Abortion: What does overturn of Roe v Wade mean?
- Published

The US Supreme Court has opened the door for individual states to ban or severely restrict the ability for pregnant women to get abortions.
In 1973, the court had ruled in Roe v Wade that pregnant women were entitled to an abortion during the first three months of their pregnancy, while allowing for legal restrictions and bans in the second and third trimester.
Now the court has overturned that earlier ruling, effectively making it possible for states to ban abortions earlier than 12 weeks.
Abortion will not automatically become illegal in the US - but individual states will now be allowed to decide if and how to allow abortions.
Which states will ban abortion?
Thirteen states had passed "trigger laws" that come into effect upon Roe v Wade being overturned. Others have left old laws on the books that banned abortion prior to 1973 - they could now go back into force.
In the days that followed the ruling, several bans came into force, but some of those have been temporarily blocked by the courts, setting things up for further legal battles.
Over the past decade, several states have also tried to pass laws making abortion illegal, except in a few circumstances such as if the pregnant woman's life is at risk. Some of those laws were struck down by lower courts, as they appeared to violate Roe v Wade. But now they will likely come back into force.
In total more than 20 states are making moves to limit access to abortion, according to Guttmacher. Some states intend to ban abortion from the moment of conception, while others are introducing bans at six or more weeks.
All states allow abortion to save the life of the mother, while some will also allow exceptions to their ban for cases of rape or incest.
Most have said they will not prosecute women for trying to end their pregnancy, reserving criminal penalties for abortion providers and others who try and help women get abortions.
Here's a look at what could happen in those states now that Roe v Wade has been overturned.
What abortion restrictions are individual states expected to introduce?
From conception
-
Alabama Exceptions: to save the health or life of the mother or in cases where the child is unlikely to survive after birth
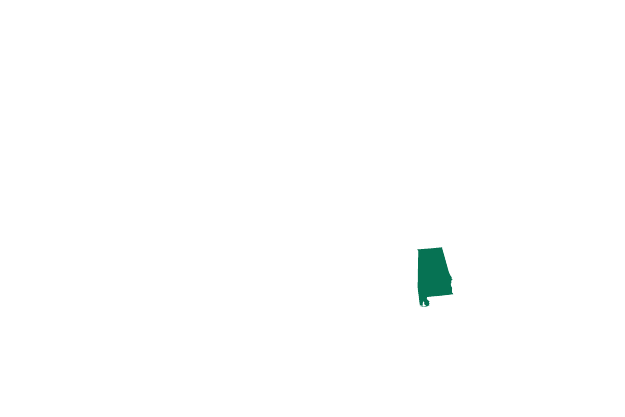
A pre-Roe abortion ban is now in effect. It only makes exceptions for the life of the mother. A 2019 law that had been blocked by a judge could be reinstated.
It would make abortions illegal at any stage of pregnancy - except in cases where it is necessary “to prevent a serious health risk” to the mother or if there is a “lethal fetal anomaly”. There is no exception for sexual assault or incest.Under the law, a doctor accused of performing an abortion could face up to 99 years in prison.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 949,900
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 8.1
- Number of abortion clinics: 5
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Arkansas Exceptions: to save the life of the mother
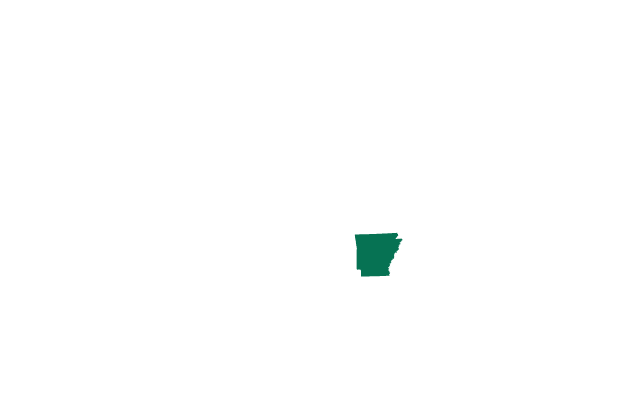
A trigger law passed in 2019 has gone into effect, banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy. The only exception is if the pregnant person’s life is in danger.
Anyone who attempted to perform an abortion could be fined up to $100,000 and serve up to 10 years in prison.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 577,400
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 6.4
- Number of abortion clinics: 3
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Idaho Exceptions: to save the life of the mother or in documented cases of rape or incest
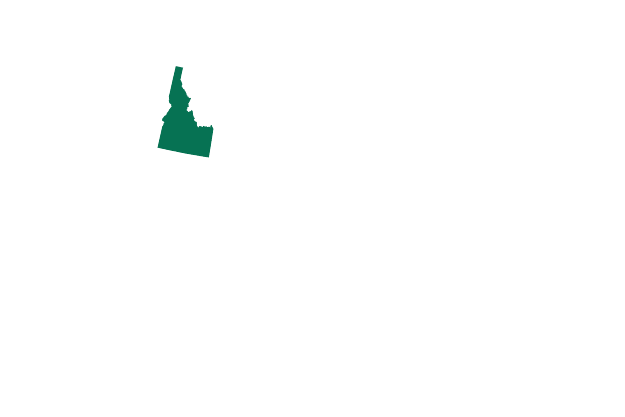
A trigger law passed in 2022 would go into effect 30 days after “the issuance of the judgment” by the Supreme Court, banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy.
There is an exception to save the pregnant person’s life. Victims of rape or incest are also exempt if the crime was previously reported to law enforcement and a police report has been provided to the physician. Medical providers who violate this could face time in prison.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 328,900
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 5.4
- Number of abortion clinics: 3
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Louisiana Exceptions: to save the health or life of the mother or in cases where the child is unlikely to survive after birth
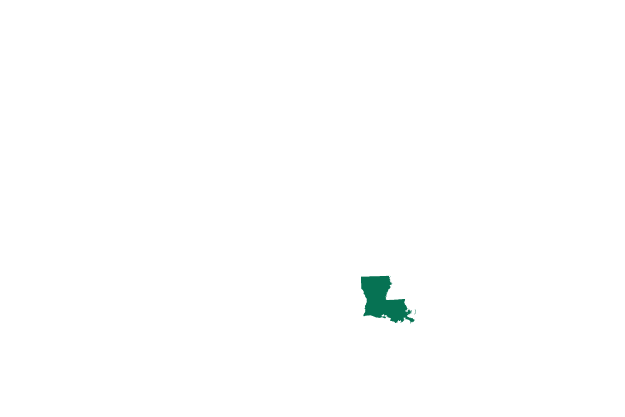
Abortion is banned at any stage after a trigger law took effect.
There is an exception if the pregnant person’s life is in danger or if the child is unlikely to survive birth. A pregnant person is shielded from criminal liability, but anyone who performs an abortion could be jailed and issued a fine of up to $100,000.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 936,100
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 10
- Number of abortion clinics: 4
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Michigan Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
Abortion is currently legal until viability, which is around 24-28 weeks, while the legality of a 1931 abortion ban, which remains on the books, is debated in court.
