Migrant crisis: EU summit divided amid migration row
- Published
Why is the Aquarius migrant rescue ship empty?
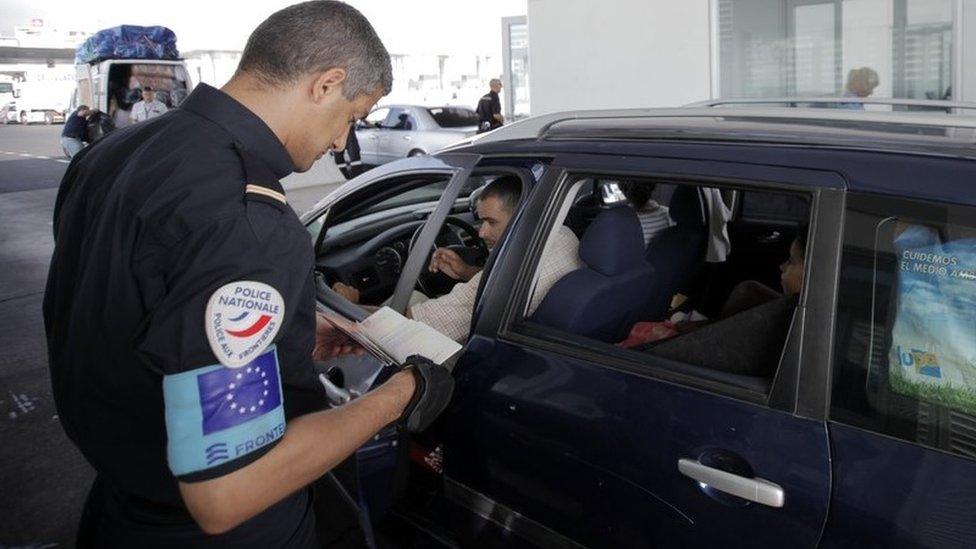
A key European Union summit may end without a deal to resolve a row over ways to tackle irregular migration.
Italy - the entry point of thousands of migrants, mainly from Africa - says it will veto a joint statement over the entire agenda if no solution is found.
Leaders were talking into the early hours of Friday to find a compromise.
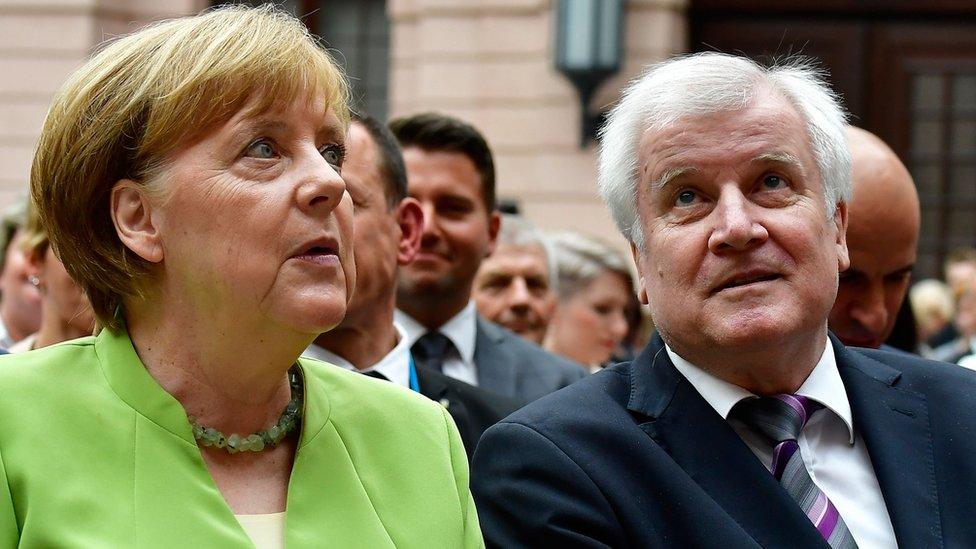
Italy wants other countries to share the burden. German Chancellor Angela Merkel has said the issue could be a defining moment for the EU.
Mrs Merkel is under pressure to come up with a deal to prevent new arrivals.
Interior Minister Horst Seehofer, from her Bavarian coalition partner the CSU, has given her until this weekend. Otherwise he has said he will start turning away migrants from the border in his home state.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.
The migrant flows also include refugees fleeing the Syrian war and other conflicts, urgently seeking asylum.
It is not a crisis on the scale of 2015, when thousands were coming ashore daily on the Greek islands. The European Council - the EU's strategic leadership - says the numbers illegally entering the EU have dropped 96% since their peak in October 2015.
But this month's tensions over migrant rescue ships barred from entry to Italian ports - most recently the German charity ship Lifeline - have put the issue firmly back in the EU spotlight.
The Lifeline was only allowed to dock in Malta after intense diplomacy among several EU states, who each agreed to take a share of the migrants on board. Malta said that Norway had now also agreed to take some migrants from the Lifeline.
The Dublin principle - that asylum seekers should stay in the country where they enter the EU - has broken down. Italy and Greece, who receive the most, are demanding that their neighbours share the burden.
Belgian PM gives UK PM his team's shirt ahead of World Cup clash on Thursday evening
There was a lighter note, as the summit got under way in Brussels. Belgium's Prime Minister Charles Michel presented UK Prime Minister Theresa May with a Belgian football shirt ahead of the two countries' World Cup clash.
It bore the number of Belgian star Eden Hazard.

