Apple forces apps to display what they do with data
- Published

Apps on all of Apple's app stores will now have to show much more detail about what data they collect and what it is used for.
From 14 December developers must show what information they gather, listed in terms of what is taken to track users and what is linked directly to them.
However, the tech giant said it was not seeking to change publishers' business models.
Apple has included its own apps in the new rule.
Location and contact information were two examples of data that app developers might take in order to track users and their activities, the firm said. It also said it would always display this information at the top, because it considered it to be of greatest interest to users.
Other data such as health and fitness, financial information and search history, may be linked directly to an individual.
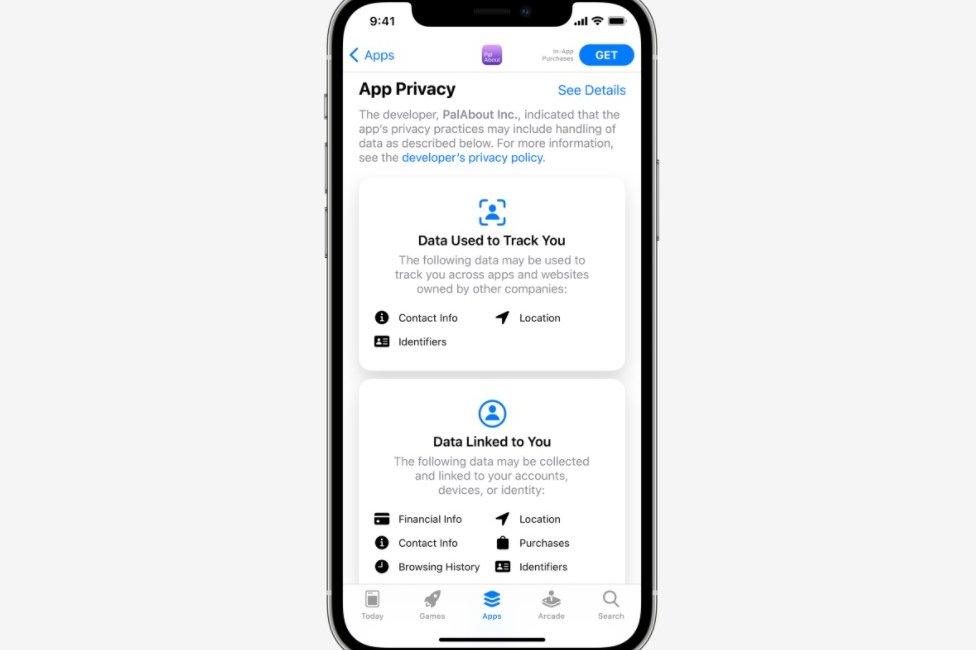
How the notification will look on an iPhone 12.
Apps will also have to state whether they collect data from other apps and websites the user has visited in order to target advertising, and what data they share with any third parties such as ad networks.
Ultimately if the user is uncomfortable with the data activity of an app they will not be able to opt out - but they can decide not to download it.
The tech giant said it hoped the new rule would "focus the minds" of both developers and consumers, and added that it would carry out spot checks to ensure that developers were being honest in their declarations.
"All the data privacy experts and lawyers will say it's a step in the right direction, and it is, but what does this change for the user?" said independent researcher Dr Stephanie Hare.
"It doesn't change the actual nature of their data and what's happening with it. It makes them more aware of privacy, but the choice about how to download the app itself hasn't changed."
Related topics
- Published4 September 2020