The pre-Roe ban from 1931 makes abortions illegal except to save the mother’s life. There are no exceptions for rape or incest. A judge ordered a preliminary ban on enforcing the old law should Roe fall.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 1,874,300
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 13.9
- Number of abortion clinics: 21
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Oklahoma Exceptions: to save the life of the mother
A trigger law that passed in 2021 has gone into effect, banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy. There are no exceptions for rape or incest. There is an exception to protect the life of the mother. Providing an abortion otherwise would be punishable with prison time.
In May, Oklahoma passed one of the most restrictive abortion laws in the country, banning abortion from the moment of fertilisation. That provision essentially bypassed Roe v Wade entirely, putting it up to private citizens, not the state, to enforce the law.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 768,800
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 6.2
- Number of abortion clinics: 4
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Ohio Exceptions: to save the life and prevent severe physical harm to the mother
A bill banning abortion after six weeks is in effect.
The bill would make exceptions only to protect the life of the mother. Doctors who perform an abortion could face up to 25 years in prison and lose their medical licence.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 2,203,300
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 9.3
- Number of abortion clinics: 9
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Kentucky Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
A judge has blocked a trigger law from going into effect that would ban abortion at any stage. The law is currently before the courts.
There would be exceptions to prevent the mother's death or the "permanent impairment of a life-sustaining organ". There are no exceptions for rape or incest. Performing an abortion would be considered a felony - punishable by time in prison.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 848,500
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 5.6
- Number of abortion clinics: 1
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Mississippi Exceptions: to save the life of the mother or in cases of rape or incest
A trigger law passed banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy is in effect.
There are exceptions for rape and to save the mother’s life. Medical providers who violate this could face imprisonment for up to 10 years.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 591,700
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 8.3
- Number of abortion clinics: 1
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Missouri Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
A trigger law passed in 2019 has gone into effect, making abortions illegal at any stage of pregnancy.
There is an exception for medical emergencies to save the mother’s life or to prevent “irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function”. There are no exceptions for rape or incest. Doctors who perform an abortion could be charged with a felony and have their medical licence revoked.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 1,171,800
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 8.3
- Number of abortion clinics: 3
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
North Dakota Exceptions: to save the life of the mother or in cases of rape or incest
A trigger law passed in 2007 would go into effect at the end of July, banning abortion at any stage.
There are exceptions for saving the life of the mother, rape or incest. Violators could face fines and imprisonment and it would make abortions a felony.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 146,200
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 6.6
- Number of abortion clinics: 1
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
South Dakota Exceptions: to save the life of the mother
A trigger law passed in 2005 has gone into effect, banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy.
There are no exceptions for rape or incest. Performing an abortion on someone, unless to save a mother’s life, would be classified as a felony.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 158,900
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 4.7
- Number of abortion clinics: 1
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Tennessee Exceptions: to save the life of the mother
Abortion is banned after 6 weeks, except to save the life of the mother or prevent severe physical harm.
A trigger law passed in 2019 would ban abortion at any stage of pregnancy, and go into effect 30 days after the Supreme Court issues a judgement.
There is an exception to save a mother’s life, but there are no exceptions for rape or incest. Providing or attempting to provide an abortion would be a felony.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 1,312,500
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 8.4
- Number of abortion clinics: 8
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Texas Exceptions: to save the life of the mother

