Autumn Statement: Who do spending cuts hit the most?
- Published
- comments

The government is expected to announce plans to raise £20bn in tax alongside extensive spending cuts, as part of its Autumn Statement on Thursday.
It's a bid to plug an estimated £55bn black hole in the nation's finances, and it echoes the original austerity plans unveiled back in 2010.
Over the last 12 years, I've seen the impact those cuts have had at a local level. From the lack of police in Hartlepool, to the cuts to addiction services in Barrow-in-Furness.
Perhaps most strikingly, I've also reported from more and more food banks across the UK. They once felt like a novelty, now their use is a fact of life in so many communities.
But what does the data show us about who those spending cuts will affect the most?
In June 2010, the government faced similarly tough choices to those Rishi Sunak is confronted with today. The UK's finances were in a mess following the 2008 global financial crisis. The government had spent hundreds of billions of pounds shoring up the economy, including rescuing several major banks.
The then chancellor, George Osborne, introduced a wide range of spending cuts in an emergency budget, which he called "tough, but fair."
It included cuts in most areas of public life, but in particular local government and welfare. Housing benefit was reduced, school buildings weren't repaired and Sure Start children's centres were cut, among many other measures.
At the time, Mr Osborne said the consequence of not trying to reduce the UK's deficit would be "severe" - he warned of "higher interest rates, more business failures, sharper rises in unemployment". He promised, while the process might be painful, "we are all in this together".
And while his cuts - alongside tax rises - did affect the whole country, evidence built up since 2010 is clear; the impact was not equally felt.
Take a look at this data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS), which shows the change in average household wealth between 2006 and 2020, after inflation.
It suggests that in London, average household wealth increased by 63%, to £340,300. By contrast, in north-east England it fell by 17%, to £168,500.
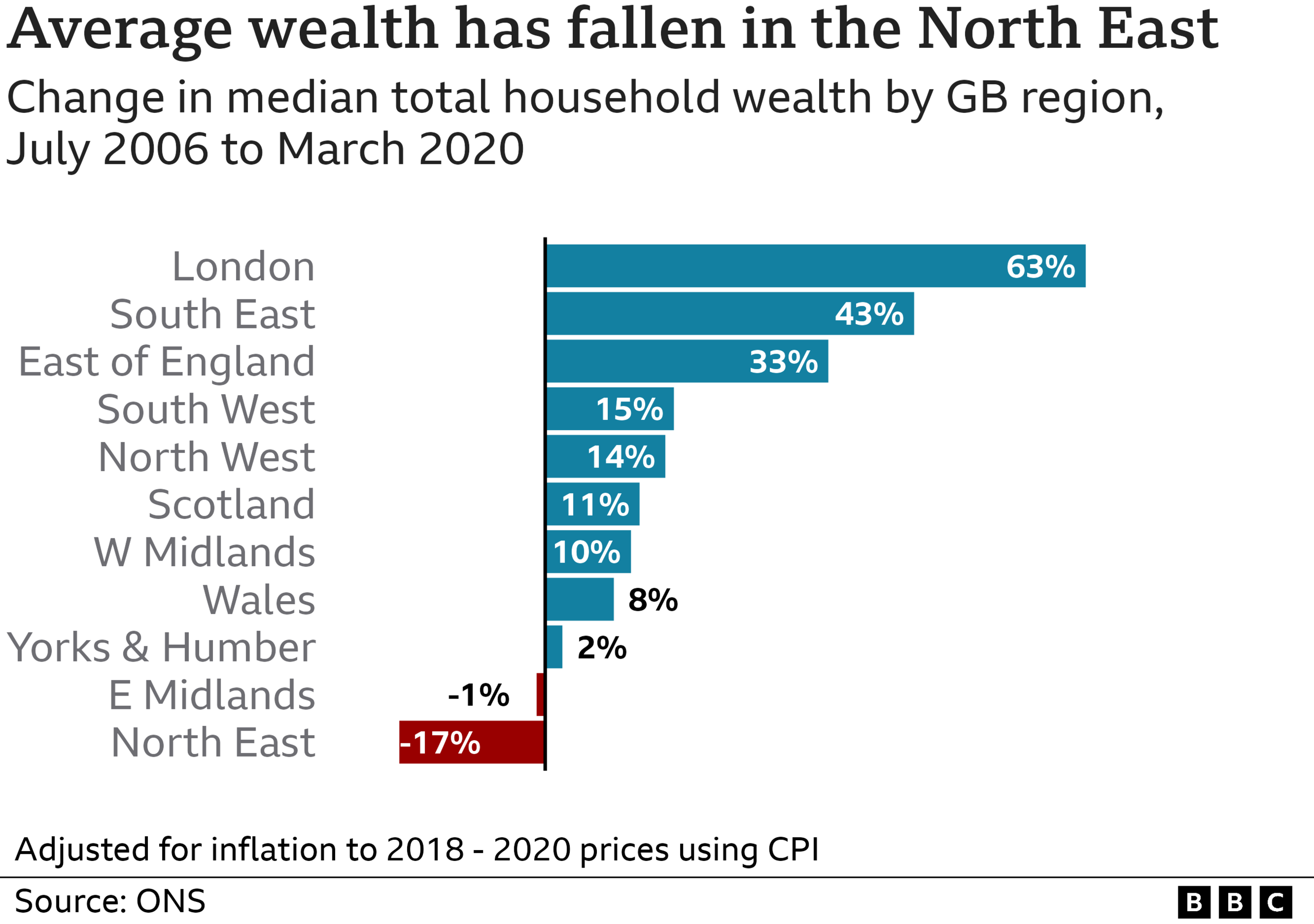
The data combines the change in the value of different sources of wealth, such as property, private pension pots and savings, and highlights how unequally England has developed in recent years.
That's something underlined in a report published by public health expert Professor Sir Michael Marmot, in 2020, external.
