Climate change: New plant in Iceland will remove carbon dioxide from the air
- Published
- comments
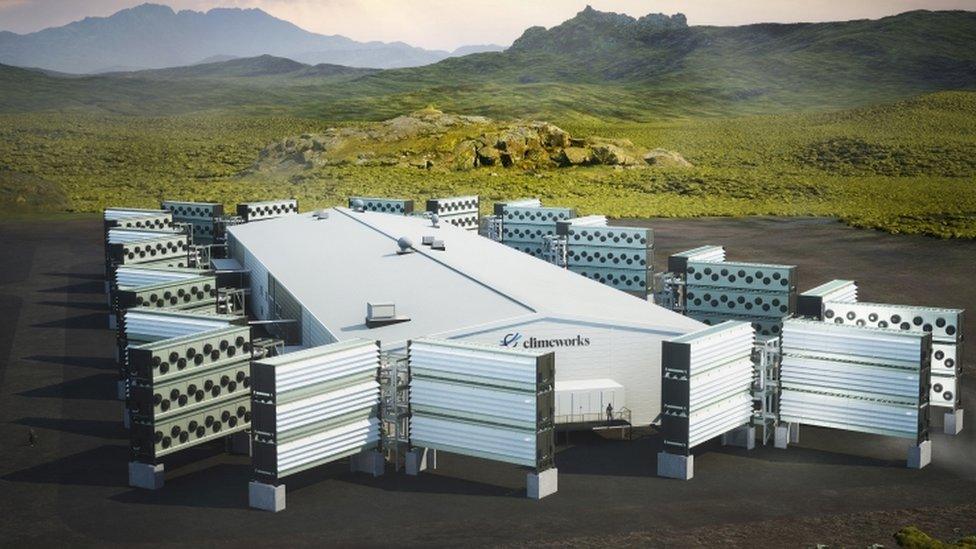
The new plant is being built in Iceland
A Swiss company has started work on what will be the biggest carbon dioxide capturing plant in the world!
The new facility, which has been named Mammoth, will be in Iceland where a similar plant called Orca already exists.
It's hoped Mammoth, which is a direct air capture and storage plant, will play an important role in tackling greenhouse gas emissions.
How does the carbon-catching machine work?
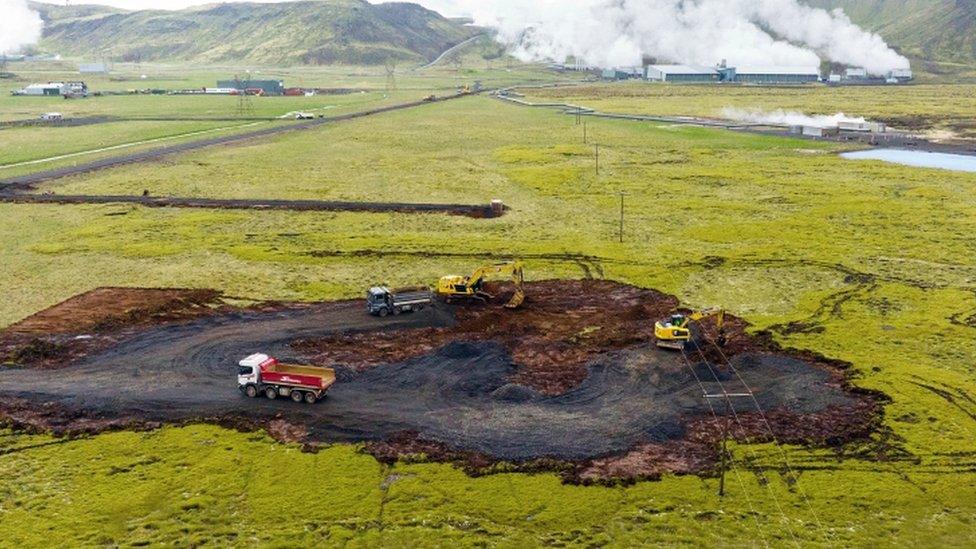

The new carbon-sucking facility will be the biggest in the world
So how does this all work? Well, direct air capture, or DAC, is a special type of technology which removes carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air.
Climeworks, which is the company behind both the Orca and Mammoth plants, says the new facility will contain around 80 large blocks of fans and filters that suck in air and extract its CO2.
This will then be mixed with water and injected underground where a chemical reaction will turn it into rock.
The new Mammoth plant, which is set to be completed within the next 18 months to two years, will be able to remove 36,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide from the air per year, according to the company behind the plant. That's about nine times the amount of CO2 that the Orca plant can extract.
However, this is just a small percentage of the 36 billion tonnes worth of CO2 emissions produced worldwide last year.
There are currently 18 direct air capture facilities in the world according to the International Energy Agency, but they aren't able to collect enough CO2 to make a significant impact on greenhouse gas emissions.
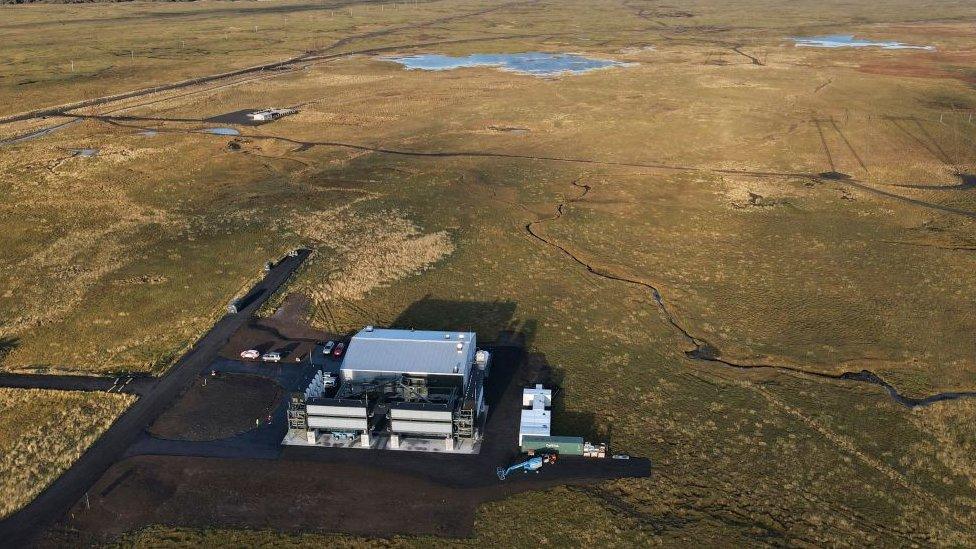

Climeworks already owns the Orca plant which is also in Iceland
Climeworks' co-CEO Christoph Gebald said the company intends to build an even bigger facility after Mammoth launches, which they say will capture about half a million tonnes of CO2 per year.
They plan to introduce more plants close to the end of the decade and other companies are also looking to build similar facilities.
There have been some concerns raised about DAC technology as lots of energy is often required to power the plants removing CO2 from the air.
Both the Mammoth and Orca plants are located in areas where they are able to rely on a form of renewable energy to carry out their processes. However, this isn't always the case.
Why is carbon dioxide a problem?
Climate change explained in 90 seconds
Carbon dioxide is what's known as a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases are those in the Earth's atmosphere which contribute to global warming. They do this by trapping the Sun's heat, causing the Earth's temperature to increase.
Some of the main greenhouse gases aside from carbon dioxide are nitrous oxide and methane, which is the second most common greenhouse gas after CO2.
Global warming can have a direct impact on climate change, which is a big problem affecting communities all over the world.
- Published28 June 2022

- Published25 May 2021

- Published11 November 2021

