Covid: Trust regulator on AstraZeneca vaccine safety, Boris Johnson says
- Published
The PM on the safety of the AstraZeneca jab
People should get their Covid-19 jab when invited, the PM has said, amid concerns about potential side effects of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine.
Boris Johnson said getting vaccinated was "the key thing" and the regulator's advice was to keep giving the jab.
It comes after a European Medicines Agency official, speaking in a personal capacity, said there appeared to be a link with the jab and rare blood clots.
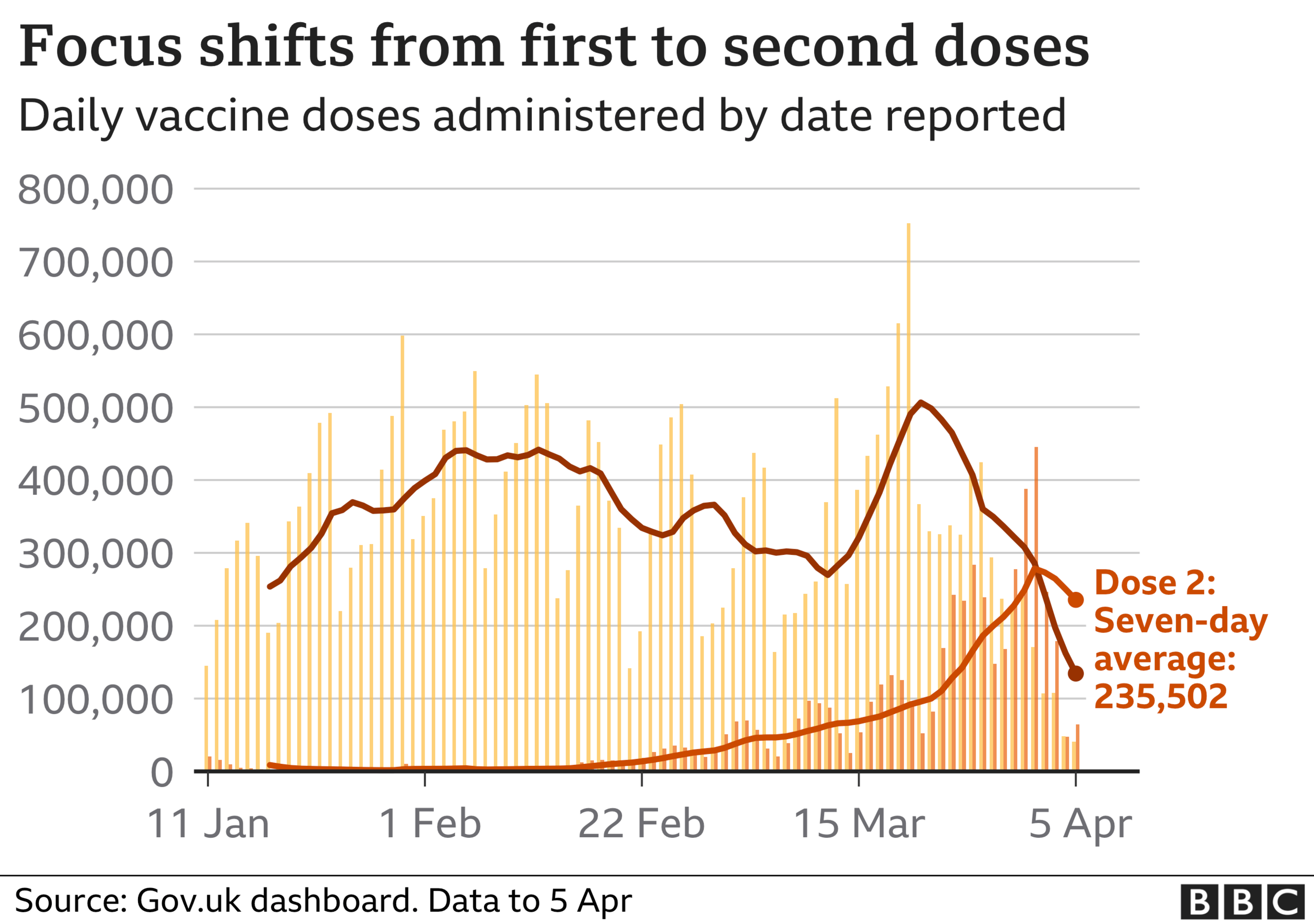
More than 31.6 million people in the UK have had a first vaccine dose.
A total of 5.4 million people have received a second dose.
Two vaccines - developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca and Pfizer-BioNtech - are being used in the UK, while A third - from Moderna - has been approved.
The European Medicines Agency's (EMA) safety committee has been reviewing very rare cases of unusual blood clots in people vaccinated with the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine.
It said that the committee had "not yet reached a conclusion and the review is currently ongoing", but it is expected to announce findings on Wednesday or Thursday.
The UK regulator the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) says the benefits of the jab continue to outweigh any risk.
During a visit to the AstraZeneca manufacturing plant in Macclesfield, Cheshire, Mr Johnson defended its vaccine.
"On the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine, the best thing people should do is look at what the MHRA say, our independent regulator - that's why we have them, that's why they are independent," said Mr Johnson, who has received the first dose of the vaccine himself.
"Their advice to people is to keep going out there, get your jab, get your second jab."
The prime minister added: "The best thing of all is to vaccinate our population, get everybody out getting the jab, that's the key thing and that's what I would advocate, number one."
Speaking to an Italian newspaper in a personal capacity, Marco Cavaleri, head of vaccines at the EMA, is reported to have suggested a clear link between the jab and rare blood clots, though admitted there was uncertainty how the vaccine would cause the complication.
The EMA has previously said that there was "no evidence" to support restricting the use of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine in any population.