A trigger law passed in 2021 would go into effect, banning abortion at any stage. A judge has temporarily blocked the law from coming into force.
There is an exception for medical emergencies to save the mother’s life. There are no exceptions for rape or incest. Anyone who performs abortions could face up to life in prison and fines, but patients themselves would be exempted from prosecution.
In the meantime, a pre-Roe ban, making it illegal to obtain an abortion after six weeks, is in effect. There is an exception to save the life of the mother.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 5,885,900
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 9.5
- Number of abortion clinics: 21
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Utah Exceptions: to save the life of the mother or in cases of rape or incest
A trigger law banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy has been temporarily blocked by a judge. There are exceptions to save the mother’s life and for rape or incest, if it was reported to law enforcement.
There are also exceptions if the fetus has a lethal defect or a “severe brain abnormality”, not including Down’s syndrome, cerebral palsy, spina bifida and other conditions that do not result in a vegetative state. Anyone who performs an abortion could be charged with a felony.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 675,100
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 4.5
- Number of abortion clinics: 3
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Wisconsin Exceptions: to save the life of the mother
A 1849 law banning most abortions could come into effect, and Planned Parenthood has ceased performing abortion services in the state. Wisconsin's Democratic governor has sued to repeal the old law.
There are no exceptions for rape or incest. There is an exception for saving the life of the mother.
The law would make it a felony to provide an abortion to someone outside those terms. The state’s Democratic attorney general has questioned the enforceability of the 173-year-old law.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 1,083,800
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 7
- Number of abortion clinics: 3
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Wyoming Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother, or in cases of rape or incest
A trigger law passed in 2022 goes into effect five days after the date that the governor certifies to the secretary of state that the Supreme Court of the United States has overruled Roe v. Wade, banning abortion at any stage of pregnancy.
There are exceptions for life endangerment, severe physical health conditions, sexual assault and incest. Anyone who performs an abortion could be charged with a felony.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 107,700
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 6.7
- Number of abortion clinics: 2
Updated: 12 July 2022
From 6 weeks
-
