What does the US Speaker of the House do?
- Published
Watch: A timeline of the McCarthy-Gaetz feud
A historic drama is playing out in the US House of Representatives after Republican congressman Matt Gaetz's successful attempt to dethrone his party's House Speaker, Kevin McCarthy.
It follows a war of words between the two men that broke out after the Speaker passed a bill with the help of Democrats to fund government agencies.
Mr Gaetz had long threatened to introduce a motion to dismiss Mr McCarthy and this week, he finally did so. On Tuesday, the US House of Representatives voted 216-210 to oust Mr McCarthy, with all Democrats voting against him along with eight Republicans who turned their backs on their leader.
The vote kicks off another potentially chaotic process to appoint the next Speaker.
The Speaker of the House is an immensely powerful role that allows for near-total control over the chamber's functions.
Here's what you need to know about one of the most important jobs in American politics.
What is a Speaker of the House?
The US Constitution established the role of Speaker of the House, which oversees the lower chamber of Congress. The Speaker is both traditionally and historically a sitting member of the majority party, though this is not a constitutional requirement.
Therefore, in addition to leading the House of Representatives, they are also leader of the majority party in the chamber.
At a practical level, the Speaker sets the House's legislative agenda, controls committee assignments, sets the vote and work calendar, and is responsible for keeping their party members unified behind major initiatives.
Why is the Speaker of the House so important?
Wielded effectively, the position of Speaker of the House is one of the most powerful in Washington. Depending on the partisan makeup of Congress, they can make or break a US president's agenda, stymie opposition, and spearhead their party's biggest legislative initiatives.
A shrewd and effective Speaker will be able to marshal their members behind their party's agenda, and control rebellious lawmakers by doling out incentives or punishments.
Former House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, a Democrat who stepped down from the position when Republicans took control of the House on 3 January 2023, was regarded as one of the most effective modern Speakers of the House.
Though the Democratic caucus she oversaw contained multiple factions, including progressives, moderates, and more conservative-leaning Democrats, she was able to use the tools available to the Speaker to keep a united front when it came to most major votes.
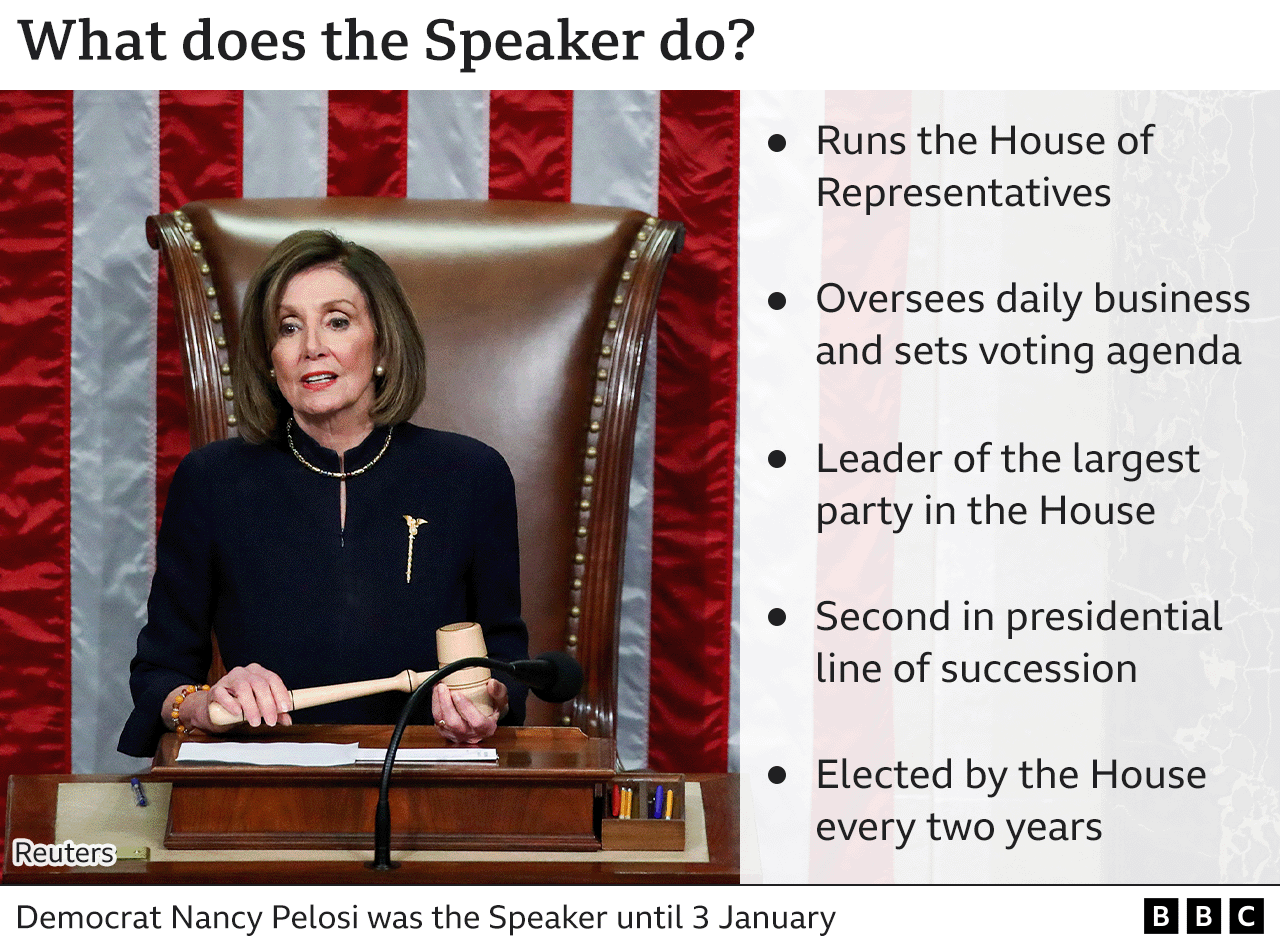
How is a Speaker chosen?
The House of Representatives functions on a two-year cycle, known as a "session." The new Congress began on 3 January 2023 and Republicans will be in the majority.
The very first thing a new session of the House of Representatives must do is vote for a Speaker of the House. Without that person in place, the chamber cannot move on to any other function, including swearing-in members. The chamber must continue to hold votes until a Speaker is elected.
The vote for Speaker requires a candidate to receive the support of a majority of the House - 218 votes. The existing leader of the majority party is usually presumed to be the person to assume the speakership.
Does the House of Representatives have a minority leader?
For the party in the minority, the head of their caucus is known simply as the "minority leader".
They do not have control over the House's functions like the Speaker does, but instead wield power within their caucus to keep lawmakers unified in opposition to the majority or advance bipartisan efforts.
In the 118th Congress, the Democrats are in the minority. Representative Hakeem Jeffries of New York was selected as the Democratic minority leader.
Related topics
- Published4 October 2023

- Published4 October 2023
