Cannabis legalisation: Does it lead to harder drug use?
- Published

There's strong disagreement among Democratic contenders for the US presidency about legalising cannabis and it's been a flashpoint in their televised debates.
Joe Biden, currently the leading contender in the race, won't be drawn either way. He wants more evidence about whether using it could act as a "gateway" to the use of harder drugs before it's legalised throughout the US.
There's not nearly enough evidence as to whether or not marijuana is a gateway drug.
"Before I legalise it nationally," said Biden, "I want to make sure we know a lot more about the science behind it."
But other Democrats, such as Cory Booker and Kamala Harris, have attacked this approach, saying the evidence is clear-cut and that cannabis use should be legalised.
Let's be clear: marijuana isn't a gateway drug and should be legalised.
Senator Booker, who supports legalisation, joked that he thought Mr Biden "might have been high" when he said he opposed legalisation. Senator Harris has said: "Let's be clear; marijuana isn't a gateway drug and should be legalised."
Other senior Democrats such as Bernie Sanders and Elizabeth Warren also say they support legalisation.
Polling by the Pew Research Center shows that public support for legalisation has steadily increased in the last decade, with two-thirds of Americans now supporting it.
What does the science say?
Some 33 states have legalised medical cannabis, while 11 states and Washington DC have also legalised recreational use. But cannabis use remains illegal at the federal level.
So is there evidence legalising cannabis could lead to the use of more dangerous substances?

Recreational cannabis is legal in 11 US states
The US government's own National Institute on Drug Abuse states that "some research suggests that marijuana use is likely to precede use of other licit and illicit substances". It cites experiments on animals that show increased responsiveness to other drugs after being exposed to substances containing cannabis., external
However, it adds that cannabis is not unique - alcohol and nicotine have a similar effect. And it states that the majority of people who use marijuana do not go on to use other, "harder" substances.
Denise Kandel, from the Mailman School of Public Health in New York, says research on animals shows changes in the way the brain responds to cocaine after exposure to alcohol, nicotine or marijuana.
She also says: "You are never able to establish a clear connection between using marijuana and using other drugs because there are so many other contributing factors that you can't control for in the research."
A paper published recently by the American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, external says: "Evidence of the impact of cannabis liberalisation on the use of other substances is inconclusive. We have limited evidence of how either alcohol or tobacco use has been impacted."

