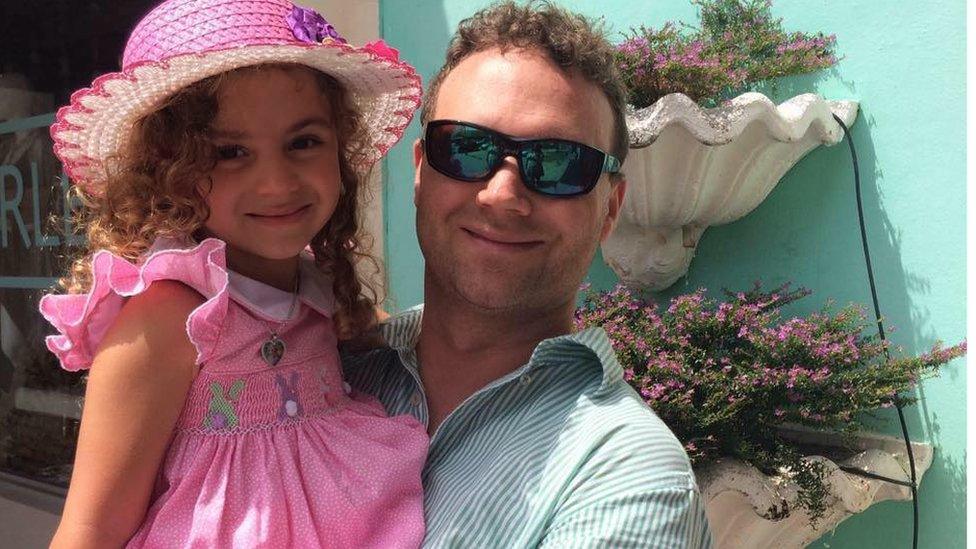

Theo Purington and his seven-year-old daughter Sienna
"If men had to sign off on an abortion, I think you would see a 50% drop, and that's why the [abortion providers] don't want men involved," says Mr Purington.
"The greatest injustice in this country today is that a man cannot protect his unborn child from abortion [in the same way as] men protecting our children is part of our responsibility."
Amy Hagstrom Miller, who runs Whole Woman's Health, a company that manages seven clinics that provide abortion in five states in the US, says: "Yes, men are clearly involved at the beginning, in terms of getting the woman pregnant."
But she adds: "When it comes to her body, then there is a line that is drawn. It is the woman's pregnancy, she is carrying it in her body, and you don't get to tell someone what to do with their body and force them to carry to term - once you do that you start going into terrifying areas."
Ms Hagstrom Miller says that the abortion rights movement hasn't helped itself by framing abortion as just a woman's issue. "Abortion benefits women and men and families. Millions of men have benefited from having access to abortion."
She notes that over 60% of abortion patients are parents already - a figure supported by the Guttmacher Institute, external - and that at her clinic many couples turn up who are wrestling with an unplanned pregnancy and all the complex issues surrounding it. Some factors they consider are what size of family they want to have and how a new child would impact their current situation or family.
But, counter those involved in post-abortive counselling, it's what can happen further down the line that is not being acknowledged or spoken about enough due to the politics and posturing.
"Because of the rhetoric out there, people can't address what is there, which is a sense of loss, and affects men and women and whether you went into it pro-choice or not," says Kevin Burke, a social worker and co-founder of Rachel's Vineyard, which runs weekend retreats for post-abortive men and women. "But you are not given permission to speak about any of that, so you can't process it."
Mr Burke adds how he has found through his counselling work with imprisoned men from racial minorities that the fallout from an abortion can be heightened if a man previously experienced difficulties growing up.
"The abortion experience for men, especially with previous father loss, abuse and trauma, can contribute to the other issues that can lead men to express their grief, loss and rage from childhood abuse, and their abortion experiences, in destructive ways," Mr Burke says. "What we have learned is they seem to interact in a kind of toxic synergy."
Commentators note you don't have to be an anti-abortion advocate to feel sorrow over an abortion, or be haunted about whether you did the right thing. Hence, Mr Burke explains, later on many men and women carry a huge amount of moral and spiritual wounding.
Are women in Alabama about to lose the right to abortion?
Ms Hagstrom Miller says she would like to see the debate "moving away from a conversation of rights to a conversation about dignity and respect, empathy and compassion" - a point not that far from sentiments held by some of those against abortion.
"I hate it when you have people outside abortion clinics shouting things like 'You are going to hell'," says Mr Locker, who has joined prayer groups outside clinics.
"For one it's not getting the job done [of dissuading the woman], and it shows no compassion, and just condemns the mother, who is feeling just as much like she has a leg caught in that trap too."
In the meantime, we could be hearing more from increasing numbers of post-abortive men, says Theresa Bonopartis, director of Lumina, an organisation that counsels post-abortive men and women. She puts this down to a combination of the technological advances in ultrasound revealing more of what is occurring in the womb and the revelations of the passage of time since the Roe v Wade decision.
"It's changing now, men are fed up," Ms Bonopartis says. "Men had bought into how they have no say in this and that if they speak out, they are against women, but now the impact is being felt by more and more of them as the repercussions of 45 years of abortion are being seen."
- Published21 May 2019
- Published18 May 2019

- Published11 June 2019

- Published7 June 2019
