Bank of England: Five things we now know about the UK economy
- Published

The outlook for the UK's economy is fairly bleak.
The Bank of England raised interest rates again on Thursday and has warned the UK is heading for its longest recession since the 1930s Great Depression.
Here are five things we learned from the central bank about the future of the economy.
1. UK set for two-year recession
The UK is facing its longest recession on record, with the Bank of England warning the country faces a "very challenging" two-year slump.
When a country is in recession, it's a sign that its economy is doing badly. A recession is when a country's economy shrinks for two three-month periods in a row.
This has been forecast in the UK for some time due to the prices of goods such as food, fuel and energy soaring, which is down to several factors, including the war in Ukraine.
Previously, the Bank had expected the UK to fall into recession at the end of this year and said it would last for all of next year.
But now it thinks the economy already entered a recession this summer, and predicts it will continue next year and into the first half of 2024.
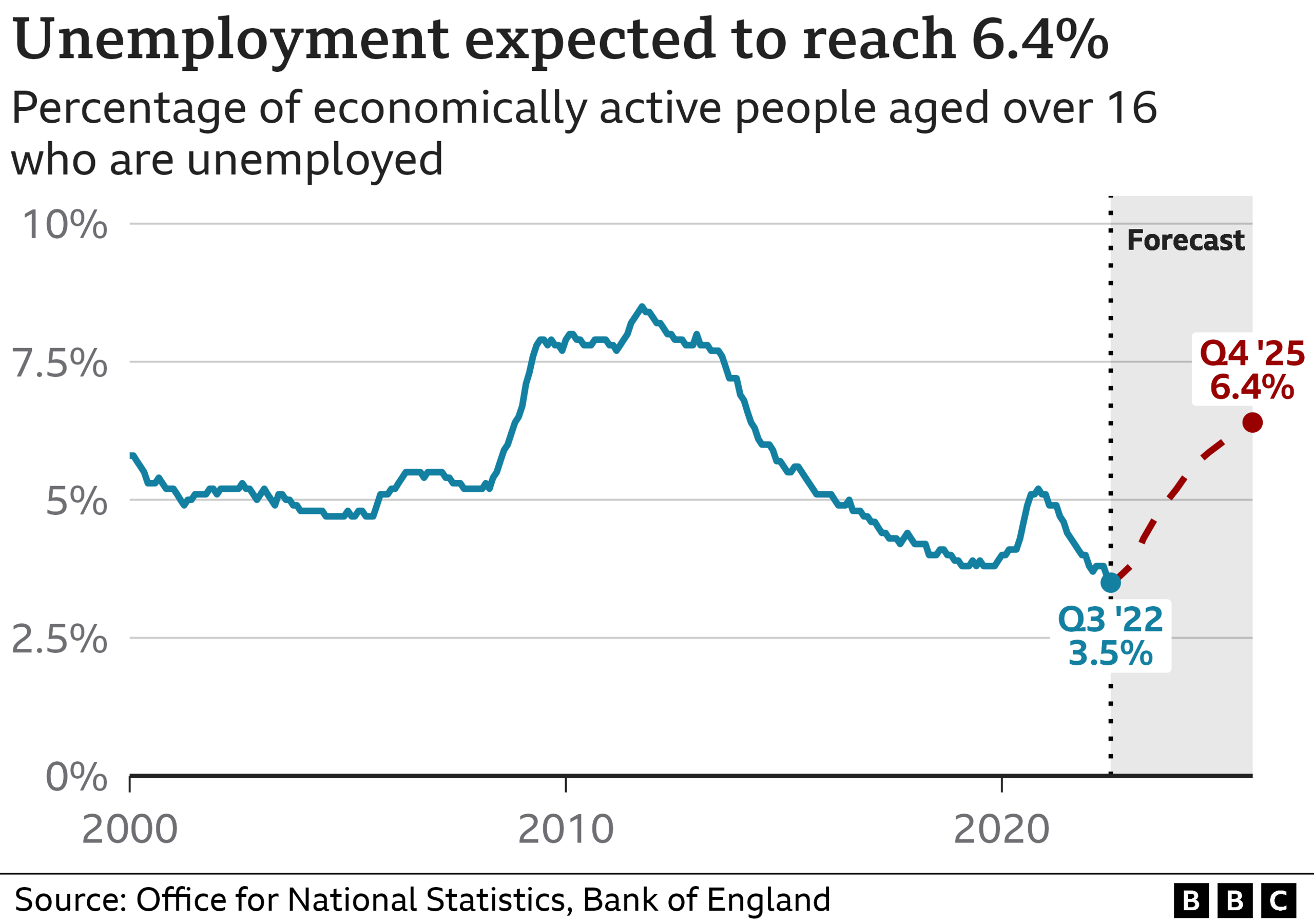
2. Unemployment rate to nearly double
Typically when a country is in recession, companies make less money and the number of people unemployed rises.
