LISA Pathfinder: Time called on Europe's gravity probe
- Published

Artwork: The LISA Pathfinder demonstration took place more than a million km from Earth
The European Space Agency (Esa) has turned off one of its most successful ever missions.
LISA Pathfinder was sent into orbit in 2015 to prove key technologies that could be used on some future project to detect gravitational waves - the ripples that disturb space-time whenever black holes collide.
The satellite spectacularly surpassed the objectives set for it.
And that success led directly to the selection in June of the LISA mission.
This billion-euro venture, which is envisaged as a trio of satellites, is expected to launch between 2030 and 2034.
It will incorporate many of Pathfinder's systems, including its all-important laser interferometer instrumentation that we now know has the means necessary to catch gravitational waves (GW) in space.
"LISA Pathfinder has shown that LISA is feasible at full sensitivity, more than we could hope for," said principal investigator Stefano Vitale.
"I think it has been a stepping stone for GW astronomy, and an incredibly rewarding experience for all the team involved. Thank you, and stay tuned on LISA!" he told BBC News.
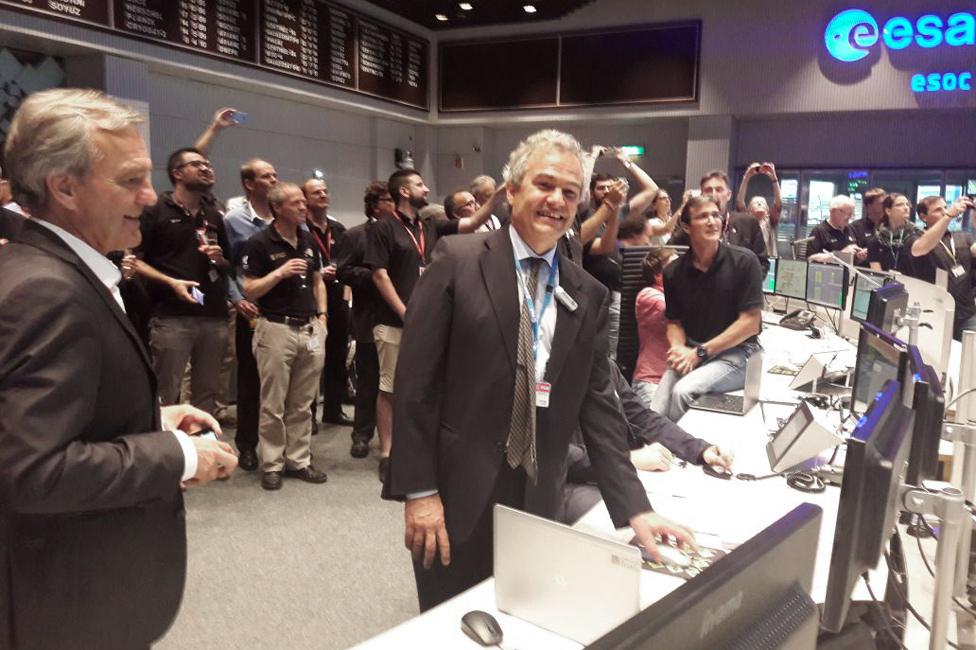

Prof Vitale sends the final commands to LISA Pathfinder
Prof Vitale was invited to send the final "kill commands" to Pathfinder, which has been conducting its measurement demonstration 1.5 million km from Earth in the sunward direction.
The commands, despatched from Esa's mission control centre in Darmstadt, Germany, tricked Pathfinder to reboot itself on to software that had already been corrupted.
It meant the gravity probe was locked down, unable to run its subsystems including its transmitter.
"The only way you could recover the spacecraft would be to go up there and attach an umbilical and restart from another computer," explained Pathfinder's spacecraft operations manager, Ian Harrison.
The kill procedure, more properly known as "passivating" the satellite, ensures there is no hazard to future missions through a collision or interference of radio communications.
The Darmstadt team in April had already fired the thrusters on Pathfinder to move it away from its station - a popular location for many Sun-studying missions.
It should now drift harmlessly around our star.
"There's a very, very small chance it could return to the Earth-Moon system; it's so remote but you can't actually say it's zero," said Ian Harrison.
"The mission analysis actually looked at the planetary positions 500 years into the future."

