Standard Chartered shares plunge on laundering charges
- Published
- comments
Standard Chartered "really has to open its books to show us what really happened," says Kroll's Penelope Lepeudry.
Shares of Standard Chartered have tumbled despite the bank denying allegations that it illegally "schemed" with Iran to launder money.
Shares in London fell 16.7%, about as much as its Hong Kong stock dropped.
The New York State Department of Financial Services said, external the UK-based bank laundered as much as $250bn (£161bn) over nearly a decade.
It said the bank hid transactions for "Iranian financial institutions" that were subject to US economic sanctions.
The regulator said that Standard Chartered had hidden 60,000 such secret transactions.
However, the bank denied the allegations, saying, external that it "strongly rejects the position or portrayal of facts as set out in the order" issued by the regulator.
'Not a full picture'
The US regulator labelled UK-based Standard Chartered a "rogue institution" and ordered the bank to "explain these apparent violations of law" from 2001 to 2010.
It accused Standard Chartered of falsifying payment directions by stripping the message of unwanted data that showed the clients were Iranian, replacing it with false entries.
"It provided step-by-step, wire-stripping instructions for any payment messages containing information that would identify Iranian clients," the complaint said.
The regulator also said that it would hold a formal hearing over the "assessment of monetary penalties". The bank, which currently only operates in the US in New York, has also been threatened with having its New York banking licence revoked.
The regulator also pointed the finger at consultancy firm Deloitte, suggesting it could have aided Standard Chartered in its alleged deception.
Deloitte had "intentionally omitted critical information" in a report, it said.
Deloitte responded by saying its financial advisory service division "performed its role as independent consultant properly and had no knowledge of any alleged misconduct by bank employees. Allegations otherwise are unsupported by the facts."
Account freeze
Standard Chartered also said the order issued by the US regulator did not present "a full and accurate picture of the facts".
It said that it had conducted a review of its transactions, primarily those relating to Iran for the period between 2001 to 2007, and had given regular updates to the US authorities on the results of the investigation.
"As we have disclosed to the authorities, well over 99.9% of the transactions relating to Iran complied with U-turn regulations," the bank said.
"The total value of transactions which did not follow the U-turn was under $14m."
The so-called U-turn transactions are those started outside the US by non-Iranian foreign banks that pass through the US financial system on the way to other non-Iranian foreign banks.
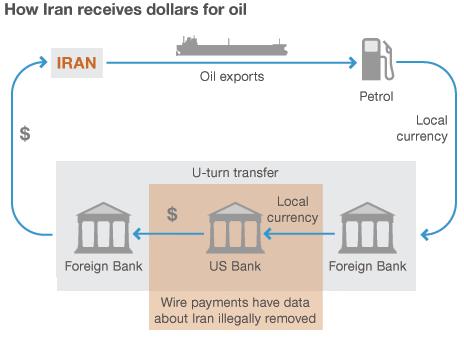
To ascertain whether these transactions are permitted or not under current regulations, US clearing banks use the wire-transfer messages they get from the banks involved.
If the banks do not have enough information, they are supposed to freeze the assets.
Senior management were also said to have codified their illegal procedures in formal operating manuals, including one labelled "Quality Operating Procedure Iranian Bank Processing".
Penelope Lepeudry, managing director of Kroll Advisory Solutions, a consulting firm specialising in financial investigations, told the BBC that "if the allegations are confirmed, this is a very serious development".
"The regulators are not going to be merely convinced by a statement from the bank - they need to see the details," she said.
Other schemes found
The regulator said it had also uncovered evidence with respect to what are apparently similar schemes to conduct business with other countries under sanctions - Libya, Burma and Sudan.
"Investigation of these additional matters is ongoing," it added.
The regulator said that its nine-month investigation, which involved looking through more than 30,000 pages of documents, including internal bank emails, showed that the bank reaped "hundreds of millions of dollars in fees".
"SCB's actions left the US financial system vulnerable to terrorists, weapons dealers, drug kingpins and corrupt regimes, and deprived law enforcement investigators of crucial information used to track all manner of criminal activity," it said.
'Staggering cover-up'
In numerous emails going back as far as 1995, Standard Chartered's lawyers advised on ways to go about circumventing US sanctions.
In March 2001, the bank's legal adviser counselled that "our payment instructions [for Iranian clients] should not identify the client or the purpose of the payment".
By 2006, there were concerns raised about the bank's conduct in its New York branch.
The chief executive for the Americas sent an email to London saying the programme needed to "evaluate if its returns and strategic benefits are... still commensurate with the potential to cause very serious or even catastrophic reputational damage to the group".
But those warnings were ignored by senior management in London in what the regulator called a "staggering cover-up".
Among the violations of the law, the bank is accused of:
falsifying business records
failing to maintain accurate books and records
failing to report misconduct to the regulator in a timely manner
evading federal sanctions
The US Treasury, which implements the sanctions, said that it treated violations "extremely seriously".
- Published7 August 2012
- Published10 December 2012
- Published6 August 2012
- Published24 July 2012
- Published2 August 2012
- Published6 August 2012
- Published11 December 2012