Georgia Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother, or cases of rape or incest before 20 weeks
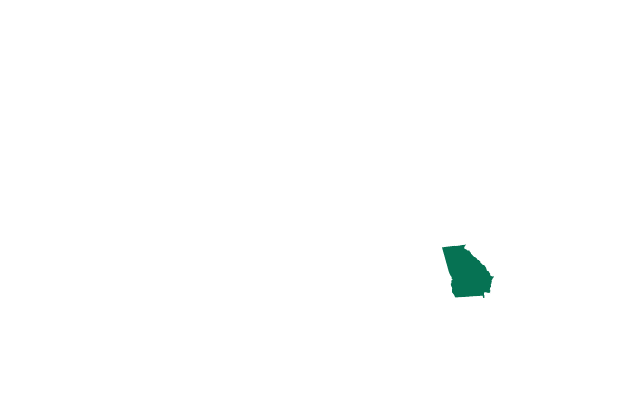
A bill banning abortions after around six weeks was passed in 2019, but then blocked by a federal judge. It could be re-enacted if Roe falls.
There are exceptions for medical emergencies, cases of rape or incest that have been documented through an official police report and are fewer than 20 weeks along.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 2,147,400
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 15.2
- Number of abortion clinics: 15
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Iowa Exceptions: to save the life of the mother, cases of rape or incest, or if the child is unlikely to survive after birth
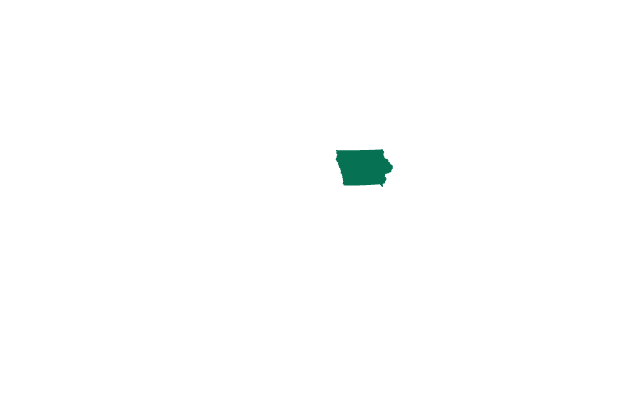
In 2018, Iowa passed a bill banning abortion after six weeks, except in cases of rape, incest, foetal anomaly, or in a medical emergency risking death or serious injury.
But a judge issued an injunction on the law. In June, the state’s highest court ruled the state constitution did not guarantee a right to abortion, setting the state for the injunction to be lifted.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 592,300
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 6.2
- Number of abortion clinics: 8
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
South Carolina Exceptions: to save the life of the mother, rape or incest, or if the child is unlikely to survive after birth
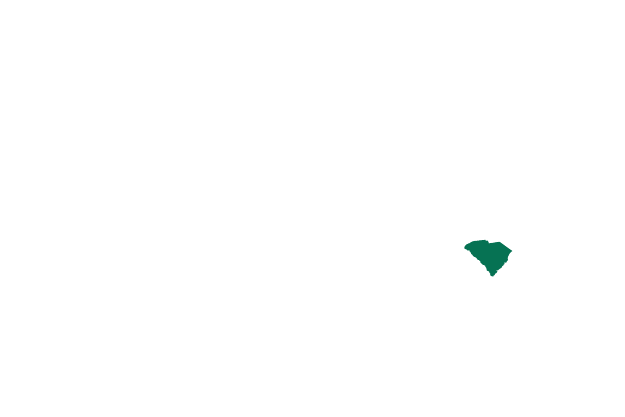
Abortion is banned after six weeks. There are exceptions to save the mother’s life, and for rape or incest if the pregnancy is before 20 weeks.
It also allows for abortion if there is a foetal anomly that would be “incompatible with sustaining life after birth”.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 965,700
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 11.8
- Number of abortion clinics: 4
Updated: 12 July 2022
From 13 weeks
-
Arizona Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
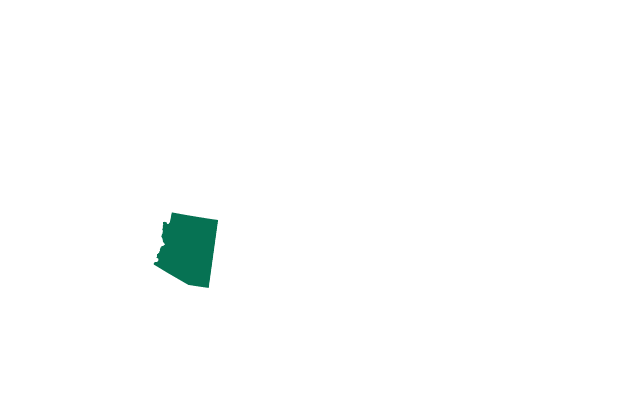
In March, Arizona passed a law banning abortion at 15 weeks, except in cases of medical emergency. There are no exceptions for rape or incest.
It will now go into force at the end of September. A doctor found to have performed an illegal abortion after 15 weeks would face a felony charge, fines and up to five years in prison. They could also have their medical licence revoked.
The state also has a pre-Roe ban that would ban all abortions, but it’s unclear which law the state would enforce. In July, a judge struck down a law granting fetuses the status of "personhood".
- Number of women aged 14-44: 1,345,800
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 9.8
- Number of abortion clinics: 8
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
Florida Exceptions: to save the health or life of the mother or in cases where the child is unlikely to survive after birth

