New giant dinosaur species discovered in Egypt

- Published
Scientists have identified a new species of giant dinosaur that lived in Egypt.
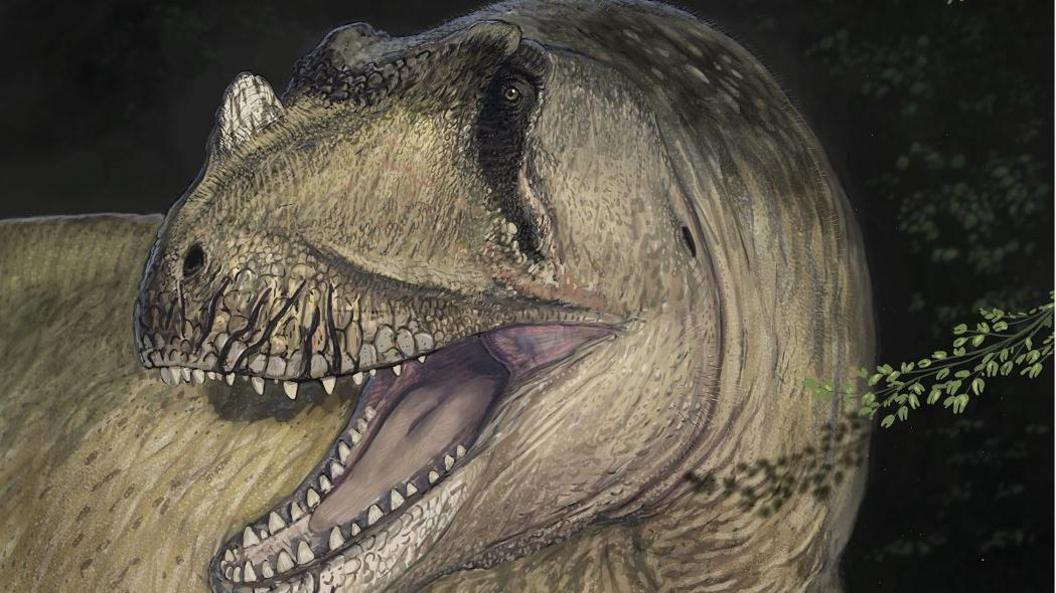
Experts have named the huge dino Tameryraptor markgrafi and it's believed to have roamed Earth more than 90 million years ago, during the Cretaceous period.
What's slightly unusual is that this discovery was made after the uncovering of some long-lost photographs of its fossils.
It measured around 10 meters in length, making it one of the largest known land dinosaurs in history.
More like this
Mystery of how flying reptiles took to the skies finally solved
- Published8 January
Biggest ever UK dinosaur footprint site discovered
- Published2 January
Imagine finding giant mastodon teeth... in your garden!
- Published20 December 2024
What did experts discover?
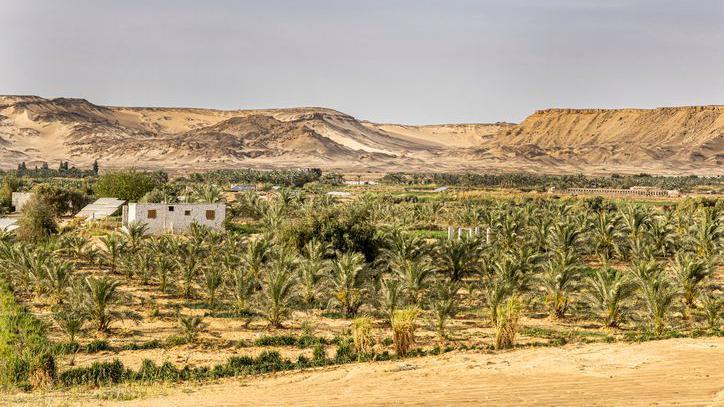

The fossils were discovered more than one hundred years ago in Egypt's Bahariya Oasis
The dinosaur's fossils were originally discovered in Egypt's Bahariya Oasis in the north-west of the country, in 1914.
The fossils were sent to the famous German palaeontologist Ernst Stromer in order for him to take a closer look.
They were then put into storage at the Bavarian State Collection for Palaeontology and Geology in the German city of Munich.
During World War Two, a fire at the museum destroyed all the dinosaur fossils.
For many years experts thought that the only records that remained were Stromer's notes, drawings and a few photos of the original fossils.
However new research, led by palaeontologist Maximilian Kellermann from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, found previously unknown photographs of the dinosaur.
These pictures showed the original skeleton – including parts of the skull, spine and back limbs.
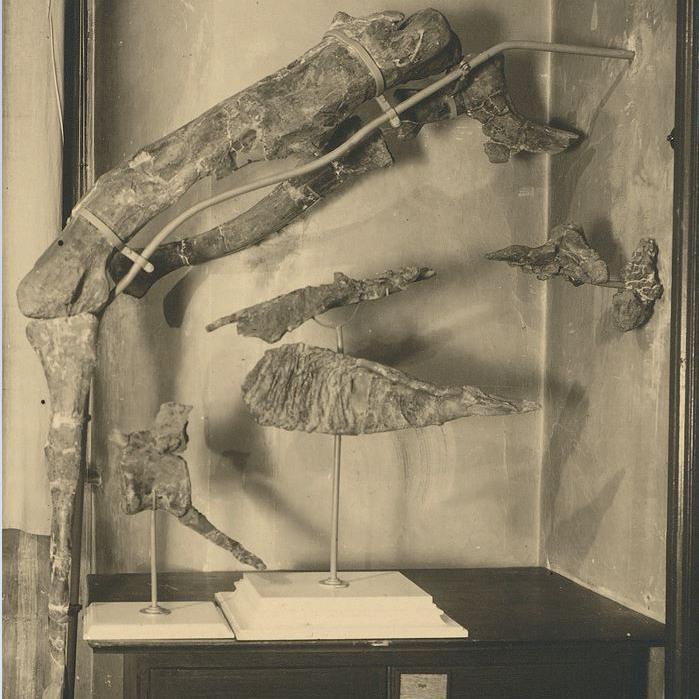
Experts found long-lost photographs of the dinosaur's fossils
Thanks to these previously unseen images, experts were able to identify the new giant dinosaur species.
They have named the dino Tameryraptor markgrafi and say that it is closely related to the Carcharodontosaurs from North Africa and South America.
It's believed the Tameryraptor was huge, nearly the same size as a T. Rex, and it had symmetrical teeth and a distinctive horn on its nose.
The team say that they are delighted with their discovery, adding that their research suggests that dinosaurs were much more varied in North Africa than previously thought.
