Coronavirus: Impact of new variant on children investigated
- Published
- comments
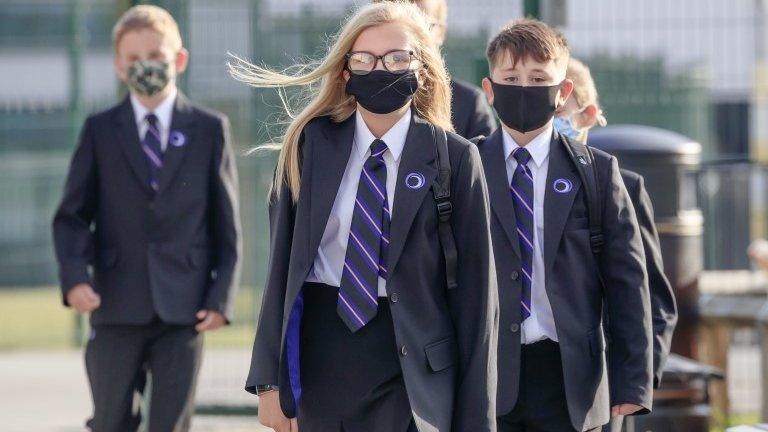

Scientists are urgently investigating hints the new variant of coronavirus spreads more easily in children.
If proven, this could account for "a significant proportion" of the increase in transmission, they say.
The claim comes from members of the government's New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats advisory group (Nervtag).
On Monday, Boris Johnson said he wanted to open schools in January "if we possibly can".
There are no suggestions the new form of the virus is a greater threat to children's health.
Children almost universally shrug off the virus, but the variant could alter the role they, and schools, play in spreading the virus.
Earlier strains of coronavirus found it harder to infect children than adults.
One explanation is children have fewer of the doorways (the ACE2 receptor) the virus uses to enter our body's cells.
A recent study of infections in schools in England found that levels of the virus in school-age children reflected levels in the local community, suggesting that closing schools would only have a temporary effect.
Lightning speed
Prof Wendy Barclay, from Nervtag and Imperial College London, said the mutations to the virus appeared to be making it easier to walk through the doorways that were there.
She said this could be putting children on a "more level playing field" with adults as the virus was "less inhibited" in children.
Prof Barclay said: "Therefore children are equally susceptible, perhaps, to this virus as adults, and therefore given their mixing patterns, you would expect to see more children being infected."
Work to understand the new variant is taking place at lightning speed and there is still much uncertainty.
It is now thought the new variant spreads 50% to 70% faster than other forms of the virus.
Early analysis of how and where it is spreading have also given "hints that it has a higher propensity to infect children", according to Prof Neil Ferguson from the MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis, who also sits on Nervtag.
He stressed the link was still being investigated and was not yet proven.
"If it were true, then this might explain a significant proportion, maybe even the majority, of the transmission increase seen," he added.
But Prof Julian Hiscox, chair in infection and global health, from the University of Liverpool, told the BBC there wasn't any evidence "at the moment" that the new variant is able to infect children more efficiently.
He said this would be looked at closely by scientists over Christmas.
Scientists involved in COG-UK, the Covid-19 Genomics UK Consortium, which detected the rapid increase in the variant, said they were not aware of any increased incidence in children.
'Retain control'
The data are continuing to be analysed, but it is thought the variant continued spreading even during the lockdown in November.
The R number - the average number of people each infected person passes the virus onto - for this variant during the tight restrictions has been estimated at 1.2, which meant cases were increasing.
At the same time the R number was 0.8 for the other forms of the virus during lockdown and they were in decline.

SOCIAL DISTANCING: Can I give my friends a hug?
FACE MASKS: When do I need to wear one?
TESTING: How do I get a virus test?

Prof Ferguson said he expected the number of infections to fall as schools closed and people hunkered down for Christmas.
He added: "The real question then is - how much are we able to relax measures in the new year, and still retain control?"
Prime Minister Boris Johnson said: "We want, if we possibly can, to get schools back in a staggered way at the beginning of January, in the way that we have set out.
"But obviously the common sensical thing to do is to follow the path of the epidemic and, as we showed last Saturday, to keep things under constant review."
Follow James on Twitter, external

A PROMISED LAND: Barack Obama reads from his new and compelling presidential memoir
GROUNDED WITH LOUIS THEROUX: Rylan Clark-Neal reveals how one of Louis’s documentaries ignited his teenage sexuality

Related topics
- Published20 December 2020
- Published15 December 2020
- Published13 November 2020