Graduates and school leavers also find it harder to get their first job.
The unemployment rate in the UK is set to rise significantly over the next two years to 6.4%, the Bank predicts.
Currently, the jobless rate is at 3.5%, its lowest level since 1974, thanks to a jobs boom as the economy started to recover from the pandemic.
But experts were already warning that the tide might be starting to turn due to the number of job vacancies falling in recent months.
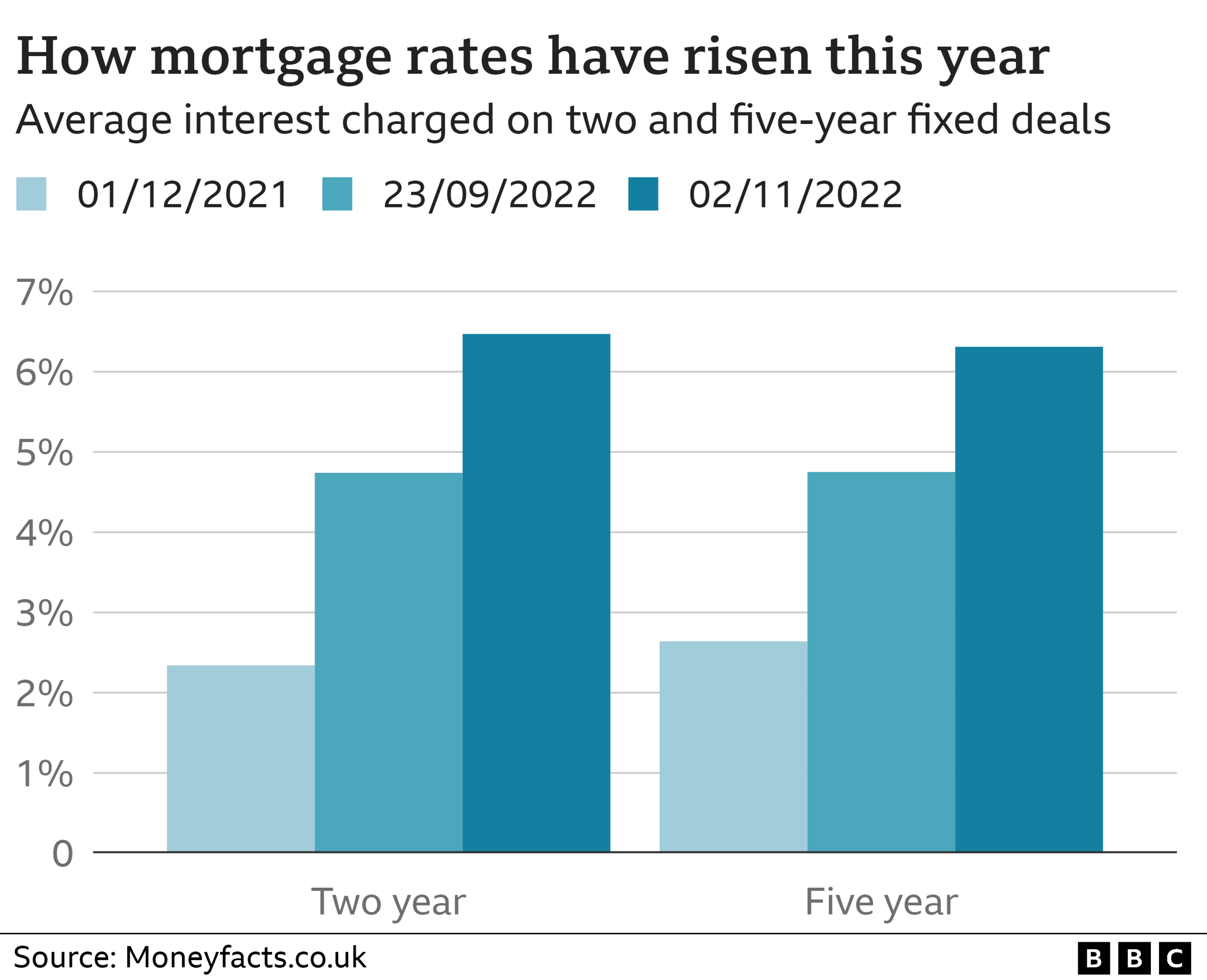
3. Some mortgages could rise by £3,000 a year
Many homeowners will probably face higher mortgage repayments in the next two years, the Bank said.
Mortgage rates have been rising and those on fixed-rate deals, which make up about 80% of mortgages, will face an increase in repayments when their fix comes to an end.
Annual payments could soar by £3,000 in some cases, according to the Bank.
But with the latest hike in interest rates from the central bank widely expected, many lenders "priced in" the rise by raising their mortgage rates in advance.
According to Simon Gammon, managing partner at mortgage advisers Knight Frank Finance, most lenders are offering fixed rates of between 5.5% and 6%, so he says further rises would come as a surprise.