A law banning abortion in Florida after 15 weeks is in effect, after a judge's temporary injunction on the ban was overturned.
The ban makes exceptions for the life of the mother or if a pregnancy could cause severe physical harm. It also makeas exceptions for cases where the child has a fetal anomoly that would make it unlikely to survive birth.
The ban was signed into law in April, but a lower court said it ran afoul of the state's constitution, which grants citizens the right to privacy.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 3,828,199
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 17.9
- Number of abortion clinics: 65
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
North Carolina Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
A 1973 law banning abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy is still on the books.
In 2015 it was amended to narrow the exceptions, allowing abortions only in cases where the life of the mother was threatened, or she risked serious physical bodily harm. Doctors who perform abortions could be charged with a felony.
But a court ruled that law was unenforceable because of Roe v Wade. It could come back into force.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 2,016,700
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 12.4
- Number of abortion clinics: 14
Updated: 12 July 2022 -
West Virginia Exceptions: to save the life or prevent severe physical harm to the mother
The state could look to restore a 19th century law which criminalises abortion as a felony.
In a 2018 ballot, voters amended the state's constitution to say there are no protections in West Virgina for the right to abortion.
In view of this recent amendment, the state's only abortion clinic said it can no longer operate.
- Number of women aged 14-44: 322,300
- Abortions per 1,000 women: 7.4
- Number of abortion clinics: 1
Updated: 12 July 2022
Who will be most affected by Supreme Court decision?
Some 40 million women of child-bearing age will live in states where abortion will become more difficult to access, according to the Guttmacher Institute, external, a research organisation that supports abortion rights.

About 630,000 abortions were performed in the US in 2019, according to the US Center for Disease Control (CDC), although Guttmacher's own research indicates it may be closer to 860,000.
The CDC says that the vast majority of abortions, 92.8%, are performed during the first trimester. Most people who get abortions are unmarried, although they may be living with a partner at the time. About one in 10 women who get an abortion are teenagers, with most being in their 20s. About 60% of people who get abortions have also given birth before, and nearly 60% had never had an abortion before.

State-specific statistics in the interactive table above are from 2017, the most recent date for which data is available from Guttmacher Institute.
The Guttmacher Institute's 2014 Abortion Patient Survey still provides the most recent national overview on the social and economic background of those having abortions in the US. However, changes in the US economy and access to abortion over the last eight years means the picture could have changed.
Update: Language in this story has been amended to more accurately reflect the specifics of the Roe v Wade ruling.
Related topics
- Published13 May 2022

- Published4 May 2022

- Published3 May 2022

- Published3 May 2022

- Published11 April 2022