He found, since 2010, while London had become the richest area in northern Europe, the UK also contained six of the 10 poorest regions.
The North East's sluggish performance has had real-world consequences.
Since 2014, child poverty in the region grew by 46% to the highest rate in England. In an average classroom of 30 children in the North East, 11 are living in poverty.
A head teacher from Wallsend, in north Tyneside, recently told me the cuts to Sure Start centres had resulted in many children starting school well below the social and academic level of previous intakes.
Benefit cuts and an increase in unstable, often zero-hour contract work, had left more families needing a referral to a local food bank - although the more recent cost of living crisis had also been a factor.
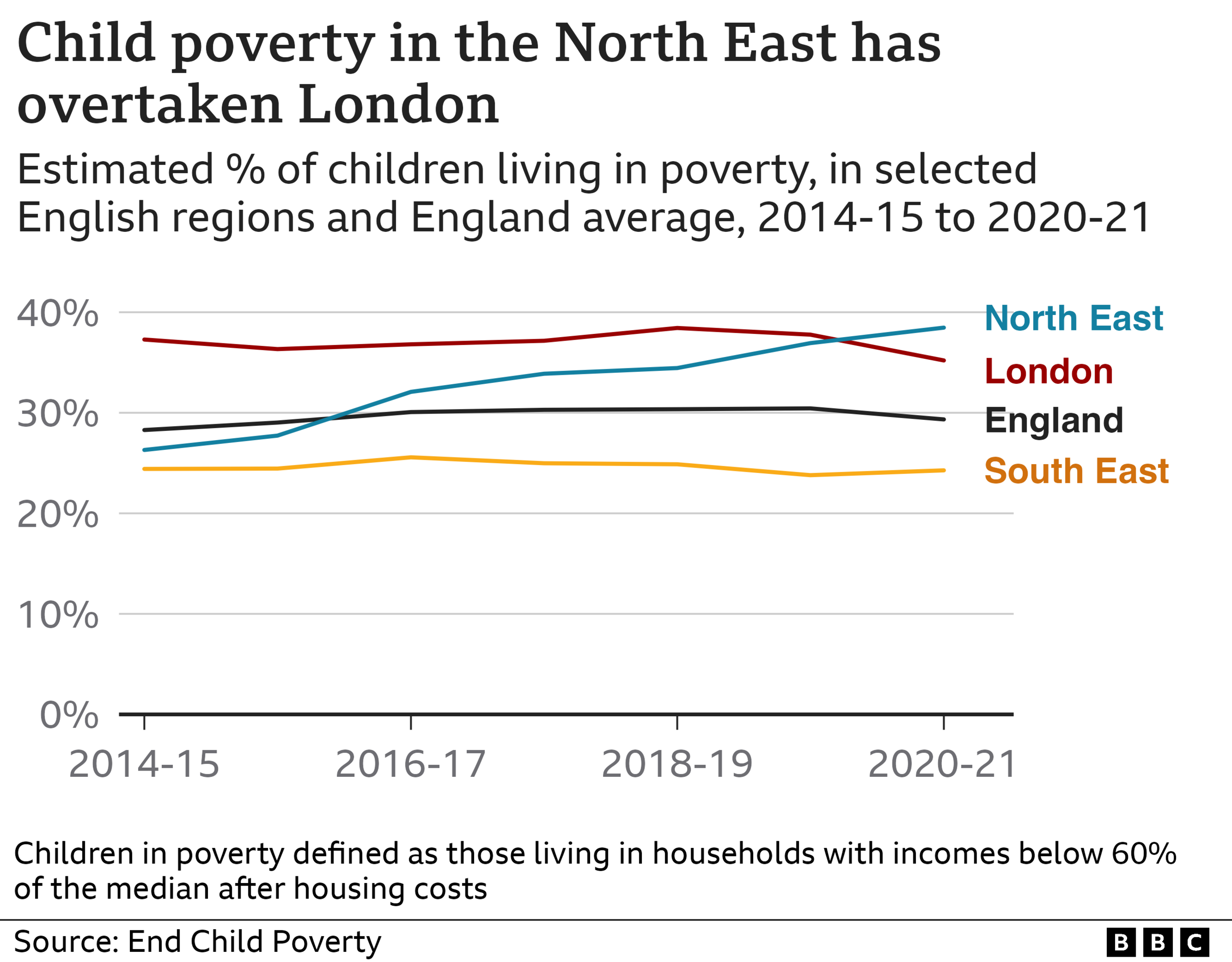
The North East saw the greatest cuts to services for children and young people, and the largest reduction in spending per person. Life expectancy also fell in some of the North East's most deprived communities.
Indeed across the UK, some experts have made a link between austerity and some people dying younger. Last month, Glasgow University researchers suggested 335,000 excess deaths in Scotland, England and Wales between 2012 and 2019 could be largely attributed to the public spending cuts first introduced in 2010, external.