Dr Rogerio Pinto de Sa Gaspar, director of regulation and prequalification at the World Health Organization, said there was "no link for the moment" between the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine and rare blood clots.
The MHRA is investigating reports of a very rare and specific type of blood clot in the brain, known as cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), occurring together with low levels of platelets (thrombocytopenia) following vaccination.
A number of countries have suspended the use of the jab among younger people, including in Germany, which has paused it for people aged below 60, and Canada, where the jab is not being given to those under 55.
In total, the UK has secured 457 million Covid vaccine doses, of which 100 million are from AstraZeneca. Vaccines from Moderna will be deployed in the UK "around the third week of April", Vaccines Minister Nadhim Zahawi has said.
The MHRA has said it identified 30 cases of rare blood clot events out of 18.1 million doses of the jab administered up to and including 24 March. There have been seven deaths among the 30 cases.
But the regulator's chief executive Dr June Raine said: "People should continue to get their vaccine when invited to do so.
"Our thorough and detailed review is ongoing into reports of very rare and specific types of blood clots with low platelets [the cells involved in clotting] following the Covid-19 vaccine AstraZeneca.
"No decision has yet been made on any regulatory action."

LOOK-UP TOOL: How many cases in your area?
LOCKDOWN RULES: What are they and when will they end?
YOUR QUESTIONS: We answer your queries
GLOBAL SPREAD: How many worldwide cases are there?

Prof Adam Finn, a member of the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI), which advises the UK government, told the BBC there was "a lot of uncertainties around" and more information was "desperately" needed.
But, he said, there were some "clear certainties around" including the facts that both of the vaccines used in the UK were "highly effective against Covid" while the risk of getting sick or dying with Covid for those who are currently being offered doses, "are far and away greater than any small theoretical risk that may exist relating to these cases".
There have been a further 2,379 coronavirus cases in the UK and another 20 deaths within 28 days of a positive Covid test, according to the latest government figures.

YOUR MENTAL HEALTH TOOLKIT: Tips and tools to look after your mental health
WHO KILLED EMMA CALDWELL?: 16 years later her murder is still unsolved...

- Published2 April 2021
- Published3 April 2021
- Published2 April 2021
- Published30 March 2021
- Published18 March 2021