Rosetta: Battery will limit life of Philae comet lander
- Published
- comments
Lead scientist Jean-Pierre Bibring shows off some of the images sent home by the Philae probe
After a historic but awkward comet landing, the robot probe Philae is now stable and sending pictures - but there are concerns about its battery life.
The lander bounced twice, initially about 1km back out into space, before settling in the shadow of a cliff, 1km from its intended target site.
It may now be problematic to get enough sunlight to charge its battery systems.
Launched in 2004, the European Space Agency (Esa) mission hopes to learn about the origins of our Solar System.
It has already sent back the first images ever taken from the crumbling, fractured terrain of a comet.
Philae got to the icy 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on the back of Esa's Rosetta satellite after a 10-year, 6.4 billion-km (4bn-mile) journey, which reached its climax on Wednesday with a seven-hour drop to the surface.
After showing an image that indicates Philae's presumed location - on the far side of a large crater that was earlier considered but then rejected as a landing site - the head of the lander team, Stephan Ulamec, said: "We could be somewhere in the rim of this crater, which could explain this bizarre… orientation that you have seen."
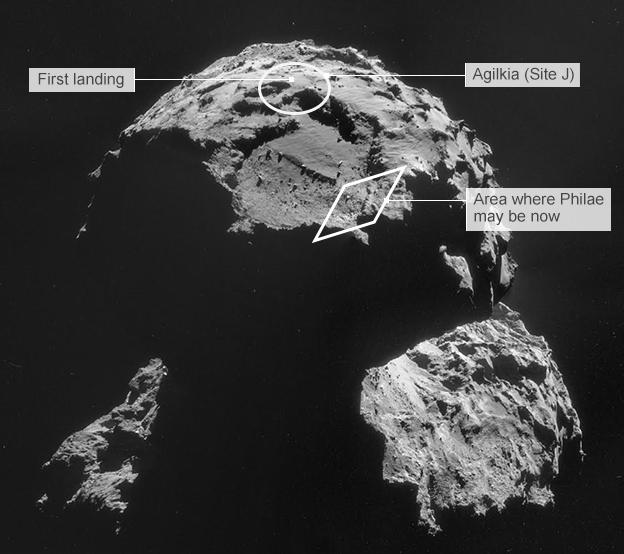

Some radio data suggests the probe may be about 1km from the intended landing site
Pictures taken by Philae of its surroundings show it pressed up against what appears to be a hard wall of some kind.
Telemetry indicates it is on a slope or perhaps even on its side.
Certainly, one of its three feet is not in contact with the surface.
The key issue vexing controllers right now is the lighting conditions.
Philae is receiving about 1.5 hours of illumination during every 12-hour rotation of the comet.
This will be insufficient to top up its battery system once the primary charge it had on leaving Rosetta runs out. That was some 60-plus hours.
It means Philae is unlikely to be operating in its present state beyond Saturday.
"We have estimations right now that go between Friday afternoon and Saturday afternoon," explained Paolo Ferri, the head of Esa's operations here in Darmstadt, Germany.
"It depends on the activities, of course. The more activities we do with the lander, the more power we will consume, and the less time we will have."

One remarkable image taken by the "mothership" Rosetta shows Philae as a tiny speck, headed for history

Another photo shows the craggy surface of the comet - looking over one of Philae's feet
Engineers are examining how they might re-orientate the robot to maximise the light reaching its solar panels.
More extreme options being considered even include using some of the moving parts on the lander to try to make a hopping motion that would carry it clear of the shadows.
But, in truth, there is probably insufficient time to plan and then execute such a strategy.

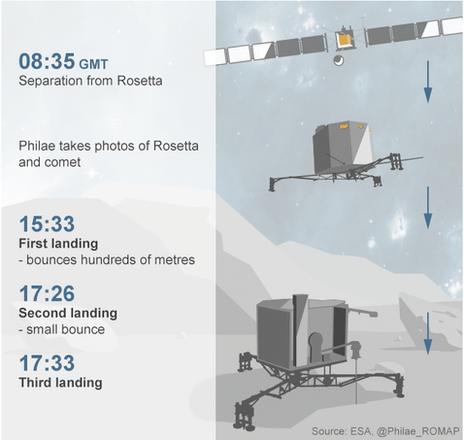
This is the team's current best guess at how events unfolded
The priority right now is to use Philae to acquire as much information as possible about the comet.
In this regard, researchers are thrilled by the performance of the probe.
However, they would dearly love to use the lander's drill. This was one of the key objectives of the mission - to pull up sub-surface material for chemical analysis in onboard labs.
But the team cannot currently contemplate such an operation with the probe so delicately positioned on only two feet. The drill's rotational forces could destabilise Philae.
"We have a 'sniffing mode' and both the Ptolemy and Cosac onboard labs have measurements from this mode," explained the lander's co-principal investigator Jean-Pierre Bibring. "But of course that doesn't give you the entire suite of chemical components in the core of the material. So, yes, we want to drill, but we don't want to drill and find that as a result the mission is over," he told BBC News.
Controllers will see what they can do to lower the third foot to the surface.
If that is not possible, drilling may be commanded towards the end of the primary battery window. By then, scientists would have little to lose anyway.
"This is a very typical operational decision," said Paolo Ferri. "You gather everything you can first, and then the risky things - you only do them at the end."
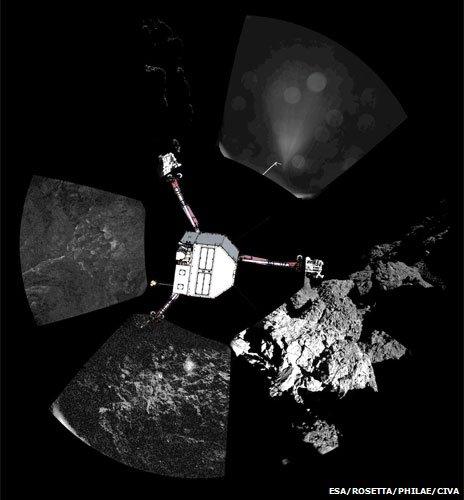