Those on tracker or variable rate mortgages will see their monthly payments go up with any future rate rises from the Bank of England.
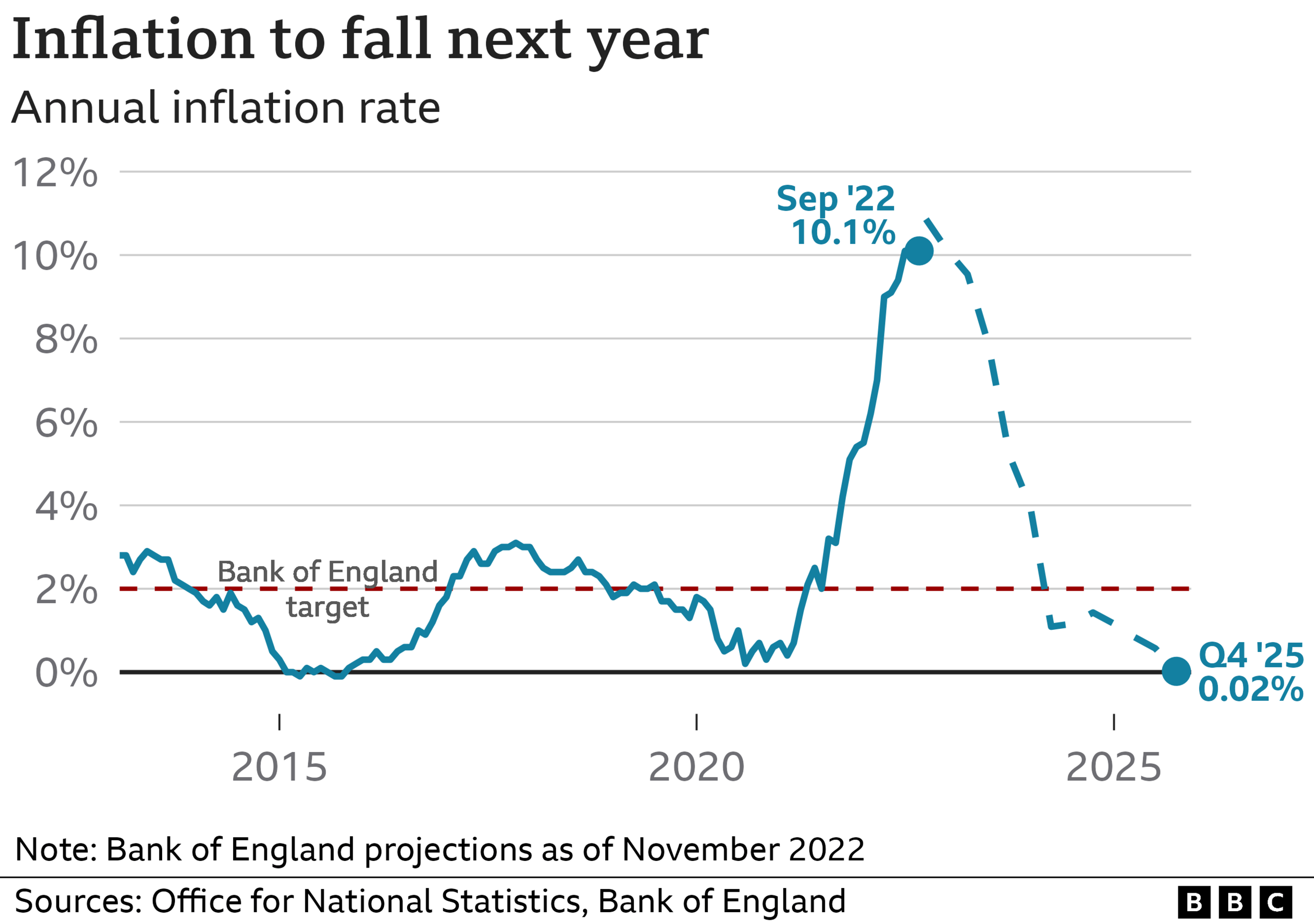
4. Inflation to slow down next year
The inflation rate is a measure of the increase in the price of something over time.
For example, if a loaf of bread costs £1 and it goes up to £1.05 a year later, then bread inflation is 5%.
Inflation hit 10.1% in September, is expected to peak at 11% this winter, before falling next year.
The Bank's target is to keep inflation at 2%.
5. Interest rates won't go up as much as previously expected
The Bank of England puts up interest rates to try to control inflation. The idea is that people will be discouraged from borrowing and in turn have less money to spend, leading to prices rising more slowly.
With inflation expected to fall next year, the Bank does not expect interest rates to rise by as much as predicted.
November's interest rate rise takes the current rate to 3%.
Further rises are on the way - so borrowing on credit cards, loans and mortgages will still get more expensive - but they won't hit the 5.25% that financial markets had predicted.
Analysts now think they could peak at around 4.75% next year.
Related topics
- Published3 November 2022