The study, the authors say, adds to the "growing evidence of deeply worrying changes to mortality trends in the UK" - particularly among deprived communities.
The rise of baby banks
The cuts and freezes to welfare benefits during the decade after 2010 have been consistently blamed for the explosion in food banks, something I looked at earlier this year.
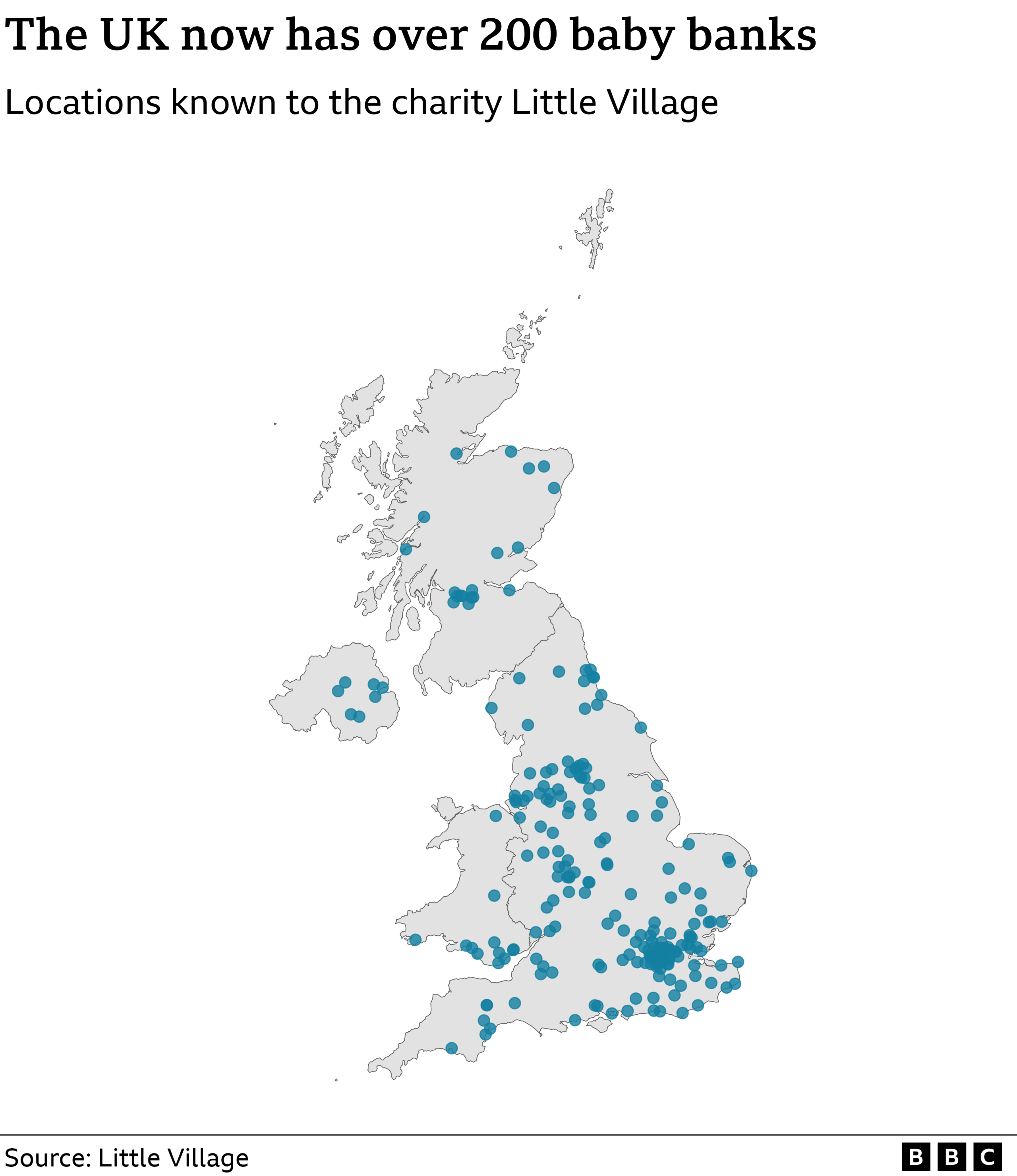
Less appreciated is the huge increase in another emergency provision - so called "baby banks", which supply nappies, clothing, shoes and sometimes school uniforms for little or no money.
There appears to have been little more than a handful of these in existence prior to 2010. Today there are more than 200 across the UK. The Little Village network, which compiled the map, acknowledges that the pandemic also had an impact.
Successive government ministers spent years denying austerity had any negative consequences.
This was a position largely held onto until, in 2019, then Prime Minister Boris Johnson said he had long thought austerity "was just not the right way forward for the UK".
Until then, most ministers had argued the cuts were unavoidable for the long-term economic health of the UK, and a less generous welfare system had been responsible for record levels of employment - in effect, forcing people to get a job.