Gravitational waves - Ripples in the fabric of space-time
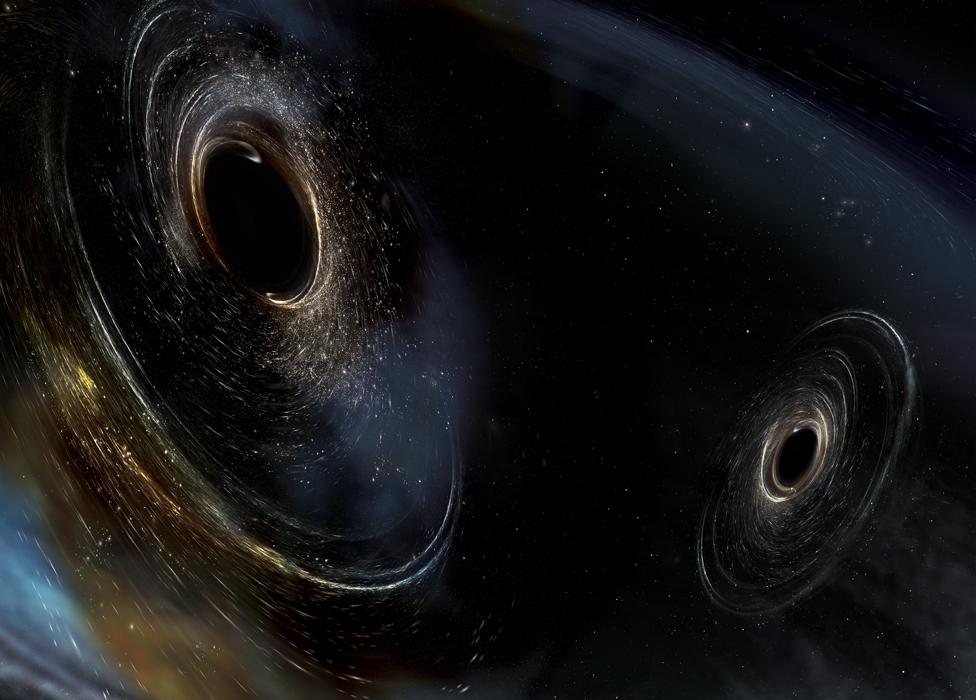

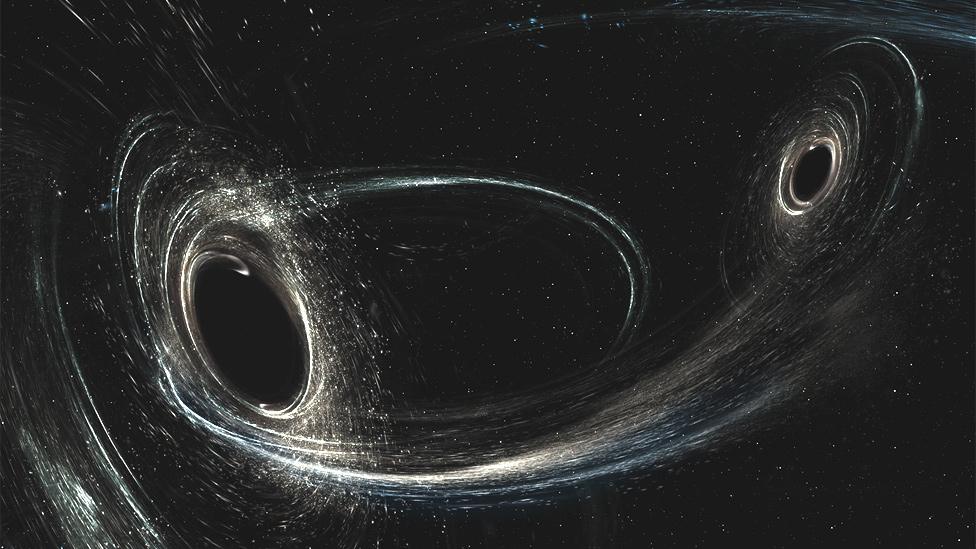
Artwork: Two coalescing black holes spinning in a non-aligned fashion
Gravitational waves are a prediction of the Theory of General Relativity
It took decades to develop the technology to directly detect them
They are ripples in the fabric of space-time generated by violent events
Accelerating masses will produce waves that propagate at the speed of light
Detectable sources ought to include merging black holes and neutron stars
LIGO fires lasers into long, L-shaped tunnels; the waves disturb the light
LISA will fire lasers between three spacecraft separated by 2.5 million km
Detecting the waves opens up the Universe to completely new investigations

Gravitational waves are the big thing in science right now.
Ground-based laboratories in the US have recently begun detecting them from coalescing objects that are 20-30 times the mass of our Sun.
But by sending an observatory into space, scientists would expect to discover sources that are millions of times bigger still, and to sense their activity all the way out to the edge of the observable Universe.
It should significantly advance our understanding of gravity and how it works; and perhaps even highlight some chinks in Einstein's so-far flawless equations.
LISA will detect gravitational waves by bouncing laser light between three spacecraft flying in a triangle formation, where the sides of the triangle are 2.5 million km long. The light beams will be measuring the precise positions of small, free-floating blocks inside the satellites.
When gravitational waves pass through the triangle, the distance between blocks of the different spacecraft should change by tiny amounts - just fractions of the width of an atom.