The sale of cannabis for recreational use has been legalised in some US states
What's happened in states that have legalised?
There's evidence that in states where cannabis has been legalised, usage of the drug among teenagers has decreased - or stayed the same.
There's also research indicating that among adults aged 26 and older, legalisation leads to more rather than less cannabis use, external.
And evidence has also emerged linking regular use of stronger strains of cannabis to an increased risk of mental health conditions, particularly among younger people.
Washington, Oregon, Alaska and Colorado all legalised between 2014 and 2016, among the first US states to do so. Do they show any particular trends for the use of harder drugs?
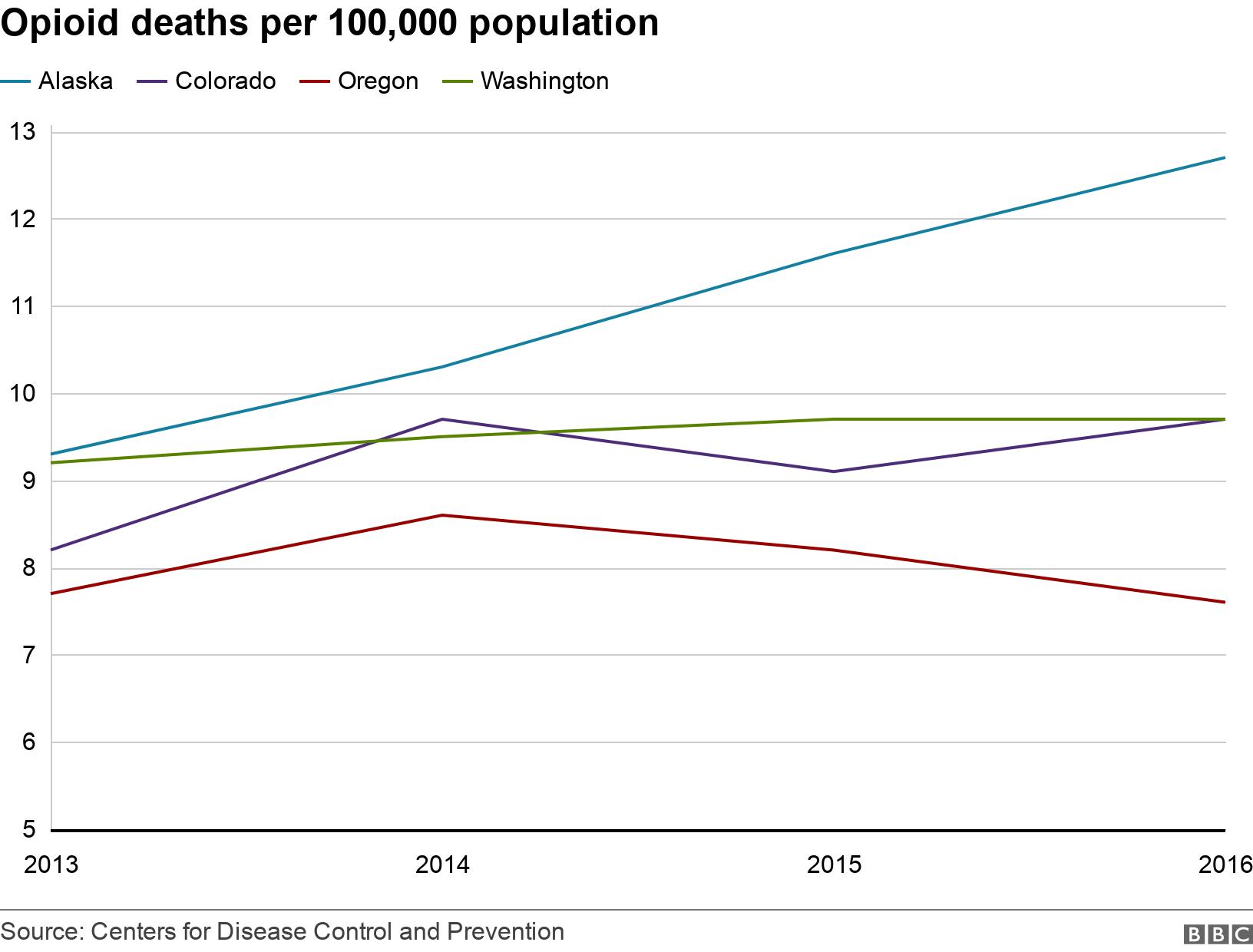
The US authorities collect data for drug overdose deaths, and between 2013 and 2017, 35 states had significant increases in deaths over that period. Alaska is among these, but Washington, Colorado and Oregon are not, external.
The majority of these fatal overdoses are due to opioids - excluding methadone.
Alaska apart, opioid deaths in Colorado, Washington and Oregon did not increase significantly between 2013 and 2016, the last year for which data is available.
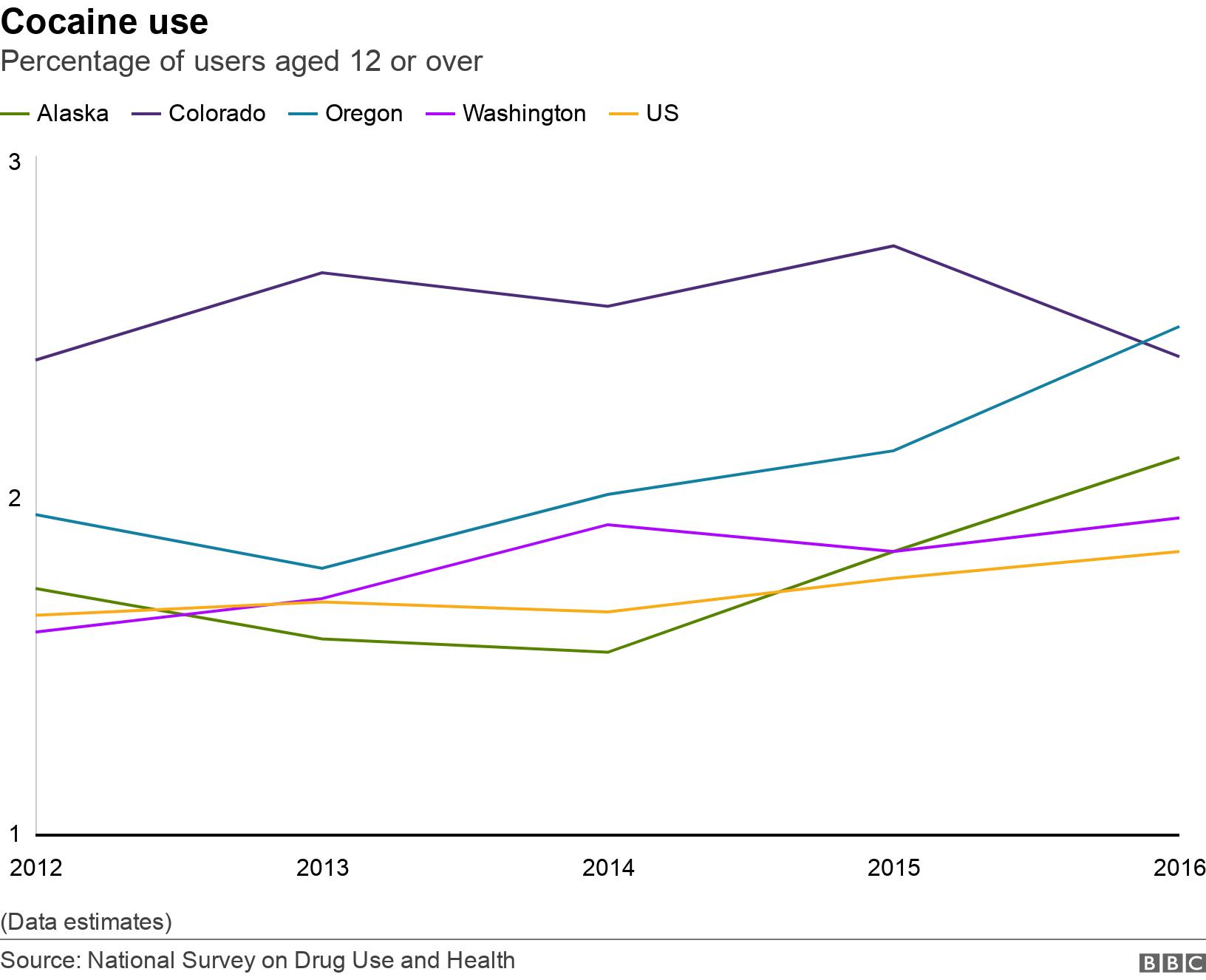
And estimates for cocaine use in the four states where marijuana is legal show it was above the national average from 2013 to 2016. But it was also higher in three of these states in 2012 before legalisation had taken effect.
Given that there are many different factors in each state that affect drug use like availability and supply, treatment and rehabilitation programmes, law enforcement priorities and social and economic conditions, it's hard to draw firm conclusions.
So more research may well be needed over a longer period to identify if there are clear trends around the use of other drugs in places where cannabis has been legalised.

- Published2 July 2019

- Published27 June 2019

- Published13 June 2019