Tough decisions
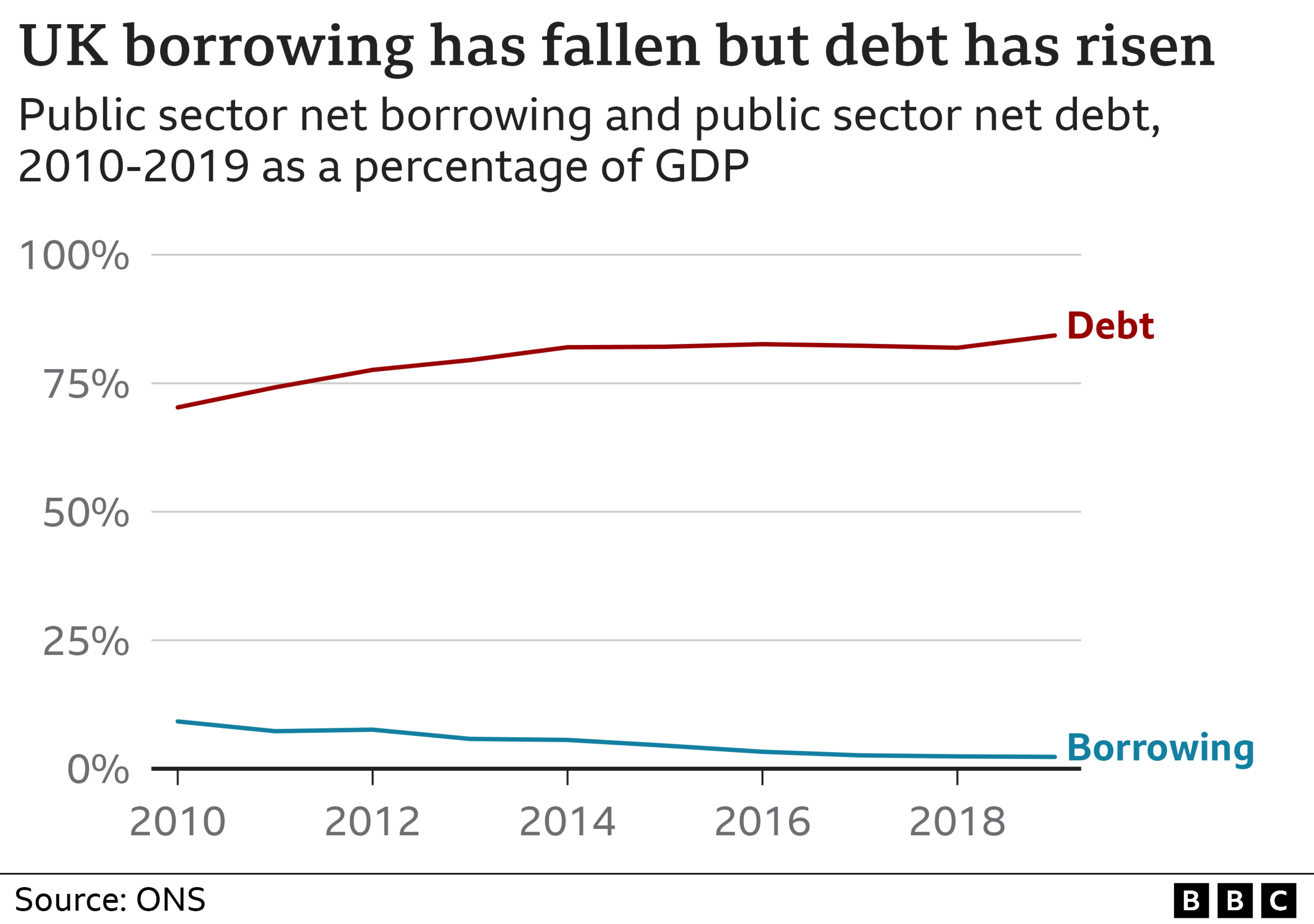
The aim of the 2010 emergency budget was to "put in order the nation's finances" by cutting the UK's debt and reducing its deficit - which is the amount a country allocates to day-to-day spending versus how much it brings in.
Economically, it did have some success, and the deficit fell by 75% between 2009 and 2019, before the Coved-19 pandemic hit. But national debt actually increased over the same period by a fifth as a percentage of GDP.
Ahead of this week's Autumn Statement, Simon Clarke, the MP for Middlesbrough South and East Cleveland, told me "there is scope for spending to come down".
The former levelling up secretary added: "I don't think people would say that their communities have been left scarred by those spending reductions. There is scope for it to come down without impacting on people's lives.
"The state has had to take too much of the strain precisely because the private sector hasn't been resilient enough and so people have therefore been disproportionately reliant on it."
In interviews this week, Chancellor Jeremy Hunt said his plan would be fair and show both compassion and support "for the most vulnerable".
But he also didn't shy away from saying difficult decisions would have to be made for the long-term health of the country's finances. It's essentially the same argument George Osborne used 12 years ago.
Whatever the government announces on Thursday, the decisions it makes are going to have real-life consequences for millions of people. And if the 2010 budget taught us one thing - it's that public spending cuts hit poorer communities harder.
Follow Michael on Twitter, external.
Data journalism by Christine Jeavans