Laser science: Lisa Pathfinder's technology demonstration

A cutaway impression of the laser interferometer system inside Lisa Pathfinder
Lisa Pathfinder carried a laser interferometer to measure the behaviour of two free-falling blocks made from a platinum-gold alloy
Placed 38cm apart, these "test masses" were held inside cages that were engineered to insulate them against all disturbing forces
Whenever this super-quiet environment is maintained, the falling blocks should follow a "straight line" that is defined only by gravity
And it is under such conditions that a passing gravitational wave could be noticed by ever so slightly changing the blocks' separation
Lisa Pathfinder demonstrated sub-femtometre sensitivity, but the satellite itself could not make a detection of the famous ripples
For that, a space-borne observatory would need to reproduce the same performance but with blocks positioned 2.5 million km apart
Lisa Pathfinder, however, proved the measurement principle and paved the way for the LISA mission's selection by Esa nations
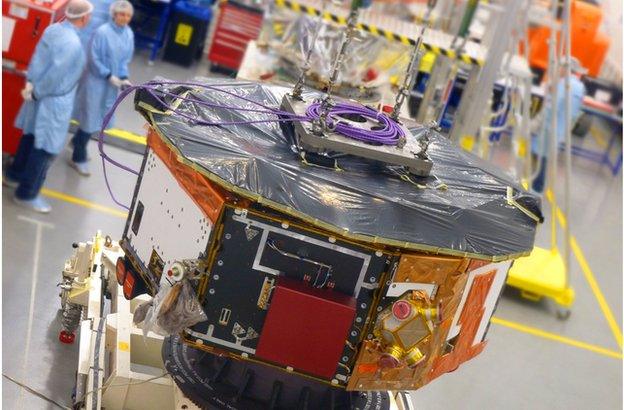

The industrial production of LISA Pathfinder was led from the UK, at Airbus Defence and Space

LISA Pathfinder's laser and gold-block monitoring system was shrunk down to fit inside a single satellite. As such, it could not itself detect gravitational waves, but the exquisite sensitivity of the instrumentation demonstrated that the metrology principles were sound.
"LISA Pathfinder did more than we ever asked for," said Paul McNamara, Esa's Pathfinder project scientist.
"It met its requirements on day one, the day we switched on its science. But we then met and surpassed the requirements of LISA. So, it's been a phenomenal mission. It's sad to turn Pathfinder off but at some point we have to look to the future," he told BBC News.
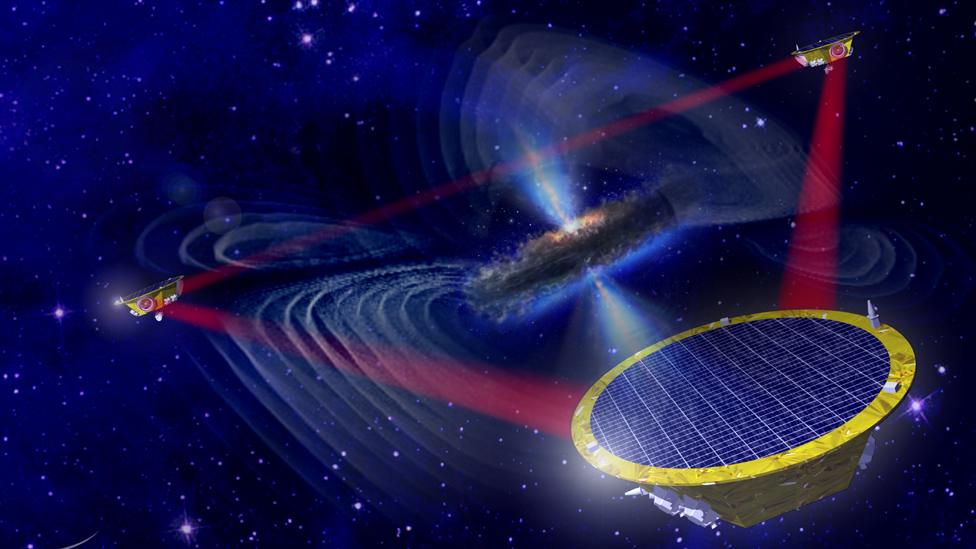
Artwork: LISA envisages three spacecraft linked by laser arms that are 2.5 million km in length
Jonathan.Amos-INTERNET@bbc.co.uk, external and follow me on Twitter: @BBCAmos, external
- Published20 June 2017
- Published1 June 2017

- Published18 February 2017

- Published15 June 2016

- Published7 June 2016

- Published12 February 2016
- Published11 February 2016
- Published11 February 2016

- Published27 June 2014