EU fissures go deeper
By Katya Adler, BBC Europe editor
Hardened Eurosceptics might love to think the EU's in trouble, but as leaders gather in Brussels for their summer summit on Thursday, dedicated Europhiles are also sounding the alarm.
"The fragility of the EU is increasing," warns EU Commission chief Jean-Claude Juncker. "The cracks are growing in size."
It's been easy to get distracted this last couple of weeks by the new Italian government and its headline-grabbing rejection of NGO migrant rescue boats.
But Mr Juncker is right: EU fissures go deeper and are more widespread.
Migration pits southern Europe against the north.
Italy and Greece smoulder with resentment at having been left alone to deal with migrant arrivals. Meanwhile, northern countries blame the south for not patrolling their Mediterranean borders better and for having, at least in the past, enabled migrants to "slip away" northwards towards richer Germany, Austria and Sweden.

What are the new pressures on EU leaders?
Italy's new populist government has made getting an EU-wide deal on immigration and asylum a priority.
The issue played a major role in the Italian election, catapulting nationalist League leader Matteo Salvini into power. But it is a powerful election issue EU-wide.
Austria's right-wing government takes over the EU's rotating presidency next month and it has a hardline stance on irregular migrants. So do its Visegrad Group neighbours: the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary and Poland. That group rejected an EU scheme to relocate 160,000 refugees from overcrowded camps in Greece and Italy.
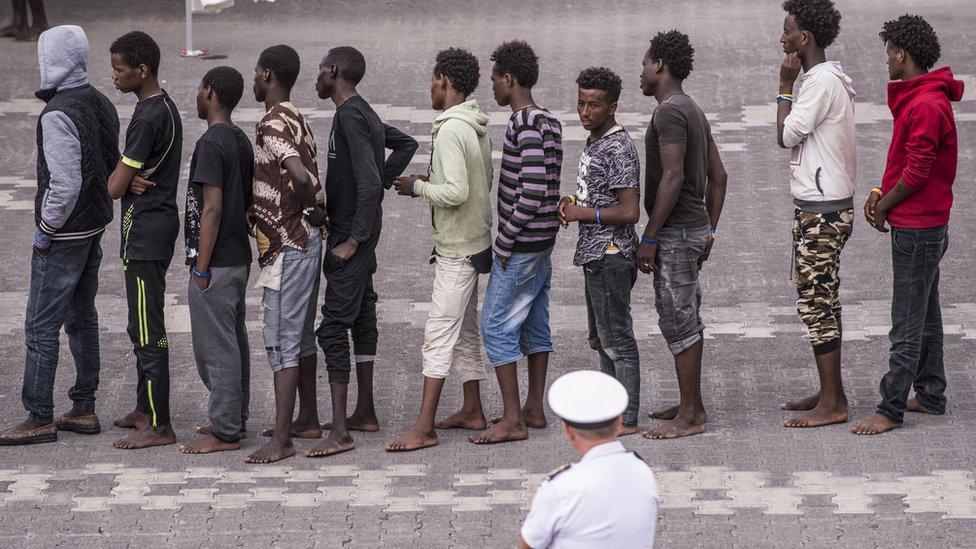