Several images have been taken on different sides of the lander, illustrated here with the pictures arrayed around it
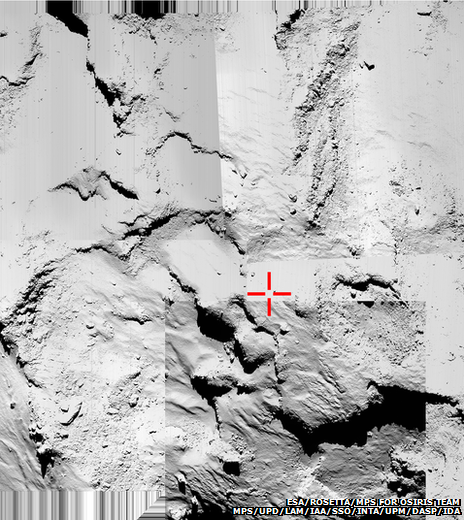

Where did Philae actually touch down? Images from the OSIRIS camera on Rosetta show the area surrounding original target site (highlighted in red)
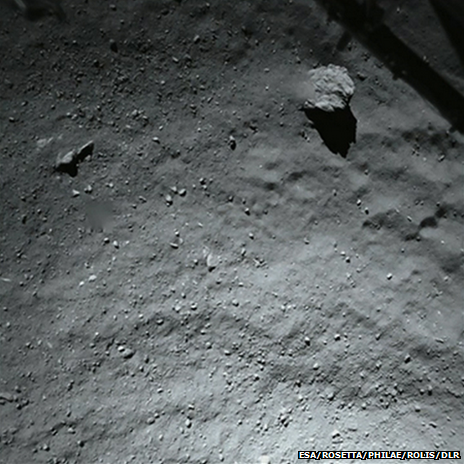

This picture was taken by the lander itself just 40m from its bumpy touchdown
Whatever happens in the hours ahead, the mission is already assured of its place in history.
Its data - and that from Rosetta which continues to observe from overhead - will transform what we know about comets, and enable researchers to test several hypotheses about the formation of the Solar System and the origins of life.
One theory holds that comets were responsible for delivering water to the planets. Another idea is that they could have "seeded" the Earth with the chemistry needed to help kick-start biology.
"It has been an absolutely magnificent two days," said Esa mission manager Fred Jansen.
"I never thought when I got this job a year and a half ago that this would be the impact.
"Of course, when you're successful, like the lander now is, taking measurements on the surface, you'd like to continue this for as long as possible. But reality tells us there is a limited amount of battery power."

The Royal Mail is commemorating the landing with a special postmark, which will be applied to all mail delivered across the UK from Friday to Saturday

Mission facts:
Philae lander
Travelled 6.4 billion km (four billion miles) to reach the comet
Journey took 10 years
Planning for the journey began 25 years ago
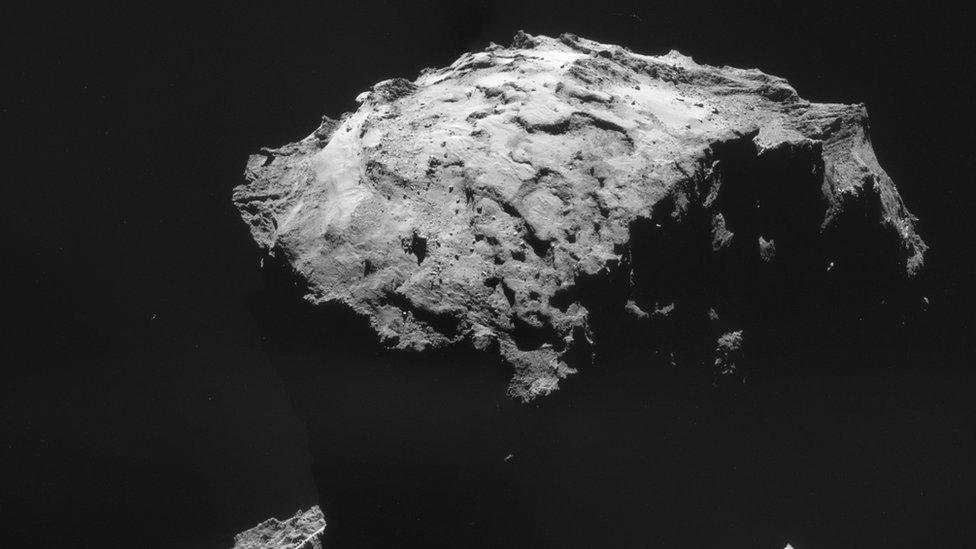
Comet 67P
More than four billion years old
Mass of 10 billion tonnes
Hurtling through space at 18km/s (40,000mph)
Shaped like a rubber duck

Comet 67P explained in 60 seconds
- Published13 November 2014

- Published13 November 2014

- Published17 June 2015

- Published13 November 2014

- Published13 November 2014

- Published13 November 2014

- Published12 November 2014

- Published12 November 2014

- Published12 November 2014
- Published12 November 2014

- Published17 June 2015

- Published12 November 2014