Italy is the main destination for migrants rescued from overloaded boats off Libya
Much of the attention is on the German chancellor, because her interior minister has threatened to start blocking migrants at the border if they have already registered in another EU country. Without his party, the CSU, she would lose her parliamentary majority.
European Council President Donald Tusk told the leaders in his pre-summit letter "the stakes are very high and time is short", external.
He warned that the EU's problems with migration policy were giving ammunition to populists, who "offer simple answers to the most complicated questions".
What solutions are on offer?
1. 'Regional disembarkation platforms'
This is an Austrian-Danish proposal, aimed at breaking the business model of the people-smuggling gangs. In the draft summit conclusions, it is seen as a way to speed up the processing of asylum claims and stopping illegal economic migrants.
Pros?
They could deter migrants from putting to sea in overloaded boats.
Gangs might then be less able to profit from migrants' desperation.
Cons?
Getting North African countries to host such centres could be very difficult. Morocco again on Thursday rejected the idea.
Close co-ordination with UN agencies will be needed, to prevent them becoming crowded, dangerous camps.
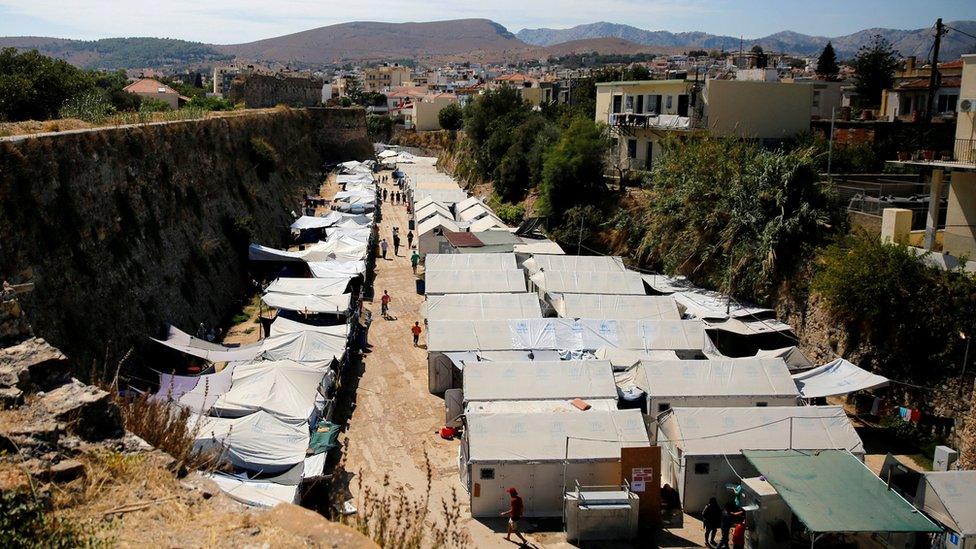

Greece says emergency action is necessary to "decongest" some of its islands
2. Beefing up EU border agency Frontex
The European Commission says this would make it a genuine border police force. The force is to be boosted from the current 1,300 (with 1,500 in reserve) to 10,000 by 2027, external.
Pros?
The force could intervene more rapidly, nipping migrant emergencies in the bud, preventing any repetition of the 2015 chaos.
Cons?
Solidarity has been lacking among the 28 member states.
Frontex still lacks some important resources that were pledged.
EU police risk usurping the role of national border guards - a sensitive issue.
Migrant crisis: EU border force Frontex explained
3. More co-operation with transit and migrants' home countries
This would allow more failed asylum seekers to be sent back; the "return" rate currently is just 36.6%, the Commission says.
Pros?
There has been effective EU co-operation with Turkey: a 2016 deal led to a drastic drop in migrants taking the Balkan route.
The EU naval mission off Libya works closely with the Libyan coastguard to stop people-smuggling.
Cons?
Conditions are dire in Libyan migrant holding centres.
Turkey is still short of €3bn (£2.6bn; $3.5bn), pledged by the EU for Syrian refugees.
Tackling poverty in Africa, from which many migrants are fleeing, requires generous EU funding. There is an EU Trust Fund for Africa, but it is short of €1.2bn in pledged funds.
- Published27 June 2018
- Published23 June 2018

- Published28 June 2018

- Published27 June 2018

- Published30 October 2015
